Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Condition Drug Class: Cardiovascular Medications
Condition Drug Class: Cardiovascular Medications
Uploaded by
Alaa DarwishOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Condition Drug Class: Cardiovascular Medications
Condition Drug Class: Cardiovascular Medications
Uploaded by
Alaa DarwishCopyright:
Available Formats
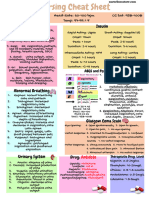
Cardiovascular Medications
Peripheral vasodilation can produce HYPOTENSION, DISSINESS, SYNCOPE
when combined with PT interventions like (hydrotherapy, aquatics, aerobic exercise)
Cardiovascular response to exercise can be limitedBETA-BLOCKERS
limits the increase in HR that can occur as exercise increases workload on the heart
NSAIDs used to treat inflammatory conditions can counteract antihypertensive effects of ACE
INHIBITORS (angiotensin- converting enzyme)
must closely monitor during exercise for elevated BP
NSAIDs have the ability to decrease secretion of DIGITALIS glycosides (Lanoxin, Crystodigin)
producing digitalis toxicity (fatigue, confusion, GI problems, arrhythmias)
Condition
Drug Class
Angina Pectoris
Organic nitrates (nitroglycerides)
Beta-blockers
Arrhythmias
Ca channel blockers
Na channel blockers
Beta-blockers
Ca channel blockers
Agents prolonging depolarization
Cardiac glycosides (DIGITALIS)
CHF
Diuretics
ACE inhibitors
Vasodilators
Diuretics
HTN
Beta-blockers
ACE inhibitors
Vasodilators
Ca channel blockers
Alpha blockers
Diuretics (Thiazides, Loop Diuretics, Posstium-sparing diuretics)
water pills
lower BP by eliminating sodium & water, thus reducing blood volume
some diuretics remove potassium from bodycausing life-threatening arrhythmias
ADVERSE EFFECTS:
o fluid and electrolyte imbalance
o muscle weakness, spasms, dizziness, headache, nausea
Beta-Blockers
end in olol (propranolol, metoprolol) Inderal, Lopressor, Tenormin
block beta receptors on the SA node & myocardial cells-heart
relax blood vessels & heart muscle
o decrease sympathetic stimulation-by blocking B1 receptors from catecholamines
(NE, epinephrine)
produce decline in force of contraction & reduce HR (eases the strain on the heart)
reduces hearts workload & oxygen consumption
decreased BP
monitor RPE (rating of perceived exertion), watch for bradycardia, depressed cardiac
function
ADVERSE EFFECTS:
o depression
o worsening of asthma
o sexual dysfunction
o fatigue
Alpha-1 Blockers
end in zocin (Prazocin, Terzocin) Minipress, Hytrin, Cardura)
A1 receptors located on vascular smooth muscle prevent catecholamines from
vasoconstricting
lower BP by dilating blood vessels
o decrease peripheral vascular resistance
observe for signs of hypotension & reflex tachycardia (HR increases to compensate
for hypotension)
ACE Inhibitors (angiotensin-converting enzyme)
end in pril (benazepril, captopril) Lotensin, Capoten, Vasotec, Prinivil, Zestril
highly selective drugs that interrupt a chain of molecular messengers that constrict blood
vessels
can improve cardiac function in individuals with heart failure
used for individuals with diabetes & early kidney damage
ADVERSE EFFECTS
o rash
o dry cough
Renin-Angiotensin System
helps maintain BP & regulate vascular perfusion throughout body
if BP decreaseskidneys release enzyme reninrenin converts angiotensinogen
(small protein) into angiotensin Iit is inactive until it contacts an ACE located in the
lungsconverts Angio 1 into a powerful vasoconstrictor angiotensin IIincrease in
vascular resistance, which increases BP
angiotensin II also stimulates release of Aldosterone helps maintain vascular fluid
volume by increasing sodium & water reabsorption
Calcium Channel Blockers
inhibit calcium from entering the blood vessel walls
o reduce strength of vascular muscle contractionhelp reduce BP
