Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Tissues1
Uploaded by
api-2778676860 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views11 pagesHUMAN TISSUES BY: DONOVAN VALDEZ TYPES of tissue and the FUNCTIONS FUNCTION OF MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Function Posture Movement Joint Stability Heat generator Skeletal muscle CELLS: Attached fibers to the skeleton WHAT DOES NERVE TISSUE DO? Nerve tissue is located through out your body Monitors change inside and outside the body Sends out movement instructions and is responsible for sending sympathetic signals
Original Description:
Original Title
human tissues1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHUMAN TISSUES BY: DONOVAN VALDEZ TYPES of tissue and the FUNCTIONS FUNCTION OF MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Function Posture Movement Joint Stability Heat generator Skeletal muscle CELLS: Attached fibers to the skeleton WHAT DOES NERVE TISSUE DO? Nerve tissue is located through out your body Monitors change inside and outside the body Sends out movement instructions and is responsible for sending sympathetic signals
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views11 pagesHuman Tissues1
Uploaded by
api-277867686HUMAN TISSUES BY: DONOVAN VALDEZ TYPES of tissue and the FUNCTIONS FUNCTION OF MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Function Posture Movement Joint Stability Heat generator Skeletal muscle CELLS: Attached fibers to the skeleton WHAT DOES NERVE TISSUE DO? Nerve tissue is located through out your body Monitors change inside and outside the body Sends out movement instructions and is responsible for sending sympathetic signals
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
HUMAN TISSUES
BY: DONOVAN VALDEZ
TYPES OF TISSUES AND THE FUNCTIONS
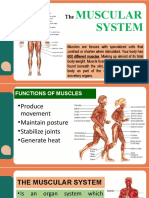
FUNCTION OF MUSCLE TISSUE
Muscle Function
Posture
Movement
Joint Stability
Heat generator
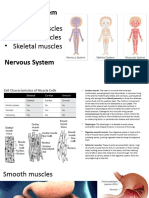
DIFFERENT TYPES OF MUSCLE CELLS
Smooth muscle cells:
Located in walls of hallow
organs except for the heart
Cardiac muscle cells:
Located in the walls of the
heart
Skeletal muscle cells:
Attached fibers to the skeleton
WHAT DOES NERVE TISSUE DO?
Nerve tissue is located through out your
body
Monitors change inside and outside the
body
Sends out movement instructions and is
responsible for sending sympathetic
signals
DIFFERENT TYPES OF NERVE TISSUES
Brain
Integrates Information
Maintains Information
Spinal Cord:
Spinal signals carry information
to and from the spinal cord
THE JOB OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE
Gives support to the body and organs
Connective tissue is also known as the
extracellular matrix
Consists of extracellular fibers
Which consists of tissue fluid
TYPES OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE
Bone
Very hard Material
Tendons
Attached to bone Muscle
Very Dense
Areolar Tissue
Allows some movement
Hypoderms
Directly under the skin
Contains lot of fat
THE USE OF EPITHELIAL TISSUE
Functions
Protection for are body from the
world
Bound together between sheets of
tissue
Cells are tightly backed together
TYPES OF EPITHELIAL TISSUE
Examples:
Simple Squamous
Very Thin tissue
Allows material to pass through
Not very protective
Simple Cubaidal
Little protection
Prevalent when material must be
secreted and absorbed
Simple columnar
Some protection
Underlying tissue
THE END
You might also like
- Introduction To Human AnatomyDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Human AnatomyJomari Kilantang100% (2)
- Body TissuesDocument29 pagesBody TissuesRod100% (1)
- 1 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument251 pages1 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsErin MontillanoNo ratings yet
- NURS1108 Lecture 8 - Nervous System Intro ENHANCEDDocument50 pagesNURS1108 Lecture 8 - Nervous System Intro ENHANCEDJacia’s SpaceshipNo ratings yet
- Body TissuesDocument29 pagesBody TissuesPurplesmilezNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System Functions of The Nervous System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1Document20 pagesThe Nervous System Functions of The Nervous System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1Ash alejoNo ratings yet
- TheCompleteMuscular SystemDocument57 pagesTheCompleteMuscular SystemAyyappan Jayavel100% (1)
- The Human Body: The Facts Book for Future Doctors - Biology Books for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Human Body: The Facts Book for Future Doctors - Biology Books for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Goal: To Describe The Structure and Function of The Muscular SystemDocument24 pagesGoal: To Describe The Structure and Function of The Muscular SystemLayne Fuentes Padillo-Mapiguid100% (1)
- Human Body Systems: Nervous /Muscles/Skeleton SystemsDocument32 pagesHuman Body Systems: Nervous /Muscles/Skeleton SystemsWilver James Satinitigan NeriNo ratings yet
- Lect 7.. Joints and CnsDocument65 pagesLect 7.. Joints and CnsDr. SaniaNo ratings yet
- Презентация На Английском Языке «Human Tissues and Muscles» (Мышцы и Ткани Человека) Для Студентов Медицинских Специальностей.Document28 pagesПрезентация На Английском Языке «Human Tissues and Muscles» (Мышцы и Ткани Человека) Для Студентов Медицинских Специальностей.Гулбахор ИсаковаNo ratings yet
- Histology Muscle & Nerve: Dr. JagadeeshDocument38 pagesHistology Muscle & Nerve: Dr. JagadeeshcheckmateNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System by Group 5Document58 pagesThe Muscular System by Group 5JeffersonDalisanNo ratings yet
