Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dynamics Worksheet 5
Uploaded by
Jennifer MooreCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dynamics Worksheet 5
Uploaded by
Jennifer MooreCopyright:
Available Formats
Dynamics Worksheet 5 - Momentum
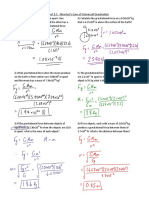
1. A 2200 kg car, travelling at 25 m/s south, comes to a stop in 10 s. Calculate (a)
the initial momentum of the car; (b) the final momentum of the car; (c) the
impulse of the net force applied by the brakes; and (d) the magnitude of the net
force applied by the brakes. (55000 kgm/s south, 0 kgm/s, 55000 kgm/s north,
5500 N north)
2. A hammer strikes a nail with a force of 55 N for a period of 0.2 s. Calculate the
impulse of the force. (11 kgm/s)
3. For how long must an explosive force of 3.3 x 104 N act on a stationary bullet of
mass 0.15 kg to give it a velocity of 220 m/s? (0.001 s)
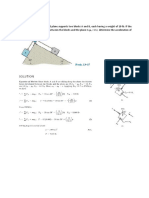
4. A mass of 2 kg experiences a varying force as given in the diagram below.
Determine the change in velocity of the mass. (10 m/s)
5. In experimental tests run by the manufacturer, a car of mass 1500 kg travelling at
20 ms-1 due east collides with an identical stationary car. If all the kinetic energy
of the moving car is transferred to the stationary car during the collision, describe
quantitatively and qualitatively the expected results of the collision. (See below
question 8 for the answer – don’t look at it yet!)
Physics Course 2018M2WS5 1
© Mr Robert Emery
6. Laboratory Trolley Car A has a mass of 0.9 kg and Laboratory Trolley Car B a
mass of 0.5 kg. For each of the situations below, describe quantitatively and
qualitatively the expected results of the collision for Car A:
a. Car A moves east at 0.5 ms-1 and collides but does not coalesce with
Car B moving west at the same speed. After collision, Car B is
moving east with a speed of 0.79 ms-1. (Car A: v = 0.22 m/s west)
b. Car A moves east at 0.5 ms-1 and collides but does not coalesce with
Car B moving east at 0.3 ms-1. After collision, Car B is moving east
with a speed of 0.56 ms-1. (Car A: v = 0.36 m/s east)
c. Car A moves east at 0.4 ms-1 and collides but does not coalesce with
Car B moving west at 0.3 ms-1. After collision, Car B is moving east
with a speed of 0.6 ms-1. (Car A: v = 0.1 m/s west)
d. Car A moving at 0.3 ms-1 east collides and coalesces with Car B
moving at 0.5 ms-1 west. (Car A & B: v = 0.014 m/s east)
(Hint: Use appropriate signs, +, -, to designate direction.)
7. A car of mass 1300 kg travelling at 25 m/s collides head-on with a solid rock cliff
face. If it takes 0.1 s for the car to come to rest, calculate the force applied to the
car in the opposite direction to its original motion. (325,000 N)
8. Go to the URL below and test out your answers to question 6 using the collision
simulation provided there. Use 100% elasticity for parts a to c inclusive. Use 0%
elasticity for part d.
https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/collision-lab/collision-lab_en.html
Answer to question 5: Upon collision, the car initially moving with a velocity of 20
ms-1 due east will come to a complete stop. The car initially stationary will move off
with a velocity of 20 ms-1 due east.