o Calcium works to CONSTRICT blood vessels
regulates cardiac rhythm
o help control arrhythmias
ADVERSE EFFECTS
o swelling in feet & ankles
o orthostatic hypotension
o headache
o nausea
2 Groups:
1. Interact w/ calcium channels on smooth muscle of peripheral arterioles
a. end in pine (amlodipine, felodipine) Norvasc, Plendil, Sular, Adalat,
Procardia
2. Calcium channel blockers work to dilate coronary arteries to lower BP & suppress
arrhythmias
a. verapamil (Verelan, Calan, Isoptin)
b. diltiazem (Cardizem, Dilacor)
Nitrates (Nitroglyerin)
dilates coronary arteries
o converts nitric oxide w/in vascular wallinhibit smooth muscle contraction
used to prevent & relieve symptoms of ANGINA
o angina pain should subside w/in 1-2 min of nitroglycerin administration & rest
angina usually less than 10 min, never more than 30 min, avg 3-5 min
o women may gets similar results from an antacid
ADVERSE EFFECTS
o headache
o dizziness
o tachycardia
o orthostatic hypotension
Anticoagulant Drugs
(heparin, warfarin) Coumadin, aspirin
prevent platelet aggregation & clot formation
Thrombolytic Drugs
streptokinase, urokinase,(t-PA)
used to break down & dissolve clots already formed in coronary arteries
Statins
Lescol, Mevacor, Pravachol, Zocor
inhibit a key enzyme responsible for cholesterol biosynthesis in the liver
decrease plasma LDL levels
can help reduce atherosclerotic plaque formation
ADVERSE EFFECTS
o myalgia: unexplained muscle pain & weakness
You might also like
- Strategic Analysis of Apple Inc. - Brian MasiDocument35 pagesStrategic Analysis of Apple Inc. - Brian MasiBrianCMasi96% (28)
- Waves That Heal (Mark Clement)Document62 pagesWaves That Heal (Mark Clement)THE NIKOLA TESLA INSTITUTE100% (6)
- Economics Igcse Revision GuideDocument180 pagesEconomics Igcse Revision GuidePolls OnlyNo ratings yet
- Patho Exam 3 Study GuideDocument5 pagesPatho Exam 3 Study GuideFarzanaAziziNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment ChecklistDocument1 pagePhysical Assessment ChecklistDMRMNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)Document2 pagesPharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)graycorypNo ratings yet
- "A Man, A Plan, A Computer: Eric Albert," by Helene HovanecDocument4 pages"A Man, A Plan, A Computer: Eric Albert," by Helene HovanecpspuzzlesNo ratings yet
- OB Drug ChartsDocument2 pagesOB Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- Medication List and InformationDocument9 pagesMedication List and InformationHealthAndFitnessGuyNo ratings yet
- Template Drug Card1Document1 pageTemplate Drug Card1Kay TaylorNo ratings yet
- Ace Inhibutors MailDocument5 pagesAce Inhibutors MailWendy AdaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNursing Cheat Sheetnazbeen.ahmadiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology A ReviewDocument15 pagesPharmacology A ReviewKathrynne MendozaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Med Charts Part 2Document2 pagesPulmonary Med Charts Part 2NursingSchoolNotes100% (3)
- Cheat Sheet Nursing Key PointsDocument3 pagesCheat Sheet Nursing Key PointsKristina EitelNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument9 pagesEmergency DrugsaldwinngNo ratings yet
- SyphilisDocument24 pagesSyphilisEvaG2012No ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology Drug Study GuideDocument15 pagesNursing Pharmacology Drug Study GuideChelsea SmithNo ratings yet
- Common Asthma MedicationsDocument1 pageCommon Asthma MedicationsHeart of the Valley, Pediatric CardiologyNo ratings yet
- Chapter (10) : Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesChapter (10) : Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemSandra GabasNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure PDFDocument9 pagesCongestive Heart Failure PDFSheryl Ann Mae BombalesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medication WorksheetDocument1 pageClinical Medication WorksheetSrkocher100% (1)