- Ha Musclar CompleDocument121 pagesHa Musclar Complehey lolNo ratings yet
- Tissues of The Human BodyDocument51 pagesTissues of The Human BodyKubun Ginta GintingNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesNervous SystemHenry ValerioNo ratings yet
- Sexies GroupDocument92 pagesSexies GroupJamie BagundolNo ratings yet
- Muscles - NervesDocument20 pagesMuscles - NervesNermeen Mostafa ElhawaryNo ratings yet
- 7 Animal Tissues Human Organ Systems IntroDocument18 pages7 Animal Tissues Human Organ Systems IntroHunzala Rasheed AlamNo ratings yet
- Histology of Nervous Tissue: - Neuroglia - Neurons - MyelinationDocument40 pagesHistology of Nervous Tissue: - Neuroglia - Neurons - MyelinationRed StoneNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: Biology IiDocument33 pagesThe Muscular System: Biology IiBibiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basic ExercisesDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Basic ExercisesAnh Thu TranNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesFunctions of The Nervous SystemAccey RamirezNo ratings yet
- NervoussysteDocument55 pagesNervoussysteaishabahaa03No ratings yet
- Chapter6 Themuscularsystem 151207133246 Lva1 App6891Document82 pagesChapter6 Themuscularsystem 151207133246 Lva1 App6891Veena MoondraNo ratings yet
- 017 Muscle PhysiologyDocument62 pages017 Muscle Physiologyapi-23664998867% (3)
- Form and FunctionDocument64 pagesForm and FunctionArifahNo ratings yet
- Understanding Animal TissuesDocument25 pagesUnderstanding Animal TissuesMs.Bangalando, S STEM 11-DNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument13 pagesFinalRi DeeNo ratings yet
- Muscles:: Types & FunctionDocument19 pagesMuscles:: Types & FunctionAmna Fatima GhayoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11-Human Body SystemDocument48 pagesChapter 11-Human Body SystemTrần MạnhNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument16 pagesMuscle PhysiologyFranci Kay SichuNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument34 pagesNervous TissueSameer MohammedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Study of Anatomy: BY Roel Cobarde M.DDocument55 pagesIntroduction To The Study of Anatomy: BY Roel Cobarde M.DMiriam JonesNo ratings yet
- The Muscular and Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesThe Muscular and Nervous SystemVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Specialised Cells-Animal CellDocument12 pages2.3 Specialised Cells-Animal CellEswary BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Human TissuesDocument41 pagesHuman TissuesMae Ann Mejico EspirituNo ratings yet
- Nervous System I: Essentials of Human AnatomyDocument40 pagesNervous System I: Essentials of Human Anatomyأمال داودNo ratings yet
- Structure & Functions of Living OrganismsDocument36 pagesStructure & Functions of Living OrganismsswacaneNo ratings yet
- 10 Q2 NervousMuscular-Skeletal-IntegumentaryDocument62 pages10 Q2 NervousMuscular-Skeletal-IntegumentaryHasmine Lara RiveroNo ratings yet
- What Are The Four Basic Types of Tissues That Make Up The Human Body?Document47 pagesWhat Are The Four Basic Types of Tissues That Make Up The Human Body?SireRyūjinSkylerNo ratings yet
- 1-Introductin To AnatomyDocument56 pages1-Introductin To AnatomyJoxNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument14 pagesAnimal TissueReshmi SanjayNo ratings yet
- Lab3 Human Anatomy 1 YearDocument51 pagesLab3 Human Anatomy 1 Yearnatheer ayedNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY: Muscular System Quiz Study Guide Part 1Document4 pagesANATOMY: Muscular System Quiz Study Guide Part 1jbradeeNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument28 pagesMuscular SystemPridas GidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - NERVOUS SYSTEM PDFDocument58 pagesChapter 7 - NERVOUS SYSTEM PDFMary LimlinganNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument24 pagesThe Muscular SystemLucky RiaNo ratings yet
- Body Organs and PartsDocument38 pagesBody Organs and PartsSoner AkımalNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument5 pagesHistologySNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument73 pagesClinical Case: Anatomy and PhysiologyGeorge KoNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument12 pagesMuscular SystemNicole EncinaresNo ratings yet
- Muscular System PowerPointDocument11 pagesMuscular System PowerPointEmerald CorrineNo ratings yet
- Muscle and NerveDocument15 pagesMuscle and NerveAnonymous 5IUoLwGSdNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous SystemDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Introductory Anatomy 1 1Document30 pagesIntroductory Anatomy 1 1Allo ForgaNo ratings yet
- The Animal Body and Principles of RegulationDocument39 pagesThe Animal Body and Principles of RegulationSweet EmmeNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: Science T. RoselleDocument12 pagesMuscular System: Science T. RoselleRoselleNo ratings yet
- Types of MusclesDocument23 pagesTypes of MusclesSONGA AmriNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary Systemapi-277867686No ratings yet
- Client 2 TrishaDocument8 pagesClient 2 Trishaapi-277938821No ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument16 pagesDigestive Systemapi-277867686No ratings yet
- Amazing Body FactsDocument8 pagesAmazing Body Factsapi-277867686No ratings yet