Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Preliminary Physics Assessment Test Questions
Uploaded by
ishOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Preliminary Physics Assessment Test Questions
Uploaded by
ishCopyright:
Available Formats
PRELIMINARY PHYSICS
ASSESSMENT TEST
MARCH 2002
Name:
1.
A small plane flies at 180 km hr-1 due east for 1 hour and then at 200 km hr-1 due north for 1
hour.
(3)
(a) What is the magnitude of displacement of the ship after two hours?
(b) What is its average velocity over the two hours?
2.
A boat sails at 8 ms-1 due north. There is a current of 15 ms-1, flowing from the west.
(a) What is the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the boat relative to the water?
(b) What is the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the boat relative to the ground?
(3)
3.
The data below shows the speed and time relationship for a car travelling in a straight line. (5)
Speed (ms-1)
Time (m)
2
0
4
1
6
2
6
3
2
4
-2
5
(a) Graph this information below.
(b) What is meant by instantaneous velocity?
(c) What is the instantaneous velocity of the car at 3..5 sec?
(d) How far did the object travel in 5 sec?
4.
A driver in a car travelling at 50 km hr-1 takes his foot off the accelerator and comes to rest in 30
sec.
(5)
(a) Explain why the driver needs to apply the accelerator to keep the car moving at a constant
velocity.
(b) What was the average deceleration of the car?
(c) If the car has a mass of 1,500 kg, what force must he apply to stop the car in 5 sec?
5.
Explain the need for a net external force to act in order to change the velocity of an object.
(3)
6.
Find the momentum of a 2400 kg truck travelling at 3.5 ms-1.
(1)
7.
Describe the energy transformations that occur in a collision between a car and a small tree. (2)
8.
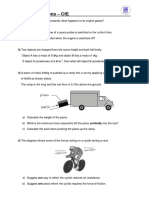
A car of mass 1000kg reaches the bottom of a hill at 20 ms-1.
(3)
(a) What is its momentum?
It then strikes a snowdrift, and is stopped in 5s
(b) What is the force exerted by the snow on the skier?
9.
A Ford Falcon of mass 1540kg travelling north at 110 kmh-1 has a head-on collision with a
Toyota Camry of mass 1325kg. The cars lock together and skid north at 10kmhr-1.
(5)
(a) What was the original velocity of the Camry?
(b) Explain why momentum is conserved in collisions
10.
Use this statement to answer the following questions:
Passengers in a car feel as if they are thrown backwards when the car starts suddenly.
(3)
(a) Define inertia
(b) Explain why the passengers in the train are not thrown backward.
12.
Explain why more damage occurs to a car which crashes into a fixed brick wall compared to a
car crashing into a wall that is free to move.
(3)
13.
(a) List 2 safety features of cars.
Feature 1:
Feature 2:
(b) For each safety feature, evaluate its effectiveness using momentum and impulse
Evaluation of feature 1:
Evaluation of feature 2:
(4)
You might also like
- Unit1 QuestionsDocument92 pagesUnit1 Questionsaadil249No ratings yet
- Physics Practice Problems Acceleration and VelocityDocument6 pagesPhysics Practice Problems Acceleration and VelocityAnonymous ZksWnQNo ratings yet
- Motion Forces Graphs SpeedsDocument4 pagesMotion Forces Graphs SpeedsabdulfcNo ratings yet
- Practise Test On Physics by Yomal AmarathungeDocument3 pagesPractise Test On Physics by Yomal AmarathungeYomal AmarathungeNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions As (Physics) 3/october/2021Document2 pagesPractice Questions As (Physics) 3/october/2021khalidNo ratings yet
- Forces Assignment: (57 Marks)Document2 pagesForces Assignment: (57 Marks)Lai Kee KongNo ratings yet
- 1 - Quiz - 1D - KinematicsDocument2 pages1 - Quiz - 1D - KinematicsMiya GomezNo ratings yet
- Practice Test. MotionDocument3 pagesPractice Test. MotionsatyamheykarNo ratings yet
- Speed, Motion & Acceleration Physics ProblemsDocument3 pagesSpeed, Motion & Acceleration Physics ProblemsAngeline DangNo ratings yet
- DOM Assignment-I 2020-21 NewDocument2 pagesDOM Assignment-I 2020-21 NewChadaram JagadishNo ratings yet
- Ss1 physics-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesSs1 physics-WPS OfficeIsamah ChukwunaluNo ratings yet
- AccelerationDocument4 pagesAccelerationMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Motion and Time - MCQ2Document15 pagesMotion and Time - MCQ2MinuteBrain LearningNo ratings yet
- Assignments 2.1 - Motion in 1DDocument5 pagesAssignments 2.1 - Motion in 1DBilly JenkinsNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Practice HighlightedDocument2 pagesKinematics Practice Highlightedjp shivelyNo ratings yet
- (25745) 6. Forces CfE Questions 2Document7 pages(25745) 6. Forces CfE Questions 2Emmanuel KiptooNo ratings yet
- Csec Kin&DynDocument12 pagesCsec Kin&DynAmanda WhippleNo ratings yet
- AptitudeDocument1 pageAptitudeShivaraman ShankarNo ratings yet
- Linear Motion and GraphDocument1 pageLinear Motion and GraphmydadawalfnNo ratings yet
