Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Es9 2
Uploaded by
sinned68Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Es9 2
Uploaded by
sinned68Copyright:
Available Formats
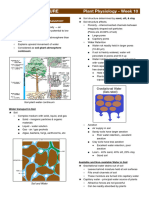
EARTH SCIENCE 9 – 2 What is groundwater?
OBJ: Explain how groundwater collects in soil.
I. PORES & GROUNDWATER - some of the rain or snow that falls to Earth soaks into
the soil.
- water collects in the spaces, or pores, between bits of
rock & soil.
Pores = tiny hole or space.
Groundwater = water that collects in pores in soil and sinks into the
ground.
- about 22% of Earth’s fresh water supply is stored
underground.
II. PROPERTIES AFFECTING - different kinds of rock & soil can hold different
GROUNDWATER amounts of groundwater.
- loosely packed – holds a lot of ground water.
- tightly packed – holds very little.
III. MOVEMENT of - moves easily through rocks & soil with large
GROUNDWATER connected pores.
- if pores not connected water cannot seep deep into
the ground.
IV. THE WATER TABLE - ground water will eventually reach bedrock, where it
almost stops.
Water Table = upper layer of saturated rock & soil.
- soil density does not let all the water sink down to
the water table.
- Some of it stays in the topsoil, and is used by plants
and trees
You might also like
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument13 pagesEarth Science ReviewerlorenzdearceusNo ratings yet
- Soil Water Holding CapacityDocument4 pagesSoil Water Holding CapacityEngr Siraj RahmdilNo ratings yet
- Groundwater AquifersDocument3 pagesGroundwater AquifersAkolbila EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Science - SoilDocument15 pagesScience - SoilSebuta HuzaimaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Soil 2Document25 pagesLecture 5 - Soil 2abdullaharoon458No ratings yet
- Groundwater BasicsDocument4 pagesGroundwater BasicsIsabella Castañeda AriasNo ratings yet
- Geography: The SoilDocument4 pagesGeography: The SoilAkiela DavidNo ratings yet
- Distribution of The Earth's Water Glaciers and Ice CapsDocument3 pagesDistribution of The Earth's Water Glaciers and Ice CapsJazmin HenriquezNo ratings yet
- 17cv742 Module 1Document10 pages17cv742 Module 1TajNo ratings yet
- II Soil-Water-Plant RelationsDocument12 pagesII Soil-Water-Plant RelationsJose Carlo Dizon0% (1)
- Soil - PPT Level OneDocument24 pagesSoil - PPT Level OneAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Geology 2Document3 pagesGeology 2Uploader101No ratings yet
- Exp SC 7 - Chapter 09Document12 pagesExp SC 7 - Chapter 09megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Asm 7685Document2 pagesAsm 7685Taranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- DL - PoldersDocument10 pagesDL - PoldersHannah ZondervanNo ratings yet
- Schedule irrigation with soil moistureDocument10 pagesSchedule irrigation with soil moistureShubhamNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Principles and Soil-Water RelationsDocument100 pagesIrrigation Principles and Soil-Water Relationsحسين شواي0% (1)
- Ground Water and Hydraulics: Asha GDocument11 pagesGround Water and Hydraulics: Asha GAsha G NaikNo ratings yet
- (Week 10) BIO125 Plant PhysiologyDocument7 pages(Week 10) BIO125 Plant PhysiologyKyla Sophia DelantarNo ratings yet
- California Avocado Society 1943 Yearbook 28: 38-39The Drainage and Permeability Characteristics of the Soils on which Avocado Tree Decline and Collapse Are PrevalentDocument3 pagesCalifornia Avocado Society 1943 Yearbook 28: 38-39The Drainage and Permeability Characteristics of the Soils on which Avocado Tree Decline and Collapse Are PrevalentABDUR REHMANNo ratings yet
- Soil-Plant-Water Relationship-5may2020Document66 pagesSoil-Plant-Water Relationship-5may2020Men Keo RathaNo ratings yet
- Soil and Its Formation EBOSDocument14 pagesSoil and Its Formation EBOSRo CkyNo ratings yet
- Lec. 03.field CapacityDocument15 pagesLec. 03.field Capacity6ng2q6xywwNo ratings yet
- Basic Soil Water RelationsDocument13 pagesBasic Soil Water RelationsRubelyn AlabadoNo ratings yet
- Soil Science Group Activity 3 (Group 3)Document2 pagesSoil Science Group Activity 3 (Group 3)John Paul RafinianNo ratings yet
- Cont. of 1Document3 pagesCont. of 1Kimber Lee BaldozNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Movement and ZonesDocument19 pagesGroundwater Movement and ZonesChris RVNo ratings yet
- Soil Water Movement: Types and Factors Impacting AvailabilityDocument15 pagesSoil Water Movement: Types and Factors Impacting AvailabilityJake Sta-anaNo ratings yet
- Esci Finals 1Document2 pagesEsci Finals 1Franz CalopeNo ratings yet
- Types of SoilDocument2 pagesTypes of SoilCharlon RamiscalNo ratings yet
- SOILDocument16 pagesSOILNorika PariharNo ratings yet
- Porosity and Permeability: Grade Level Duration Setting Cademic TandardsDocument7 pagesPorosity and Permeability: Grade Level Duration Setting Cademic TandardsIce BearNo ratings yet
- Soil Formation and CompositionDocument5 pagesSoil Formation and Compositionanju singhNo ratings yet
- Collapsible Peat Swelling Soils: in EgyptDocument5 pagesCollapsible Peat Swelling Soils: in EgyptOmarfath FathNo ratings yet
- HydrologyDocument8 pagesHydrologyBhanu Prakash100% (2)
- Subsurface Water PresentationDocument90 pagesSubsurface Water PresentationJosal Sinon100% (2)
- Components of GroundwaterDocument7 pagesComponents of GroundwaterAlchie Tentativa BaltoresNo ratings yet
- STD X: Hiranandani Foundation School, Thane Geography Soil ResourcesDocument9 pagesSTD X: Hiranandani Foundation School, Thane Geography Soil ResourcesleenaapNo ratings yet
