Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 25
Uploaded by
KelvinYongOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 25
Uploaded by
KelvinYongCopyright:
Available Formats
WEEKLY LESSON PLAN
WEEK: 21(19/5-23/5/2014)
MATHEMATICS
CLASS: 4A
LEARNING
AREA
SUB TOPIC
LEARNING
OBJECTIVE
LEARNING OUTCOMES
NOTES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
NOTES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
NOTES
Correction for term 1 exam
CLASS: 5A
LEARNING
SUB TOPIC
AREA
Correction for term 1 exam
LEARNING
OBJECTIVE
CHEMISTRY
CLASS: L6
LEARNING
AREA
2 Electronic
Structure of
Atoms
SUB TOPIC
LEARNING
OBJECTIVE
Students will be
2.1 Electronic
taught to:
energy levels of
atomic hydrogen 1.1
Fundamental
2.2 Atomic
particles of an
orbitals: s, p and
atom
d
1.2 Relative
2.3 Electronic
atomic, isotopic,
configuration
molecular and
2.4 Classification of formula masses
elements into s, p, d 1.3 The mole
and f blocks in the and the
Avogadro
Periodic Table
constant
Students will be able to:
(a)
Thinking skill
and scientific
explain the formation of the skill:
emission
Interpreting
line spectrum of atomic hydrogen in thedata
Classifying
Lyman and Balmer series using
Bohrs
Atomic Model.
(b) predict the behaviour of
beams of protons, neutrons
and electrons in both electric
and magnetic fields;
(c) describe the distribution
of mass and charges within
an atom;
(d) determine the number of
protons, neutrons and
electrons present in both
neutral and charged species
of a given proton number
and nucleon number;
(e) describe the contribution
of protons and neutrons to
atomic nuclei in terms of
proton number and nucleon
number;
(f) distinguish isotopes based
on the number of neutrons
present, and state examples
of both stable and unstable
isotopes.
(g) define the terms relative
atomic mass, Ar, relative
isotopic mass, relative
molecular mass, Mr, and
relative formula mass based
on 12C;
(h) interpret mass spectra in
terms of relative abundance
Scientific
attitudes and
noble values:
Having an
interest and
curiosity
towards the
environment
Being thankful
to God
of isotopes and molecular
fragments;
(i) calculate relative atomic
mass of an element from the
relative abundance of its
isotopes or its mass
spectrum.
(j) define mole in terms of
the Avogadro constant;
(k) calculate the number of
moles of reactants, volumes
of gases, volumes of
solutions and concentrations
of solutions;
(l) deduce stoichiometric
relationships from the
calculations above.
You might also like
- A Level Chemistry Exam Questions PDFDocument513 pagesA Level Chemistry Exam Questions PDFClive Doyce100% (1)
- BC Science 9 Chemistry Unit Study GuideDocument2 pagesBC Science 9 Chemistry Unit Study Guideerinyth100% (2)
- Cdu Unit Chemistry Informal Diagnostics: Grade Level: 9 Stream: ADV The Year 2023/2024Document27 pagesCdu Unit Chemistry Informal Diagnostics: Grade Level: 9 Stream: ADV The Year 2023/2024alshamsi5001010No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Courtesy: Waec Uploaded byDocument41 pagesChemistry: Courtesy: Waec Uploaded byAkpevweoghene Kelvin IdogunNo ratings yet
- 21UPH33CC04Document3 pages21UPH33CC04rjoshittaNo ratings yet
- Boardworks IBO Chemistry Diploma A-Level Mapping GridDocument28 pagesBoardworks IBO Chemistry Diploma A-Level Mapping GridMary MannuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document18 pagesAssignment 1Ain Nabilah RamzanNo ratings yet
- 23.11.08 Worksheet 3Document2 pages23.11.08 Worksheet 3mmoghimi014No ratings yet