Physics Course 2018M2WS5 2
© Mr Robert Emery
You might also like
- SACE Stage 2 Physics Uniform Circular Motion: F V M R 10) 0 - 1) (0 - 1 (R 2 V V R 2 T 0 - 1) 1 - 0 (2Document3 pagesSACE Stage 2 Physics Uniform Circular Motion: F V M R 10) 0 - 1) (0 - 1 (R 2 V V R 2 T 0 - 1) 1 - 0 (2hihi hello100% (1)
- Circular Motion WorksheetDocument1 pageCircular Motion WorksheetNipun Fernando100% (1)
- Grade 9 Physics worksheetDocument4 pagesGrade 9 Physics worksheetKassahun100% (1)
- Coefficient of Friction and Inclined PlaneDocument2 pagesCoefficient of Friction and Inclined PlanePhysics Class100% (1)
- One-Dimensional KinematicsDocument50 pagesOne-Dimensional KinematicsStephen Correa100% (1)
- Gravitation WorksheetDocument1 pageGravitation WorksheetVishesh Kumar100% (1)
- Projectile Motion WorksheetDocument2 pagesProjectile Motion WorksheetSuta PinatihNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Additional Problems With AnswersDocument5 pagesProjectile Motion Additional Problems With AnswersJanu Golez100% (1)
- Kinematics WorksheetDocument3 pagesKinematics WorksheetDyanie PlummerNo ratings yet
- Notes-Unit-1 - 1d Kinematics StudentDocument12 pagesNotes-Unit-1 - 1d Kinematics StudenttrucksrcoolNo ratings yet
- 3 Kinetics of A Particle Force and AccelerationDocument10 pages3 Kinetics of A Particle Force and AccelerationAndrésDamiánVallejoNo ratings yet
- Sph3Ui: Unit 2: KinematicsDocument26 pagesSph3Ui: Unit 2: KinematicsPOONAM MONDAL100% (1)
- Gravitation Worksheet 1Document3 pagesGravitation Worksheet 1Sharadchandra KashettiwarNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Worksheet 2 - ForcesDocument2 pagesDynamics Worksheet 2 - ForcesJennifer Moore100% (1)
- Kinematics Review Worksheet 2010Document2 pagesKinematics Review Worksheet 2010Matthew GreesonNo ratings yet
- Mass and Inertia: Dynamics 1Document11 pagesMass and Inertia: Dynamics 1Joe West100% (2)
- Linear Motion and GraphDocument1 pageLinear Motion and GraphmydadawalfnNo ratings yet
- Worksheet No.3 in PHYSICS 1Document9 pagesWorksheet No.3 in PHYSICS 1Joshua DellosaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - (Worksheet)Document3 pagesCurrent Electricity - (Worksheet)s.hiruthivNo ratings yet
- 10 Dynamics FrictionDocument6 pages10 Dynamics Frictioneltytan100% (1)
- Forces and VectorsDocument4 pagesForces and VectorsFrancis Ho Ho100% (1)
- Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)Document41 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion (SHM)neoeverestNo ratings yet
- Law of Univeral Gravitation Key PDFDocument2 pagesLaw of Univeral Gravitation Key PDFIvanovka03100% (1)
- Worksheet On Kinematics KeyDocument6 pagesWorksheet On Kinematics KeyelenaNo ratings yet
- Practice Momentum TestDocument5 pagesPractice Momentum TestKinalPatelNo ratings yet
- SPEED AND VELOCITY PROBLEMSDocument3 pagesSPEED AND VELOCITY PROBLEMSteja eashanNo ratings yet
- Motion Graphs-Good-S CaesarDocument31 pagesMotion Graphs-Good-S CaesarNYL BRIAN BUISER100% (1)
- Acceleration WorksheetDocument2 pagesAcceleration WorksheetRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Friction On Level SurfaceDocument2 pages5.3 Friction On Level SurfaceBenNo ratings yet
- Ch06 ISMDocument67 pagesCh06 ISMThai-Son LeNo ratings yet
- Ding Thethe Effects of A ForceDocument18 pagesDing Thethe Effects of A Forcenik mohamad solehinNo ratings yet
- Mechanics For Systems of Particles and Extended BodiesDocument19 pagesMechanics For Systems of Particles and Extended Bodiesraghib83No ratings yet
- Kinematics WorksheetDocument9 pagesKinematics WorksheetLai Kee KongNo ratings yet
- AP Physc M Dynamics Presentation 2018-10-23Document176 pagesAP Physc M Dynamics Presentation 2018-10-23Sadi Sonmez100% (1)
- Impulse and Momentum Word ProblemsDocument3 pagesImpulse and Momentum Word ProblemsHartantoNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Introduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Wilson Higgins TorresDocument17 pagesTest Bank For Introduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Wilson Higgins TorresaimeeNo ratings yet
- Circulat Motion ProblemsDocument15 pagesCirculat Motion ProblemsSadiki WallaceNo ratings yet
- 16 WEP-Work and PowerDocument6 pages16 WEP-Work and PowereltytanNo ratings yet
- POGIL - KinematicsDocument4 pagesPOGIL - KinematicsmagiclcjNo ratings yet
- How Does Force Affect MotionDocument5 pagesHow Does Force Affect MotionSiti Nurul Ain100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Written Problem SolutionsDocument4 pagesChapter 7 Written Problem SolutionsdavparanNo ratings yet
- H2 Physics DynamicDocument22 pagesH2 Physics DynamicTa Minh Trang100% (1)