- MOTHER TERESA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DYNAMICS OF MACHINE QUESTIONSDocument3 pagesMOTHER TERESA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DYNAMICS OF MACHINE QUESTIONSG VENKATESWARARAONo ratings yet
- AccelerationDocument4 pagesAccelerationMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Kinematics ReviewDocument2 pagesKinematics Reviewapi-237070241No ratings yet
- Inbound 2728845430788939890Document9 pagesInbound 2728845430788939890Eric Alvarado SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Mirnal MungraNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement Chapter 2 Force and MotionDocument5 pagesReinforcement Chapter 2 Force and MotionNurlini SulimanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 (Circular & Rotational Motion)Document2 pagesTutorial 7 (Circular & Rotational Motion)TenielleNo ratings yet
- Engineering Science (OENG1209) - Class Test 1 - Group 1 Total Mark: 35 Points - Duration: 90 Minutes Name: Student IDDocument3 pagesEngineering Science (OENG1209) - Class Test 1 - Group 1 Total Mark: 35 Points - Duration: 90 Minutes Name: Student IDfacebookduongtalonNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam Paper-1 Yr 12Document28 pagesMock Exam Paper-1 Yr 12hey ur momgqwy lolNo ratings yet
- CALC 102Document1 pageCALC 102mrdurangoNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Worksheet 5Document2 pagesDynamics Worksheet 5Jennifer Moore100% (1)
- 7th Grade Physics Mid Test Prep - Semester 2Document7 pages7th Grade Physics Mid Test Prep - Semester 2William RyandinataNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 KinematicsDocument3 pagesTutorial 4 Kinematicsapi-3827354No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machinery exam questionsDocument8 pagesDynamics of Machinery exam questionstyagaraju batchalaNo ratings yet
- PPA6 EOC CH 02 MacDocument13 pagesPPA6 EOC CH 02 Macdevonna.wolfeNo ratings yet
- Good - Farrwell Higher Phy Q&ADocument256 pagesGood - Farrwell Higher Phy Q&AGkid Gkid100% (1)
- QUIZ ASSIGNMENT NO. 2 Dynamic of Rigid Bodies Answer Key 1Document26 pagesQUIZ ASSIGNMENT NO. 2 Dynamic of Rigid Bodies Answer Key 1AicelleNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment - Boats & StreamDocument2 pagesHome Assignment - Boats & StreamChetan BhartiaNo ratings yet
- Section A and B MechanicsDocument7 pagesSection A and B MechanicsJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- TCS Aptitude Placement Paper QuestionsDocument2 pagesTCS Aptitude Placement Paper QuestionsRavi ChandraNo ratings yet
- Uka Tarsadia UniversityDocument4 pagesUka Tarsadia UniversityRishit ShahNo ratings yet
- Force and Laws of Motion WorksheetDocument2 pagesForce and Laws of Motion Worksheethoney1002100% (4)
- Lesson 01 To 16 ReviewDocument3 pagesLesson 01 To 16 Reviewi5piritiNo ratings yet
- O IIDocument14 pagesO IIShwe EainNo ratings yet
- University of Zambia PHY1015 Tutorial Sheet 4 2021/2022 Newton’s Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesUniversity of Zambia PHY1015 Tutorial Sheet 4 2021/2022 Newton’s Laws of MotionAngel JereNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Set 1Document2 pagesClass 9 Set 1Indian GamerNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines II ExamsDocument2 pagesMechanics of Machines II ExamsCharles Ondieki100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Assignment For IitjeeDocument25 pagesChapter 2 Assignment For IitjeeShashank ShekharNo ratings yet
- Crash Physics Classes Xi - 2021 Chapter No. 3: Engr. Kamran Ali SoomroDocument5 pagesCrash Physics Classes Xi - 2021 Chapter No. 3: Engr. Kamran Ali SoomroKamran Ali0% (1)
- Most Important Physics Questions on MotionDocument6 pagesMost Important Physics Questions on Motioniiimb_loop1777No ratings yet
- Nav Plot C-41 Assignment: Inbox XDocument2 pagesNav Plot C-41 Assignment: Inbox Xalexander WasongaNo ratings yet
- Mech. & Dynamics Tut. 2Document4 pagesMech. & Dynamics Tut. 2Conrod Wayne SmithNo ratings yet
- Science 1206 Physics Worksheet 12 AccelerationDocument4 pagesScience 1206 Physics Worksheet 12 Accelerationawash0takuNo ratings yet
- Physics kinematics problems: speeds, velocities, accelerationsDocument16 pagesPhysics kinematics problems: speeds, velocities, accelerationsGabriel TorresNo ratings yet
- PLP Physics Worksheets - 2023-24Document8 pagesPLP Physics Worksheets - 2023-24Titiksha MisraNo ratings yet
- Numerical Sheet 1Document1 pageNumerical Sheet 1Nishant MayekarNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Physics: Chapter-4 Momentum Study QuestionDocument2 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Physics: Chapter-4 Momentum Study QuestionMahbub KhanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Physics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument1 pageCBSE Physics Multiple Choice Questionsraghavendra jNo ratings yet
- PH Handout QnsDocument31 pagesPH Handout QnsAZORYNo ratings yet
- Assignment: A and A Wheel WeighingDocument1 pageAssignment: A and A Wheel WeighingIshfaqurNo ratings yet