Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C6-L12 Saponification
Uploaded by
Mohamed Abdou0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
186 views8 pagesSoaps are compounds which act as emulsifiers. Soaps form a scum with hard water, meaning it is more difficult to produce a lather. Soapless detergents can be made from crude oil, rather than vegetable oils or animal fats.
Original Description:
Original Title
C6-L12 Saponification.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSoaps are compounds which act as emulsifiers. Soaps form a scum with hard water, meaning it is more difficult to produce a lather. Soapless detergents can be made from crude oil, rather than vegetable oils or animal fats.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
186 views8 pagesC6-L12 Saponification
Uploaded by
Mohamed AbdouSoaps are compounds which act as emulsifiers. Soaps form a scum with hard water, meaning it is more difficult to produce a lather. Soapless detergents can be made from crude oil, rather than vegetable oils or animal fats.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
What is soap?
If oil is added to water, the two liquids do not mix.
Because of this, grease stains can be difficult to remove
during washing.
Soaps are compounds
which act as emulsifiers.
soap molecule
water
This means that they
help the oil to mix
with the water.
oil
How do soaps work?
How are soaps made?
Soaps are usually made from vegetable fats and oils.
These consist of 3 fatty acid chains, held together by a
glycerol molecule.
The reaction used to make soap from fats and oils is
called saponification.
How are soaps made?
What are soapless detergents?
Soapless detergents can be made from crude oil, rather than
vegetable oils or animal fats.
Soapless detergents are still made of long, hydrophobic
carbon chains, but the hydrophilic end of the molecule is a
sulfonate:
sodium octadecylsulfonate
hydrophobic end interacts
with oil molecules
hydrophilic end interacts
with water molecules
Soaps vs. soapless detergents
What are the advantages and disadvantages of soapless
detergents over soaps?
Soaps form a scum with hard water, meaning that it is
more difficult to produce a lather. Soapless detergents
react with the substances in hard water to form soluble
compounds, and so do not form a scum.
Soapless detergents can be made from the by-products
of the oil refining process, so can be cheaper to produce
than soaps.
Some soapless detergents are not biodegradable.
This means that they stay in the water system causing
froth in rivers and streams.
Biological and non-biological
detergents
Biological detergents
are soapless
detergents that
contain enzymes.
The enzymes
are used to break
down chemicals,
e.g. in stains on
clothes.
Non-biological detergents do not contain enzymes, but just
rely on the action of the detergent to remove grease and
stains from items.
Advantage or disadvantage?
You might also like
- Lab Soap BiochemDocument7 pagesLab Soap Biochemfatin afinaNo ratings yet
- Sublimation - LAB REPORTDocument1 pageSublimation - LAB REPORTPatricia Camryne AmbidaNo ratings yet
- Expt On Solubility of Organic CompoundsDocument4 pagesExpt On Solubility of Organic CompoundsJasmine Juit100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Different TestDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry Different TestNera AyonNo ratings yet
- Color Reactions of Protein Lab ReportDocument2 pagesColor Reactions of Protein Lab ReportBlack PastelNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 LipidsDocument4 pagesExperiment 3 LipidsLaelannie MagpayoNo ratings yet
- (BIO 024) LAB ACTIVITY 7 - ENZYMESDocument3 pages(BIO 024) LAB ACTIVITY 7 - ENZYMESAlyanna CamarilloNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab ReportDocument6 pagesChemistry Lab ReportJustice NNo ratings yet
- 6 Properties of Soap PrelabDocument7 pages6 Properties of Soap PrelabRio SurNo ratings yet
- Biochem Experiment (Sakaguchi Test)Document2 pagesBiochem Experiment (Sakaguchi Test)CamilogsNo ratings yet
- Experiment A Test For Lipid Result: Result When Added To WaterDocument5 pagesExperiment A Test For Lipid Result: Result When Added To WaterSuu Wan0% (2)
- Chapter 3 Lipids PDFDocument55 pagesChapter 3 Lipids PDFVinz TombocNo ratings yet
- Exp. 5 Test For Fats and ProteinsDocument5 pagesExp. 5 Test For Fats and ProteinsDoc Zay VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 Pre-Lab Comparative Reactions of Carboxylic Acid DerivativesDocument3 pagesExperiment 8 Pre-Lab Comparative Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivativesgian odell100% (1)
- General CharacteristicsDocument145 pagesGeneral CharacteristicsMuhammad Akbar SiddiqNo ratings yet
- EXercise 2 (Recrystallization and Melting Point Determination)Document3 pagesEXercise 2 (Recrystallization and Melting Point Determination)fangirltonNo ratings yet
- Exp. 7 Analysis of Milk For The Lipids Carbohydrates and ProteinsDocument6 pagesExp. 7 Analysis of Milk For The Lipids Carbohydrates and ProteinsClarice CatorceNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project: Gravimetric AnalysisDocument18 pagesChemistry Project: Gravimetric AnalysisTirth BatraNo ratings yet
- BuffersDocument4 pagesBuffersMarione Thea RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab NotesDocument6 pagesChem Lab NotesEyvette GoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate - Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesCarbohydrate - Lecture NotesKate Taylor100% (1)