- Chapter 9 Skill BuildingDocument21 pagesChapter 9 Skill BuildingLisa LimNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument19 pagesMomentumReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- Momentum and ImpulseDocument10 pagesMomentum and ImpulseYuniar AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Momentum ProblemsDocument14 pagesMomentum ProblemsHasmaye PintoNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Worksheet AnswersDocument11 pagesProjectile Motion Worksheet AnswersSHEENDY CLAIRE BELJOTNo ratings yet
- Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration WorksheetDocument1 pageSpeed, Velocity, and Acceleration WorksheetFreddo WonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Uniform Circular MotionDocument1 pageWorksheet Uniform Circular Motionbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Understanding FrictionDocument36 pagesUnderstanding FrictionShourya JainNo ratings yet
- Potential and KineticDocument42 pagesPotential and Kineticmirza_2010No ratings yet
- Using A Graph To Get The General Equation For DisplacementDocument11 pagesUsing A Graph To Get The General Equation For DisplacementAndrea KusickiNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument52 pagesLaws of Motion ExplainedAmeen ShaikNo ratings yet
- AccelerationDocument4 pagesAccelerationMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Circular MotionDocument18 pagesCircular MotionAlfi NurlailiyahNo ratings yet
- ProbSet Impulse-Momentum PDFDocument1 pageProbSet Impulse-Momentum PDFcriscab12345No ratings yet
- Momentum and Impulse Worksheet 1Document2 pagesMomentum and Impulse Worksheet 1Juriel PoguillaNo ratings yet
- Unit IX: Test 1: Name Date PDDocument4 pagesUnit IX: Test 1: Name Date PDapi-590983365No ratings yet
- Conservation Laws ReviewDocument6 pagesConservation Laws ReviewAnanya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Accident Studies: Partha Partim Dey IIT BhubaneswarDocument33 pagesAccident Studies: Partha Partim Dey IIT Bhubaneswarsandeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Worksheet 3: Equations of Uniformly Accelerated MotionDocument1 pageKinematics Worksheet 3: Equations of Uniformly Accelerated MotionJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Worksheet 4 - Work, Energy & PowerDocument1 pageDynamics Worksheet 4 - Work, Energy & PowerJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Worksheet 3 - Forces: Physics Course 2018M2WS3 1 © MR Robert Emery 2017Document3 pagesDynamics Worksheet 3 - Forces: Physics Course 2018M2WS3 1 © MR Robert Emery 2017Jennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- MDFA Reseach Update 586 26-6-23Document6 pagesMDFA Reseach Update 586 26-6-23Jennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Worksheet 2 - ForcesDocument2 pagesDynamics Worksheet 2 - ForcesJennifer Moore100% (1)
- Week 4 Quiz BusterDocument7 pagesWeek 4 Quiz BusterJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Worksheet 1Document2 pagesKinematics Worksheet 1Hanh Vo100% (1)
- Kinematics Worksheet 2: Relative Velocity in A Straight LineDocument1 pageKinematics Worksheet 2: Relative Velocity in A Straight LineJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Kinematics PracticalsDocument17 pagesKinematics PracticalsJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Research Methods (LT2) - Study DesignDocument4 pagesResearch Methods (LT2) - Study DesignJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Z-score Worksheet: Probability & PercentagesDocument2 pagesZ-score Worksheet: Probability & PercentagesJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- PASS Week 6 Take Home Worksheet QuestionsDocument4 pagesPASS Week 6 Take Home Worksheet QuestionsJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Principles of study design summary sheetDocument5 pagesPrinciples of study design summary sheetJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Statistics Worksheet AnswersDocument6 pagesWeek 5 Statistics Worksheet AnswersJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Research Methods (S5) - Research in ActionDocument1 pageResearch Methods (S5) - Research in ActionJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Week 5 WorksheetDocument4 pagesWeek 5 WorksheetJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Research Methods (S6) - Qualitative Health ResearchDocument6 pagesResearch Methods (S6) - Qualitative Health ResearchJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- 1002msc NotesDocument2 pages1002msc NotesJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- SPSS Workshop TableDocument1 pageSPSS Workshop TableJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- SAFETY and EFFECTIVENESS of Drugs Used To Treat Metabolic SyndromeDocument2 