- Electrolytes ImbalancesDocument4 pagesElectrolytes ImbalancesPeter John Ruiz100% (1)
- Alpha Adrenergic BlockersDocument7 pagesAlpha Adrenergic BlockersNadine BacalangcoNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs ChartDocument15 pagesCommon Drugs Chartforminsko100% (1)
- Assessment Info NotesDocument3 pagesAssessment Info NotesDiana DeckerNo ratings yet
- Head To Toe AssessmentDocument3 pagesHead To Toe Assessmentsandaman2225No ratings yet
- Antidotes To Commn MedicationDocument1 pageAntidotes To Commn Medicationjosephabram051590No ratings yet
- Of Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart FailureDocument31 pagesOf Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart Failurenaikram420No ratings yet
- Adrenergic and Anti-Adrenergic DrugsDocument54 pagesAdrenergic and Anti-Adrenergic DrugsNelNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Diagnosis and InterventionsDocument3 pagesConcept Map Diagnosis and Interventionsmenickel3No ratings yet
- Common Medications UsedDocument3 pagesCommon Medications UsedRay Michael CasupananNo ratings yet
- Guide To Oxygen Delivery SystemDocument3 pagesGuide To Oxygen Delivery SystemDarwin Villestas0% (1)
- Pharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarDocument33 pagesPharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarfaizaNo ratings yet
- Stroke SGDocument10 pagesStroke SGChalcey Polson100% (1)
- Patho Exam 3Document7 pagesPatho Exam 3menickel3No ratings yet
- Mnemonics PDFDocument15 pagesMnemonics PDFbeingfiredNo ratings yet
- Clinical Med CardsDocument26 pagesClinical Med CardsLila DanielsNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug ChartsDocument3 pagesGastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenDocument23 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenItsMe AJNo ratings yet
- Ace Inhibitors 6Document10 pagesAce Inhibitors 6api-316574434No ratings yet
- Disorders of The BoneDocument2 pagesDisorders of The BoneRPh Krishna Chandra JagritNo ratings yet
- Guide To Diabetes MedicationsDocument2 pagesGuide To Diabetes MedicationsJianhua ShiNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesThe Male Reproductive SystemJrp AneworNo ratings yet
- Labs 1.19 ABG AnalysisDocument1 pageLabs 1.19 ABG AnalysisMonica GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Drugs HypertensionDocument5 pagesCardiac Drugs HypertensionEciOwnsMeNo ratings yet
- Ischaemic Heart DiseaseDocument30 pagesIschaemic Heart DiseaseEB100% (1)
- Cardiac Meds To MemorizeDocument4 pagesCardiac Meds To MemorizekellyaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08: Injectable Medications Mulholland: The Nurse, The Math, The Meds, 3rd EditionDocument13 pagesChapter 08: Injectable Medications Mulholland: The Nurse, The Math, The Meds, 3rd EditionadenNo ratings yet
- Pain Med ChartsDocument4 pagesPain Med ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Drugs Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesHypertension Drugs Cheat Sheet: by ViaGulzaib KhokharNo ratings yet
- Drugs in Cardiac EnmergenciesDocument94 pagesDrugs in Cardiac EnmergenciesVijayan VelayudhanNo ratings yet
- ElectrolytesDocument5 pagesElectrolytesChariza Trompeta100% (1)
- Sirs & ModsDocument5 pagesSirs & Modsmarlou agananNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemAlliyah SalindoNo ratings yet
- ECG Dysrhthmias IIIDocument31 pagesECG Dysrhthmias IIIAmani Kayed100% (1)
- 3 Step ABG Interpretation - 2Document1 page3 Step ABG Interpretation - 2Sibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- 4x6 Module 6 Drug CardsDocument10 pages4x6 Module 6 Drug CardsQueennitaNo ratings yet
