Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gravitation Worksheet 1
Uploaded by
Sharadchandra Kashettiwar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
73 views3 pagesThis document contains a worksheet for a 9th grade physics chapter on gravitation. It includes 12 multiple choice questions testing concepts such as the acceleration due to gravity on different celestial bodies, how gravitational force depends on mass and distance, and Newton's law of universal gravitation. It also includes 5 short answer questions about topics like the centripetal force on planets and falling objects on Earth. Finally, it contains 3 long answer questions about how weight depends on mass and radius, gravitational force dependence on mass and distance, and comparing falling times of objects with different masses and initial heights.
Original Description:
Original Title
GRAVITATION WORKSHEET 1 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a worksheet for a 9th grade physics chapter on gravitation. It includes 12 multiple choice questions testing concepts such as the acceleration due to gravity on different celestial bodies, how gravitational force depends on mass and distance, and Newton's law of universal gravitation. It also includes 5 short answer questions about topics like the centripetal force on planets and falling objects on Earth. Finally, it contains 3 long answer questions about how weight depends on mass and radius, gravitational force dependence on mass and distance, and comparing falling times of objects with different masses and initial heights.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
73 views3 pagesGravitation Worksheet 1
Uploaded by
Sharadchandra KashettiwarThis document contains a worksheet for a 9th grade physics chapter on gravitation. It includes 12 multiple choice questions testing concepts such as the acceleration due to gravity on different celestial bodies, how gravitational force depends on mass and distance, and Newton's law of universal gravitation. It also includes 5 short answer questions about topics like the centripetal force on planets and falling objects on Earth. Finally, it contains 3 long answer questions about how weight depends on mass and radius, gravitational force dependence on mass and distance, and comparing falling times of objects with different masses and initial heights.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
SRI SRI RAVISHANKAR VIDYA MANDIR, PUNE
AY: 2022-23
CLASS: IX CHAPTER NO.: __10_ WORKSHEET NO.: __1__
CHAPTER NAME: GRAVITATION____________________
Name: ______________________ Div.: ____ Roll No.: _____
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Two objects of different masses falling freely near the surface of moon would
(a) have same velocities at any instant
(b) have different accelerations
(c) experience forces of same magnitude
(d) undergo a change in their inertia
2. The value of acceleration due to gravity
(a) is same on equator and poles
(b) is least on poles
(c) is least on equator
(d) increases from pole to equator
3. The gravitational force between two objects is F. If masses of both objects are halved without
changing distance between them, then the gravitational force would become
(a) F/4
(b) F/2
(c) F
(d) 2 F
4. A boy is whirling a stone tied with a string in an horizontal circular path. If the string breaks,
the stone
(a) will continue to move in the circular path
(b) will move along a straight line towards the centre of the circular path
(c) will move along a straight line tangential to the circular path
(d) will move along a straight line perpendicular to the circular path away from the boy
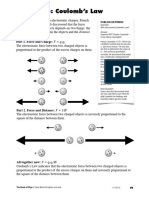
5. In the relation F = G M m/d2, the quantity G
(a) depends on the value of g at the place of observation
(b) is used only when the earth is one of the two masses
(c) is greatest at the surface of the earth
(d) is universal constant of nature
6. Law of gravitation gives the gravitational force between
(a) the earth and a point mass only
(b) the earth and Sun only
(c) any two bodies having some mass
(d) two charged bodies only
7. The value of quantity G in the law of gravitation
(a) depends on mass of earth only
(b) depends on radius of earth only
(c) depends on both mass and radius of earth
(d) is independent of mass and radius of the earth
8. Two particles are placed at some distance. If the mass of each of the two particles is doubled,
keeping the distance between them unchanged, the value of gravitational force between
them will be
(a) 1 / 4 times
(b) 4 times
(c) 1 / 2 times
(d) unchanged
9. The atmosphere is held to the earth by
(a) gravity
(b) wind
(c) clouds
(d) earth’s magnetic field
10. The force of attraction between two unit point masses separated by a unit distance is called
(a) gravitational potential
(b) acceleration due to gravity
(c) gravitational field
(d) universal gravitational constant
11. The weight of an object at the centre of the earth of radius R is
(a) zero
(b) infinite
(c) R times the weight at the surface of the earth
(d) 1/R2 times the weight at surface of the earth
12. An apple falls from a tree because of gravitational attraction between the earth and apple. If
F1 is the magnitude of force exerted by the earth on the apple and F2 is the magnitude of force
exerted by apple on earth, then
(a) F1 is very much greater than F2
(b) F2 is very much greater than F1
(c) F1 is only a little greater than F2
(d) F1 and F2 are equal
Short Answer Type Questions
13. What is the source of centripetal force that a planet requires to revolve around the Sun? On
what factors does that force depend?