pagesSAFETY and EFFECTIVENESS of Drugs Used To Treat Metabolic SyndromeJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Index: See Alkanols SeeDocument4 pagesIndex: See Alkanols SeeJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Appendix D - Flora and FaunaDocument73 pagesAppendix D - Flora and FaunaJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- James Cook 2011 3U HYDocument8 pagesJames Cook 2011 3U HYJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Soic Exam AnswersDocument4 pagesSoic Exam AnswersJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- 2805NRS T1 2017 - StudyChartDocument3 pages2805NRS T1 2017 - StudyChartJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Weekly Exercises For 10eDocument2 pagesWeekly Exercises For 10eJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Arthur Phillip 1999 3U HYDocument7 pagesArthur Phillip 1999 3U HYJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- 2007 CSSA Mathematics Ext 1.text - MarkedDocument4 pages2007 CSSA Mathematics Ext 1.text - MarkedJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Practising ScientistsDocument5 pagesPractising ScientistsJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- 731 Loss On Drying: Water Determination 921Document1 page731 Loss On Drying: Water Determination 921wilNo ratings yet
- HPLC - GCDocument28 pagesHPLC - GCTayyaba SadaqNo ratings yet
- 622 MBPS, 1310 NM Uncooled Fabry-Perot Laser Diode Module With MonitorDocument9 pages622 MBPS, 1310 NM Uncooled Fabry-Perot Laser Diode Module With MonitorIsaac Huixtlaca CuatecatlNo ratings yet
- Welding Machines Monomig 200ikDocument1 pageWelding Machines Monomig 200ikLucioNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT124Document5 pagesASSIGNMENT124Joshua Michael AlonzoNo ratings yet
- G101evn01 0Document27 pagesG101evn01 0amir baroughNo ratings yet
- Ac Cassette 1Document1 pageAc Cassette 1Surya LiemNo ratings yet
- EP Mini ProjectDocument11 pagesEP Mini ProjectAKSHAT CHAURASIANo ratings yet
- As 23a WavesDocument42 pagesAs 23a WavesHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- Superalloys 2000 19 27 PDFDocument9 pagesSuperalloys 2000 19 27 PDFrahul m nairNo ratings yet
- CR 35-X - Service Manual For DownloadDocument565 pagesCR 35-X - Service Manual For DownloadMohsenNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor Design: EE-3202: Sessional On Electrical Machine DesignDocument23 pagesInduction Motor Design: EE-3202: Sessional On Electrical Machine Design106 MOMENUL ISLAM KHAN 17No ratings yet
- Physics Learners Book 16 May 2017 - DanielsDocument352 pagesPhysics Learners Book 16 May 2017 - DanielsMUHIRE FERDINANDNo ratings yet
- Masibus 8208 User ManualDocument42 pagesMasibus 8208 User ManualMẫn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- AKU EB - Chemistry - XI - Paper I - 2010 - MayDocument8 pagesAKU EB - Chemistry - XI - Paper I - 2010 - MayZulkaif IrshadNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry-Experi. 1Document13 pagesDepartment of Chemistry-Experi. 1ThabisoNo ratings yet
- UPCAT 2020 Reviewer4Document21 pagesUPCAT 2020 Reviewer4Aye100% (4)
- Estane GP 72Db Tpu: Advancing MaterialsDocument2 pagesEstane GP 72Db Tpu: Advancing MaterialsDanielNo ratings yet
- Final Promaths Paper 2 Physical Sciences Last Push - 231002 - 205842Document207 pagesFinal Promaths Paper 2 Physical Sciences Last Push - 231002 - 205842Masentle MonicaNo ratings yet
- Final - Module - Math 8 - Exterior Angle Inequality TheoremDocument5 pagesFinal - Module - Math 8 - Exterior Angle Inequality TheoremshaiDroTv 11100% (3)
- Dayton Parallel Shaft High: Torque AC GearmotorsDocument12 pagesDayton Parallel Shaft High: Torque AC GearmotorsFelipe Ivan Escudero VidalNo ratings yet
- 0340 Lecture Notes - Conservation of Charge Example ProblemsDocument2 pages0340 Lecture Notes - Conservation of Charge Example ProblemsRashmi VermaNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Magnetic Torque, Moment, MagnetizationDocument42 pages6.3 Magnetic Torque, Moment, Magnetizationannambaka satishNo ratings yet
- Tech2 Gr9 LBDocument168 pagesTech2 Gr9 LBPride Shayne MwakNo ratings yet
- HW05Document4 pagesHW05Potatoes123No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Grade 12Document10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Grade 12Shylene Mae JapsonNo ratings yet
- Volume TableDocument2 pagesVolume TableMARINELA CademiaNo ratings yet
- Xenon Test Chambers: We Make Testing SimpleDocument9 pagesXenon Test Chambers: We Make Testing SimpleAman KumarNo ratings yet
- Nust ChemistryDocument137 pagesNust Chemistryahmed ilyasNo ratings yet
- 1 - General Brochure L3MW - EnglDocument2 pages1 - General Brochure L3MW - EnglpietroNo ratings yet