Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Numerical Sheet 1
Uploaded by
Nishant MayekarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Numerical Sheet 1
Uploaded by
Nishant MayekarCopyright:
Available Formats
AGNEL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND
DESIGN
AGNEL TECHNICAL EDUCATIONAL COMPLEX
ASSAGAO, BARDEZ-GOA. 403 507
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
Numerical Sheet - 1
Topic: Gyroscope - Aeroplane & Ship
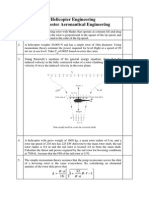
1. An aeroplane makes a complete half circle of 50 metres radius, towards left, when flying
at 200 km per hr. The rotary engine and the propeller of the plane has a mass of 400 kg
and a radius of gyration of 0.3 m. The engine rotates at 2400 r.p.m. clockwise when viewed
from the rear. Find the gyroscopic couple on the aircraft and state its effect on it.
2. An aeroplane flying at 240km/h turns towards the left and completes a quarter circle of
60m radius. The mass of the rotary engine and the propeller of the plane is 450 kg with a
radius of gyration of 320 mm. The engine speed is 2000 rpm clockwise when viewed from
the rear. Determine the gyroscopic couple on the aircraft and state its effect. In what way
is the effect changed when the (i) aeroplane turns towards right (ii) engine rotates
clockwise when viewed from the front (nose end) and the aeroplane turns (a) left (b) right?
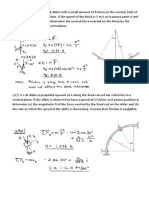
3. The turbine rotor of a ship has a mass of 3500 kg. It has a radius of gyration of 0.45 m
and a speed of 3000 r.p.m. clockwise when looking from stern. Determine the gyroscopic
couple and its effect upon the ship: 1. when the ship is steering to the left on a curve of
100 m radius at a speed of 36 km/h. 2. when the ship is pitching in a simple harmonic
motion, the bow falling with its maximum velocity. The period of pitching is 40 seconds
and the total angular displacement between the two extreme positions of pitching is 12
degrees.
4. A ship propelled by a turbine rotor which has a mass of 5 tonnes and a speed of 2100
r.p.m. The rotor has a radius of gyration of 0.5 m and rotates in a clockwise direction
when viewed from the stern. Find the gyroscopic effects in the following conditions: (i).
The ship sails at a speed of 30 km/h and steers to the left in a curve having 60 m radius.(ii).
The ship pitches 6 degree above and 6 degree below the horizontal position. The bow is
descending with its maximum velocity. The motion due to pitching is simple harmonic
and the periodic time is 20 seconds. (iii). The ship rolls and at a certain instant it has an
angular velocity of 0.03 rad/s clockwise when viewed from stern. Determine also the
maximum angular acceleration during pitching. Explain how the direction of motion due
to gyroscopic effect is determined in each case.
5. The turbine rotor of a ship has a mass of 2000 kg and rotates at a speed of 3000 r.p.m.
clockwise when looking from a stern. The radius of gyration of the rotor is 0.5 m.
Determine the gyroscopic couple and its effects upon the ship when the ship is steering to
the right in a curve of 100 m radius at a speed of 16.1 knots (1 knot = 1855 m/hr). Calculate
also the torque and its effects when the ship is pitching in simple harmonic motion, the
bow falling with its maximum velocity. The period of pitching is 50 seconds and the total
angular displacement between the two extreme positions of pitching is 12°. Find the
maximum acceleration during pitching motion.
You might also like
- Mechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandMechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Problems On GyrocopeDocument1 pageProblems On GyrocopeSachi DhanandamNo ratings yet
- GyroscopicDocument10 pagesGyroscopicHemaNo ratings yet
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Gyroscope (Worksheet)Document1 pageGyroscope (Worksheet)tewodros100% (1)
- Second Series Examination, April 2019 Time: 2 Hrs ME-S6 Max Marks: 40 Answer Any Two QuestionsDocument2 pagesSecond Series Examination, April 2019 Time: 2 Hrs ME-S6 Max Marks: 40 Answer Any Two QuestionssubNo ratings yet
- Md-Ii Focused Short Answer Question (Gyroscope)Document2 pagesMd-Ii Focused Short Answer Question (Gyroscope)Amit Singh DehuryNo ratings yet
- Gyroscope ProblemsDocument8 pagesGyroscope Problemsmane prathameshNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1Document1 pageWorksheet 1sharmashnNo ratings yet
- BASIC GYRO (Compatibility Mode)Document7 pagesBASIC GYRO (Compatibility Mode)E5251888No ratings yet
- Assignment: A and A Wheel WeighingDocument1 pageAssignment: A and A Wheel WeighingIshfaqurNo ratings yet
- Lesson 01 To 16 ReviewDocument3 pagesLesson 01 To 16 Reviewi5piritiNo ratings yet
- AISSMSCOEDocument3 pagesAISSMSCOEAtharva ChoudhariNo ratings yet
- 8d9ddsample Problems R&MDocument5 pages8d9ddsample Problems R&Mgirithik14No ratings yet
- MOTHER TERESA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DYNAMICS OF MACHINE QUESTIONSDocument3 pagesMOTHER TERESA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DYNAMICS OF MACHINE QUESTIONSG VENKATESWARARAONo ratings yet