14. On the earth, a stone is thrown from a height in a direction parallel to the earth’s surface
while another stone is simultaneously dropped from the same height. Which stone would
reach the ground first and why?
15. Suppose gravity of earth suddenly becomes zero, then in which direction will the moon begin
to move if no other celestial body affects it?
16. Identical packets are dropped from two aeroplanes, one above the equator and the other
above the north pole, both at height h. Assuming all conditions are identical, will those
packets take same time to reach the surface of earth. Justify your answer.
17. The weight of any person on the moon is about 1/6 times that on the earth. He can lift a mass
of 15 kg on the earth. What will be the maximum mass, which can be lifted by the same force
applied by the person on the moon?
18. Calculate the average density of the earth in terms of g, G and R.
19. The earth is acted upon by gravitation of Sun, even though it does not fall into the Sun. Why?
Long Answer Type Questions
23. How does the weight of an object vary with respect to mass and radius of the earth. In a
hypothetical case, if the diameter of the earth becomes half of its present value and its mass
becomes four times of its present value, then how would the weight of any object on the
surface of the earth be affected?
24. How does the force of attraction between the two bodies depend upon their masses and
distance between them? A student thought that two bricks tied together would fall faster
than a single one under the action of gravity. Do you agree with his hypothesis or not?
Comment.
25. Two objects of masses m1 and m2 having the same size are dropped simultaneously from
heights h1 and h2 respectively. Find out the ratio of time they would take in reaching the
ground. Will this ratio remain the same if
(i) one of the objects is hollow and the other one is solid and
(ii) both of them are hollow, size remaining the same in each case. Give reason.
You might also like
- Physical World-Units-Measurements (Physics) Bit BankFrom EverandPhysical World-Units-Measurements (Physics) Bit BankRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Coefficient of Friction and Inclined PlaneDocument2 pagesCoefficient of Friction and Inclined PlanePhysics Class100% (1)
- Measurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankFrom EverandMeasurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Physics worksheetDocument4 pagesGrade 9 Physics worksheetKassahun100% (1)
- Gravitation WorksheetDocument1 pageGravitation WorksheetVishesh Kumar100% (1)
- SACE Stage 2 Physics Uniform Circular Motion: F V M R 10) 0 - 1) (0 - 1 (R 2 V V R 2 T 0 - 1) 1 - 0 (2Document3 pagesSACE Stage 2 Physics Uniform Circular Motion: F V M R 10) 0 - 1) (0 - 1 (R 2 V V R 2 T 0 - 1) 1 - 0 (2hihi hello100% (1)
- 11 Phy - Gravitation - QN Bank - Only QnsDocument3 pages11 Phy - Gravitation - QN Bank - Only QnsMohit DhaundiyalNo ratings yet
- Extra Solved Questions Class Ix Term II ChemistryDocument3 pagesExtra Solved Questions Class Ix Term II Chemistrychhabra navdeep100% (1)
- Magnetic Effect of Current WorksheetDocument1 pageMagnetic Effect of Current WorksheetTajiriMollelNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Chapter SummaryDocument2 pagesGravitation Chapter Summaryasamad54No ratings yet
- Kinematics WorksheetDocument3 pagesKinematics WorksheetDyanie PlummerNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Additional Problems With AnswersDocument5 pagesProjectile Motion Additional Problems With AnswersJanu Golez100% (1)
- PhysicsDocument20 pagesPhysicsAnthony HugillNo ratings yet
- SPEED AND VELOCITY PROBLEMSDocument3 pagesSPEED AND VELOCITY PROBLEMSteja eashanNo ratings yet
- Force & PressureDocument2 pagesForce & PressureNandini SahaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Worksheet 5Document2 pagesDynamics Worksheet 5Jennifer Moore100% (1)
- Circular Motion WorksheetDocument1 pageCircular Motion WorksheetNipun Fernando100% (1)
- Assignment XiDocument3 pagesAssignment XiKamran AliNo ratings yet
- Linear Motion and GraphDocument1 pageLinear Motion and GraphmydadawalfnNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Chapter 8 Assignment 1Document1 page11 Physics Chapter 8 Assignment 1nellai kumarNo ratings yet