- Detailed Course Outline SCH 102, 3112 and 306Document9 pagesDetailed Course Outline SCH 102, 3112 and 306Wesley Omwoyo NyaigotiNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry: Electron ConfigurationDocument2 pagesInorganic Chemistry: Electron ConfigurationArah LlamasNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic TheoryDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic TheoryAlakaaa PromodNo ratings yet
- 1 6a Lesson Plan Electron ConfigurationDocument2 pages1 6a Lesson Plan Electron ConfigurationMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry The Central Science 14th Edition by Brown LeMay Bursten Murphy Woodward Stoltzfus ISBN 0134292812 9780134292816Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry The Central Science 14th Edition by Brown LeMay Bursten Murphy Woodward Stoltzfus ISBN 0134292812 9780134292816jordansmithdfmigejpaq100% (28)
- Xi Chem Chapt3 PEriodic Properties of Elements WorksheetDocument10 pagesXi Chem Chapt3 PEriodic Properties of Elements WorksheetNandini Classes,City Light ,Surat. Cell (9429090525No ratings yet
- Chem F213 1118Document6 pagesChem F213 1118Utkarsh BansalNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument2 pagesChemistryUjjwal KumarNo ratings yet
- Module Electron Configuration Chemical PeriodicityDocument31 pagesModule Electron Configuration Chemical PeriodicityEllah Iracielli TevesNo ratings yet
- Kech 10302 EtextDocument9 pagesKech 10302 EtextParul PriyaNo ratings yet
- Bcme SyllabusDocument17 pagesBcme SyllabusRAJASEKHAR KNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Teacher HandbookDocument110 pagesA Level Chemistry Teacher HandbookHawk Blacket100% (1)
- IIITP - FYBTech - Curriculum - Structure& Syllabus PDFDocument29 pagesIIITP - FYBTech - Curriculum - Structure& Syllabus PDFDeepBhaleraoNo ratings yet
- IIITP FYBTech Curriculum Structure& SyllabusDocument29 pagesIIITP FYBTech Curriculum Structure& SyllabusshaileshvcNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: Learning OutcomesDocument5 pagesCourse Outline: Learning OutcomesCUT nchimwazaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science Grade 8 I.ObjectivesDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in Science Grade 8 I.ObjectivesKristel Joy ManceraNo ratings yet
- Exercise: SMK Seksyen 10 Kota Damansara 47810 Petaling Jaya, SelangorDocument3 pagesExercise: SMK Seksyen 10 Kota Damansara 47810 Petaling Jaya, SelangorTeoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9Document6 pagesLesson 9api-349567441No ratings yet
- Idk QPDocument26 pagesIdk QPalshamsi5001010No ratings yet
- 220 ProjectDocument15 pages220 ProjectEcem ÇevikNo ratings yet
- Course E1 ECE (05-07-19)Document5 pagesCourse E1 ECE (05-07-19)Sravani SravsNo ratings yet
- G S Electron-ConfigurationDocument7 pagesG S Electron-ConfigurationShyra May GalendezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry IGCSE SpecificationDocument14 pagesChemistry IGCSE SpecificationStudent Marc Sanchis VilaNo ratings yet
- B8 Sci WK1Document4 pagesB8 Sci WK1shabanfusseini44No ratings yet
- Sample Editable Scheme of WorkDocument1 pageSample Editable Scheme of WorkjacksonmuriukiNo ratings yet
- Correction For Term 1 Exam: MathematicsDocument2 pagesCorrection For Term 1 Exam: MathematicsKelvinYongNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Electromagnetic Fields and WavesDocument10 pagesSyllabus For Electromagnetic Fields and WavesHalefom HaileNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 9 Q2 PDFDocument104 pagesScience Grade 9 Q2 PDFAnalisa Burac PesimoNo ratings yet
- ECE1003 - EMFT CO UpdatedDocument3 pagesECE1003 - EMFT CO UpdatedNandan AnnamrajuNo ratings yet