- Flashcards 2601-2800Document191 pagesFlashcards 2601-2800kkenNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Acidosis - Alkalosis Study GuideDocument1 pageMetabolic Acidosis - Alkalosis Study GuideJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Equine Infectious Diseases, 2nd Edition (VetBooks - Ir)Document930 pagesEquine Infectious Diseases, 2nd Edition (VetBooks - Ir)Dana UrueñaNo ratings yet
- Group I Study Material, Telugu Medium & English Medium, Sakshieducation2Document1 pageGroup I Study Material, Telugu Medium & English Medium, Sakshieducation2Ravi Kumar MogilsettiNo ratings yet
- 802-CBN-00-PR-CE-LIFTING PROCEDURE-049-B of Civil Construction and Infrastructure Works, Stage 2Document12 pages802-CBN-00-PR-CE-LIFTING PROCEDURE-049-B of Civil Construction and Infrastructure Works, Stage 2Agus SupriadiNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary DOP Submrsible Dredge PumpDocument24 pagesExecutive Summary DOP Submrsible Dredge PumpingartgNo ratings yet
- HAITHAM A. HALOUSH, BASEM MELHEM, and Bashar Malkawi, Equality of Arms in The Digital AgeDocument13 pagesHAITHAM A. HALOUSH, BASEM MELHEM, and Bashar Malkawi, Equality of Arms in The Digital AgeAnonymous 8B8RUOss8No ratings yet
- Histology of Umbilical Cord in MammalsDocument16 pagesHistology of Umbilical Cord in MammalsFia NisaNo ratings yet
- MD070 Wells Fargo ACH 1.0Document20 pagesMD070 Wells Fargo ACH 1.0harshaNo ratings yet
- Modeling Bio ElectricalDocument332 pagesModeling Bio ElectricalEduardo HidalgoNo ratings yet
- White Genoa ID ResearchDocument7 pagesWhite Genoa ID ResearchКлиментий РанчуковNo ratings yet
- DVS Technical Codes On Plastics Joining TechnologiesDocument11 pagesDVS Technical Codes On Plastics Joining Technologiesmarlon gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Exit Ticket Report #7: SDG 7 Affordable & Clean Energy: Sample TemplateDocument2 pagesExit Ticket Report #7: SDG 7 Affordable & Clean Energy: Sample TemplateNino Joycelee TuboNo ratings yet
- Digital Media Assignment Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesDigital Media Assignment Lesson Planapi-245443624No ratings yet
- KT 15Document6 pagesKT 15nischal_babuNo ratings yet
- Calfus Wentworth Drummond, A075 443 280 (BIA Nov. 22, 2013)Document8 pagesCalfus Wentworth Drummond, A075 443 280 (BIA Nov. 22, 2013)Immigrant & Refugee Appellate Center, LLCNo ratings yet
- Flow Around A Cylinder PDFDocument15 pagesFlow Around A Cylinder PDFSANDOVAL ANDREA VALENTINA NORE�ANo ratings yet
- FE Credit System SyllabusDocument36 pagesFE Credit System SyllabusHarshvardhanUpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Direct Memory AccessDocument16 pagesDirect Memory AccessHerambh DubeyNo ratings yet
- VPL LabDocument16 pagesVPL LabTalha MansoorNo ratings yet
- United States v. Steven Chin Leung, 360 F.3d 62, 2d Cir. (2004)Document13 pagesUnited States v. Steven Chin Leung, 360 F.3d 62, 2d Cir. (2004)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- How To Be A Pilot Junior WebDocument16 pagesHow To Be A Pilot Junior WebNextgen AviationNo ratings yet
- Final Report Allied BankDocument70 pagesFinal Report Allied BankIfzal Ahmad100% (6)
- Bay AniDocument6 pagesBay Aniphelenaphie menodiado panlilioNo ratings yet
- Balashov - Et Al - 2021 - Metacognitive Awareness and Academic Self-Regulation of HEI StudentsDocument12 pagesBalashov - Et Al - 2021 - Metacognitive Awareness and Academic Self-Regulation of HEI StudentsHernán Robledo NakagawaNo ratings yet
- Premier 300Document2 pagesPremier 300Malitha PeirisNo ratings yet
- Boeing Case SolutionDocument6 pagesBoeing Case SolutionNeha SinghNo ratings yet
- A Level Entrepreneurship Revision Questions Based On Syllabus Phase 2Document18 pagesA Level Entrepreneurship Revision Questions Based On Syllabus Phase 2humpho45No ratings yet