- 10th Class Physics Notes Chapter 13 AjkDocument3 pages10th Class Physics Notes Chapter 13 AjkAsher KabirNo ratings yet
- Motion And Time GraphsDocument26 pagesMotion And Time GraphsJatin GuptaNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion WorksheetDocument2 pagesProjectile Motion WorksheetSuta PinatihNo ratings yet
- Worksheet No.3 in PHYSICS 1Document9 pagesWorksheet No.3 in PHYSICS 1Joshua DellosaNo ratings yet
- Momentum MCQ 211Document4 pagesMomentum MCQ 211Kariem Mohamed Ragab Hamed100% (1)
- One-Dimensional KinematicsDocument50 pagesOne-Dimensional KinematicsStephen Correa100% (1)
- Dynamics Worksheet 2 - ForcesDocument2 pagesDynamics Worksheet 2 - ForcesJennifer Moore100% (1)
- Worksheet On Kinematics KeyDocument6 pagesWorksheet On Kinematics KeyelenaNo ratings yet
- NTSE Question Bank for Physics RevisionDocument33 pagesNTSE Question Bank for Physics RevisionQSQFNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesGravitation Practice QuestionsVebhha GargNo ratings yet
- Linear Motion ExerciseDocument5 pagesLinear Motion ExercisePei JingNo ratings yet
- Straight Line - QuestionsDocument7 pagesStraight Line - QuestionsNameet JainNo ratings yet
- IX Chemistry Revision Test PaperDocument4 pagesIX Chemistry Revision Test PaperTeja RajarameshNo ratings yet
- Kinematics WorksheetDocument9 pagesKinematics WorksheetLai Kee KongNo ratings yet
- Kinematics WorksheetDocument4 pagesKinematics WorksheetRobertYue100% (2)
- Ch04 05 Force Problem BankDocument11 pagesCh04 05 Force Problem Banknicky1213aNo ratings yet
- FlotationDocument14 pagesFlotationAbhinav BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Class 9 GravitationDocument11 pagesClass 9 GravitationShubhendu KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Moments: Turning Effect of A ForceDocument21 pagesMoments: Turning Effect of A ForceAnki AccountNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Mathematics Worksheet - Playing With NumbersDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 8 Mathematics Worksheet - Playing With NumbersAnoop Sahu100% (1)
- Motion in A Straight Line Test 1Document10 pagesMotion in A Straight Line Test 1meemansa12No ratings yet
- TEST (FORCE & Laws of Motion)Document2 pagesTEST (FORCE & Laws of Motion)Kumar Sushil100% (1)
- 10 Science Life Process Test 01Document1 page10 Science Life Process Test 01Dhiraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- STD-09 CBSE CH-8 Graphical Representation of Motion (Velocity-Time Graph) WORKSHEET-2021 4Document4 pagesSTD-09 CBSE CH-8 Graphical Representation of Motion (Velocity-Time Graph) WORKSHEET-2021 4Taksh KapatelNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Worksheet on Work and EnergyDocument1 pageCBSE Class 9 Science Worksheet on Work and EnergyAlok Kumar TiwariNo ratings yet
- Lines and Angles Class 6 CBSEDocument13 pagesLines and Angles Class 6 CBSEIhtesham Hussain0% (1)
- Class IX (Physics) Unit-1-Edited PDFDocument96 pagesClass IX (Physics) Unit-1-Edited PDFKanhaiya Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- 9bio AssignmentDocument2 pages9bio AssignmentKrishna GovilNo ratings yet
- Understanding FrictionDocument36 pagesUnderstanding FrictionShourya JainNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum WorksheetDocument4 pagesConservation of Momentum Worksheetmarvsloves13No ratings yet
- Physical World Unit Dimensions ErrorDocument20 pagesPhysical World Unit Dimensions ErrorkakuNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Year 6Document12 pagesModule 5 Year 6radenesNo ratings yet
- Honors Physics Midterm Review GuideDocument8 pagesHonors Physics Midterm Review GuideEarl averzosaNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and PowerDocument3 pagesWork, Energy and PowerUJJVAL GAHOINo ratings yet
- Class 9 Forces & Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesClass 9 Forces & Laws of MotionAmita RanaNo ratings yet
- Forces Worksheet-2 (Ol)Document5 pagesForces Worksheet-2 (Ol)Shabbir H. Khan100% (1)
- Work Energy Chapter Problems-2009-05-13Document21 pagesWork Energy Chapter Problems-2009-05-13Liam ReillyNo ratings yet