- ALL-ECE S3 2019-Scheme-Syllabus Ktustudents - inDocument68 pagesALL-ECE S3 2019-Scheme-Syllabus Ktustudents - inShakiraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 2 FTF & NFTF Question 21-22Document7 pagesTutorial Chapter 2 FTF & NFTF Question 21-22MOHAMAD AFIQ HAIKAL BIN MOHD ZAIDI MoeNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Entrance TestDocument37 pagesSyllabus: Entrance TestJunaid AlamNo ratings yet
- EmtDocument13 pagesEmtAnonymous VASS3z0wTHNo ratings yet
- Lecture Plan - Chem - Spring 2022-23 - 17weekDocument3 pagesLecture Plan - Chem - Spring 2022-23 - 17weekreduan sadikNo ratings yet
- Subject Title: Analog Circuits Course Code: Year and Semester: II & IIDocument8 pagesSubject Title: Analog Circuits Course Code: Year and Semester: II & IIgiribabukandeNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE ChemistryDocument11 pagesEdexcel IGCSE ChemistrySamuel Muabia Plānet0% (1)
- Periodic Table and Electron Shell ConfigurationDocument25 pagesPeriodic Table and Electron Shell ConfigurationCarlton GrantNo ratings yet
- 1 Aqa ChemistryDocument50 pages1 Aqa Chemistryoliviaojemen15No ratings yet
- Syylabus BSC DuDocument61 pagesSyylabus BSC DuDheeraj YadavNo ratings yet
- Nutricion Animales FantasticosDocument2 pagesNutricion Animales FantasticosadnyNo ratings yet
- Sylabus MunaDocument4 pagesSylabus MunaSiti MunawarohNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanElgaliza Karina DeviNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics - Course StructureDocument22 pagesApplied Physics - Course Structurelandur_lalNo ratings yet
- Hour 3 - Periodic Classification of Elements - AssignmentDocument3 pagesHour 3 - Periodic Classification of Elements - AssignmentAnoopNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism Course Outline RevisedDocument3 pagesElectricity and Magnetism Course Outline RevisedShanna-Kay Wood-DavidsonNo ratings yet
- ENT145/3 Materials Engineering Tutorial 1 (Answer)Document9 pagesENT145/3 Materials Engineering Tutorial 1 (Answer)Hữu Danh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Damascus University Telecommunication Subject DescriptionDocument19 pagesDamascus University Telecommunication Subject DescriptionfearfreesNo ratings yet
- Macaorog - SDLP Grade 9 Quarter 2Document3 pagesMacaorog - SDLP Grade 9 Quarter 2liamacaorog98No ratings yet
- SOW 2014 3G13G3 - GopiDocument12 pagesSOW 2014 3G13G3 - GopiGopi KupuchittyNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 1 Validated 1Document7 pagesScience 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 1 Validated 1MYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- Simulation of Transport in NanodevicesFrom EverandSimulation of Transport in NanodevicesFrançois TriozonNo ratings yet
- Timss Model KbatDocument61 pagesTimss Model KbatKelvinYongNo ratings yet
- Timss: S.Kanageswari Suppiah Shanmugam, PHDDocument58 pagesTimss: S.Kanageswari Suppiah Shanmugam, PHDKelvinYongNo ratings yet
- ... Debriefing Session Report: Daniel Leong at RECSAM-Program Latihan KBAT Bagi Jurulatih Utama Matematik 2013Document4 pages... Debriefing Session Report: Daniel Leong at RECSAM-Program Latihan KBAT Bagi Jurulatih Utama Matematik 2013KelvinYongNo ratings yet
- Exp 6Document10 pagesExp 6KelvinYongNo ratings yet
- Analysis Chemistry SPMDocument3 pagesAnalysis Chemistry SPMKelvinYongNo ratings yet
- Beaker (Glassware) : Titration PH ReagentDocument2 pagesBeaker (Glassware) : Titration PH ReagentKelvinYongNo ratings yet
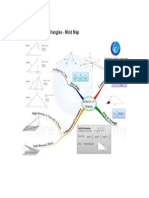
- Chapter 10: Solution of Triangles - Mind MapDocument1 pageChapter 10: Solution of Triangles - Mind MapKelvinYongNo ratings yet
- Word SearchDocument4 pagesWord SearchKelvinYongNo ratings yet