- Exp. 6 Biuret Test For The Presence of ProteinsDocument4 pagesExp. 6 Biuret Test For The Presence of ProteinsClarice CatorceNo ratings yet
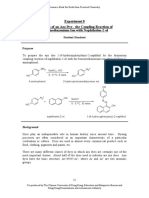
- Experiment 8 Synthesis of An Azo Dye - The Coupling Reaction of Benzenediazonium Ion With Naphthalen-2-OlDocument9 pagesExperiment 8 Synthesis of An Azo Dye - The Coupling Reaction of Benzenediazonium Ion With Naphthalen-2-Olana pertiwiNo ratings yet
- A. Experiment Title: The Making of N-Butyl Acetate B. Experiment Started Date: Wednesday, March 4Document21 pagesA. Experiment Title: The Making of N-Butyl Acetate B. Experiment Started Date: Wednesday, March 4Era MelaniaNo ratings yet
- Bar and Liquid Soap: Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument8 pagesBar and Liquid Soap: Department of Chemical EngineeringErnie Mark Patosa MaratasNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab ReportDocument4 pagesBiochem Lab ReportChryza Faith QuicoyNo ratings yet
- Lab Qualitative Tests For LipidsDocument6 pagesLab Qualitative Tests For LipidsJana Beatrize FerrerNo ratings yet
- Polysaccharides: Submitted By:Dph Momina, Fallah, Noor, Cemal, Ayesha, Uzma, Nimra & AmmaraDocument21 pagesPolysaccharides: Submitted By:Dph Momina, Fallah, Noor, Cemal, Ayesha, Uzma, Nimra & AmmaraCemal SarwarNo ratings yet
- Fehling's Test: Comparative Test Reactions of CarbohydratesDocument33 pagesFehling's Test: Comparative Test Reactions of CarbohydratesTom Anthony Tonguia100% (1)
- Classification of Carbonyl and Hydroxyl Containing CompoundsDocument7 pagesClassification of Carbonyl and Hydroxyl Containing CompoundsSamantha Hope SyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test For MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesLaboratory Test For MacromoleculesOdessa KwonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions PDFDocument43 pagesChemical Reactions PDFFranciscoNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM EXAM in Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesMIDTERM EXAM in Organic ChemistryAurora corpuzNo ratings yet
- Acid Base TitrationDocument12 pagesAcid Base TitrationMsfaeza HanafiNo ratings yet
- Determination of Starch Concentration by Spectrophotometry Final 20110803Document10 pagesDetermination of Starch Concentration by Spectrophotometry Final 20110803Nda FaridaNo ratings yet
- Reducing and Enlarging Formulas: Pharmacy 2 (Pharm. Calculations)Document12 pagesReducing and Enlarging Formulas: Pharmacy 2 (Pharm. Calculations)Diniela CaballesNo ratings yet
- Solution, Colloids, Suspension - Experiment, Viva VoceDocument19 pagesSolution, Colloids, Suspension - Experiment, Viva VoceVaibhav KumarNo ratings yet
- HydrolysisDocument4 pagesHydrolysisDanica Millesca100% (2)
- Experiment 1: CARBOHYDRATES: A. Qualitative Tests and Analysis of UnknownDocument21 pagesExperiment 1: CARBOHYDRATES: A. Qualitative Tests and Analysis of UnknownJamie FloresNo ratings yet
- The Chemicals of Life: Test Yourself QuestionsDocument6 pagesThe Chemicals of Life: Test Yourself Questions송준혁0% (1)
- SugarDocument22 pagesSugarSnehaNo ratings yet
- Biochem-Experiment 2-CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesBiochem-Experiment 2-Carbohydrateslofej57555No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lipids Study GuideDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Lipids Study GuideJanNo ratings yet
- MODULE - FINALS - Biochem - 1Document5 pagesMODULE - FINALS - Biochem - 1Cyril CauilanNo ratings yet
- Emulsification Lab ReportDocument6 pagesEmulsification Lab Reportapi-328025071100% (1)
- Org Chem Ost LabDocument21 pagesOrg Chem Ost Labjullian marasiganNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Gen Chem 2018Document8 pagesActivity 2 Gen Chem 2018Jennifer SpringaelNo ratings yet
- 1 Bio ChemDocument23 pages1 Bio ChemRuwi Loren Villocino100% (2)
- 5.1 Analysing Soap and DetergentDocument28 pages5.1 Analysing Soap and DetergentNor HusseinNo ratings yet
- Csi Lab Report 2Document3 pagesCsi Lab Report 2api-374131693No ratings yet
- Pre Lab!Document4 pagesPre Lab!Lamirah ThomasNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Exp 5 Phy ChemDocument13 pagesLab Report Exp 5 Phy Chemamirulhaqim_97No ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Report 3Document6 pagesChemistry Lab Report 3Jinyoung KimNo ratings yet
- Properties and Composition of Most OrganDocument7 pagesProperties and Composition of Most OrganChris TurffNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ExperimentsDocument9 pagesLaboratory ExperimentsSandra MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6 (Hydrocarbons)Document6 pagesExercise 6 (Hydrocarbons)Wendell Kim Llaneta0% (2)
- Food Science Invisible Fats Lab ReportDocument5 pagesFood Science Invisible Fats Lab Reportapi-286256497No ratings yet
- Gadde Venkata Naresh Yadav 11B Biophysics Lab Activity1Document6 pagesGadde Venkata Naresh Yadav 11B Biophysics Lab Activity1Nárēsh Yadav Gäddē100% (1)
- Chem Proj 1Document10 pagesChem Proj 1Mrinaal RoshanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document35 pagesChapter 6Mohamed AbdouNo ratings yet
- 5 Oil Refinery ProcessesDocument108 pages5 Oil Refinery ProcessesMohamed AbdouNo ratings yet
- Chem Unit 2 CorrosionAndItsControl PDFDocument18 pagesChem Unit 2 CorrosionAndItsControl PDFMohamed AbdouNo ratings yet
- 2003 Petroleum Waxes PDFDocument37 pages2003 Petroleum Waxes PDFMohamed AbdouNo ratings yet