- Work and PowerDocument15 pagesWork and Powersujayan2005No ratings yet
- Forces IGCSE PHYSICSDocument12 pagesForces IGCSE PHYSICSNayeemAhmedNo ratings yet
- Day 9 GravitationDocument13 pagesDay 9 GravitationDivyanshi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Phys12 c06 6 1Document9 pagesPhys12 c06 6 1Ruby Angel MannNo ratings yet
- Physics 21st Century A Compilation of Contemporary and Emerging TechnologiesDocument239 pagesPhysics 21st Century A Compilation of Contemporary and Emerging TechnologiesJuiced-IN it100% (1)
- Phrasal Verbs about Science 1Document14 pagesPhrasal Verbs about Science 1Alicia MartinNo ratings yet
- Gravity Conceptual ProblemsDocument96 pagesGravity Conceptual ProblemsElvis100% (1)
- G-Coulombs LawDocument2 pagesG-Coulombs LawTrisno SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Second Term SS1 PhysicDocument23 pagesSecond Term SS1 PhysicADEYI KAYODE SAMUELNo ratings yet
- Class Ix Science Compiled Work Book 2023Document124 pagesClass Ix Science Compiled Work Book 2023traptisharma3342No ratings yet
- Force and Motion: Guimbal National High School Guimbal, IloiloDocument42 pagesForce and Motion: Guimbal National High School Guimbal, IloiloBrent AlexanderNo ratings yet
- The Genesis of General Relativity: An Inter-Theoretical ContextDocument33 pagesThe Genesis of General Relativity: An Inter-Theoretical ContextРинат НугаевNo ratings yet
- Week008-009 Rotational Motion and GravityDocument4 pagesWeek008-009 Rotational Motion and GravityDianna Katherine SalazarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - GravitationDocument13 pagesChapter 10 - Gravitationnitika chawlaNo ratings yet
- Physics: GravitationDocument66 pagesPhysics: GravitationGagandeep Wadhawan100% (2)
- 9th Gravitation 2014 45 Solved QuestionsDocument9 pages9th Gravitation 2014 45 Solved Questionsapi-242227794No ratings yet
- Ce 123 Dynamics of Solids: Prof. Beda M. Mutagahywa Faculty of Engineering. SAUTDocument16 pagesCe 123 Dynamics of Solids: Prof. Beda M. Mutagahywa Faculty of Engineering. SAUTAwadhiNo ratings yet
- Motion: James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar TorresDocument34 pagesMotion: James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar TorresArvin RescatorNo ratings yet
- Solving Differential EquationsDocument10 pagesSolving Differential EquationsEmmanuel DelantarNo ratings yet
- GRAVITATIONDocument3 pagesGRAVITATIONvaniak01028No ratings yet
- Kepler's Law of Planetary Motion For CBSE Class 11thDocument11 pagesKepler's Law of Planetary Motion For CBSE Class 11thiProfIndia100% (4)
- Mod 9 - Gravity and Periodic MotionDocument40 pagesMod 9 - Gravity and Periodic MotionJr YansonNo ratings yet
- Planetary and Satellite MotionDocument17 pagesPlanetary and Satellite MotionIstihad EmonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - PH101 - Chapter 13 - Slides and Examples - DR NaderDocument29 pagesLecture 6 - PH101 - Chapter 13 - Slides and Examples - DR NaderHebatallah Mujahed Mohmoud KanaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of Universal GravitationDocument4 pagesNewton's Law of Universal Gravitationej lumantaNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument15 pagesIsaac NewtonSamanNo ratings yet
- Precis: Capf 2021Document46 pagesPrecis: Capf 2021Kabang DupakNo ratings yet
- The Student's Guide To HSC PhysicsDocument165 pagesThe Student's Guide To HSC PhysicsRomesh Abeysuriya98% (46)
- Acceleration, Force, Momentum and EnergyDocument28 pagesAcceleration, Force, Momentum and Energyjayesh1997No ratings yet
- Calculating Forces of MotionDocument39 pagesCalculating Forces of MotionRhea Blny MñgNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Coulomb's Law Sample ProblemsDocument7 pages7.2 Coulomb's Law Sample ProblemsMeeriya NewtonNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Astrodynamics 250115Document690 pagesFundamentals of Astrodynamics 250115Keshav Kant100% (2)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (409)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (76)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombFrom EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)