- The Structure of the Hydrosphere - Where Our Water Is LocatedDocument19 pagesThe Structure of the Hydrosphere - Where Our Water Is Locatedmuneeba khanNo ratings yet
- Esci Finals 2Document3 pagesEsci Finals 2Franz CalopeNo ratings yet
- Build Your Own Wetland Biebighauser PDFDocument2 pagesBuild Your Own Wetland Biebighauser PDFDaniel UngureanuNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6_060821Document21 pagesCHAPTER 6_060821Erica Mae CastilloNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Hydrosphere: 8 Grade ScienceDocument19 pagesThe Structure of The Hydrosphere: 8 Grade ScienceKeon JonesNo ratings yet
- Groundwater BasicsDocument5 pagesGroundwater BasicsNamasivayam KaliappanNo ratings yet
- How soil water moves and impacts plant growthDocument29 pagesHow soil water moves and impacts plant growthRonald obasieNo ratings yet
- University of Guyana: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument19 pagesUniversity of Guyana: Faculty of Engineering and Technologyshan singhNo ratings yet
- Stormwater As A Resource: How To Harvest and Protect A Dryland TreasureDocument24 pagesStormwater As A Resource: How To Harvest and Protect A Dryland TreasureGreen Action Sustainable Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of SoilDocument50 pagesPhysical Properties of SoilAngge CortesNo ratings yet
- GROUNDWATER BaluyotDocument40 pagesGROUNDWATER BaluyotTrexay ReigoNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Soil and IrrigationDocument18 pagesLecture On Soil and IrrigationMuniru QudusNo ratings yet
- James - Science - Observation Soil and Other EarthDocument2 pagesJames - Science - Observation Soil and Other EarthPriyantoBudiLaksonoNo ratings yet
- Word AfterDocument1 pageWord AfteramyjakubekNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 4 - Chapter 06Document7 pagesExp SC 4 - Chapter 06megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Do Deeper Wells Mean Better WaterDocument8 pagesDo Deeper Wells Mean Better Waterwilliam MadingNo ratings yet
- Study of Infiltration Rates in Different Soil TypesDocument3 pagesStudy of Infiltration Rates in Different Soil TypesEdmar CardenasNo ratings yet
- Study of Infiltration Capacity of Different SoilsDocument3 pagesStudy of Infiltration Capacity of Different SoilsAbhjth RavikumarNo ratings yet
- Soil Physics 2023 2024Document114 pagesSoil Physics 2023 2024Deron C. De CastroNo ratings yet
- Week 7 and 8 2.3.4 Effects of Abiotic FactorsDocument13 pagesWeek 7 and 8 2.3.4 Effects of Abiotic Factorskobep4894No ratings yet
- Part of The Hydrosphere: Water ResourcesDocument12 pagesPart of The Hydrosphere: Water ResourcesKarol Josef CastilloNo ratings yet
- LS10 7Pg1Document1 pageLS10 7Pg1sinned68No ratings yet
- East Los Angeles College Pass ProtectionDocument15 pagesEast Los Angeles College Pass Protectionsinned68No ratings yet
- Laguna Hills El Toro Capo Valley Woodbridge: Pacifica Newport Harbor Irvine UniversityDocument1 pageLaguna Hills El Toro Capo Valley Woodbridge: Pacifica Newport Harbor Irvine Universitysinned68No ratings yet
- Offensve Line Blocking ProgressionDocument9 pagesOffensve Line Blocking Progressionsinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 8Document1 pageLS10 8sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 6clozeDocument1 pageLS10 6clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 7Pg1ClozeDocument1 pageLS10 7Pg1Clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 7Pg2ClozeDocument1 pageLS10 7Pg2Clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 7Pg2Document1 pageLS10 7Pg2sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 1Pg2ClozeDocument1 pageLS10 1Pg2Clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 6Document1 pageLS10 6sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 5Pg2ClozeDocument1 pageLS10 5Pg2Clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 5Pg2Document1 pageLS10 5Pg2sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 5Pg1Document1 pageLS10 5Pg1sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 4clozeDocument1 pageLS10 4clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 5Pg1Document1 pageLS10 5Pg1sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 4Document1 pageLS10 4sinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 8ClozePg1Document1 pageLS9 8ClozePg1sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 1Pg2Document1 pageLS10 1Pg2sinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 10clozeDocument1 pageLS9 10clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 1Pg1Document1 pageLS10 1Pg1sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 1Pg1ClozeDocument1 pageLS10 1Pg1Clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 9Document1 pageLS9 9sinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 10Document1 pageLS9 10sinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 8ClozePg2Document1 pageLS9 8ClozePg2sinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 8Document1 pageLS9 8sinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 9clozeDocument1 pageLS9 9clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 7clozeDocument1 pageLS9 7clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LIFE SCIENCE 9-6 What Are Echinoderms?: OBJ: List Common Characteristics of Echinoderms. Name Some EchinodermsDocument1 pageLIFE SCIENCE 9-6 What Are Echinoderms?: OBJ: List Common Characteristics of Echinoderms. Name Some Echinodermssinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 7Document1 pageLS9 7sinned68No ratings yet