- Gyroscope Effects on Ship Steering, Pitching & RollingDocument29 pagesGyroscope Effects on Ship Steering, Pitching & RollingEssKayNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion ProblemsDocument5 pagesCircular Motion ProblemsMelissa A. BernardoNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machinery Question Bank PDFDocument10 pagesDynamics of Machinery Question Bank PDFSree MurthyNo ratings yet
- Std. XII Physics (Numericals) Question Bank PDFDocument34 pagesStd. XII Physics (Numericals) Question Bank PDFPaul Levis RioNo ratings yet
- Energy and Momentum Problem SetDocument4 pagesEnergy and Momentum Problem SetPranjal DhamNo ratings yet
- Gyroscopic effects and balancing of rotating machineryDocument2 pagesGyroscopic effects and balancing of rotating machineryvishalNo ratings yet
- A808777825 - 16445 - 6 - 2021 - Assignment 3 219Document2 pagesA808777825 - 16445 - 6 - 2021 - Assignment 3 219FREE FIRE OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- 2 ND Internal emDocument1 page2 ND Internal emranjeemitNo ratings yet
- GyroscopeDocument116 pagesGyroscopeSAI PRAMOD RAVADANo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument15 pagesCircular Motionpraveen alwisNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review ProblemsDocument8 pagesFinal Exam Review ProblemsIrina StefaniaNo ratings yet
- Centripetal acceleration and force problemsDocument2 pagesCentripetal acceleration and force problemsRenor SagunNo ratings yet
- PBR VISVODAYA ENGINEERING COLLEGE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING UNIT-IDocument7 pagesPBR VISVODAYA ENGINEERING COLLEGE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING UNIT-Ihod mechNo ratings yet
- Gyroscope - Gyroscopic Effects On The Movement Of: Airplanes and Ships - Gyroscope StabilizationDocument25 pagesGyroscope - Gyroscopic Effects On The Movement Of: Airplanes and Ships - Gyroscope StabilizationAbdur Rahman100% (1)
- DOM Assignment 2022-23Document11 pagesDOM Assignment 2022-23Pratham DakoriaNo ratings yet
- 6.assignment QuestionsDocument10 pages6.assignment QuestionsideepujNo ratings yet
- Exp 6 GyroscopeDocument25 pagesExp 6 GyroscopeBikash ChoudhuriNo ratings yet
- CH 2 - Problems 2023-12-27 22 - 14 - 56Document2 pagesCH 2 - Problems 2023-12-27 22 - 14 - 56rb8q9sz8hrNo ratings yet
- Gyroscope and Flywheel EffectsDocument2 pagesGyroscope and Flywheel EffectsSree MurthyNo ratings yet
- Physics 50problemsDocument6 pagesPhysics 50problemsQuicksilver 1975No ratings yet
- Gyroscopic CoupleDocument10 pagesGyroscopic CoupleAnandha RamanNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment ProblemsDocument2 pagesHome Assignment ProblemsAneesh KumarNo ratings yet
- I-Taalem Task - Chapter 6Document3 pagesI-Taalem Task - Chapter 6ruzaimi98No ratings yet
- P13ME51 BN AjanaDocument3 pagesP13ME51 BN AjanaRocky FxNo ratings yet
- GyroscopeDocument2 pagesGyroscopeSang Ka KalaNo ratings yet
- DOM AssignmentDocument2 pagesDOM AssignmentBharath NNo ratings yet
- Navigation Test Paper (156 Q.)Document33 pagesNavigation Test Paper (156 Q.)Dipanjan Choudhury60% (5)
- Diagnostic Exam Review Phy10Document24 pagesDiagnostic Exam Review Phy10Kayla DollenteNo ratings yet
- HE Q-BankDocument6 pagesHE Q-Bankmanikandan_murugaiahNo ratings yet
- 106 C 12 InclassDocument5 pages106 C 12 InclassSarvesh KanaujiaNo ratings yet
- Plates 1Document3 pagesPlates 1Rowel Gonzaga GulleNo ratings yet
- Solve Curvilinear MotionDocument3 pagesSolve Curvilinear Motionصادق سلام محمود شوطNo ratings yet
- Physics Components and ForcesDocument22 pagesPhysics Components and ForcesRed Crazy0% (1)
- UAV Launch Force CalculatorDocument7 pagesUAV Launch Force Calculatornam NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Saint Joseph Catholic School-Adama: Grade 11 Physics Worksheet April 2012 (2020)Document3 pagesSaint Joseph Catholic School-Adama: Grade 11 Physics Worksheet April 2012 (2020)Nardos AlemayewNo ratings yet
- 174 Gyroscopic Effect On Naval ShipsDocument4 pages174 Gyroscopic Effect On Naval ShipsAniket SankpalNo ratings yet
- UZB352E Spring2018 HW2Document1 pageUZB352E Spring2018 HW2BellatrixMacabreNo ratings yet
- AP C Review Guide CH6Document5 pagesAP C Review Guide CH6مشاعر مكتومهNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion 1 QPDocument8 pagesCircular Motion 1 QPNovi Juniati PitrianaNo ratings yet
- U.S.N. BMS College of Engineering, Bengaluru-560019 Dynamics Of Machines exam questionsDocument3 pagesU.S.N. BMS College of Engineering, Bengaluru-560019 Dynamics Of Machines exam questionsyyy 4uNo ratings yet
- DOM Question BankDocument4 pagesDOM Question BankGomish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Home Package 3Document5 pagesPhysics Home Package 3Patrick NkwabiNo ratings yet
- all impDocument48 pagesall impdevrarimanish72No ratings yet
- Numerical Sheet 8Document2 pagesNumerical Sheet 8Nishant MayekarNo ratings yet
- Balancing of rotating and reciprocating massesDocument3 pagesBalancing of rotating and reciprocating massesNishant MayekarNo ratings yet
- Damped Vibrations Problems and SolutionsDocument2 pagesDamped Vibrations Problems and SolutionsNishant MayekarNo ratings yet
- Numerical Sheet 3Document2 pagesNumerical Sheet 3Nishant MayekarNo ratings yet
- AM Need and IntroductionDocument13 pagesAM Need and IntroductionNishant MayekarNo ratings yet
- QB It4Document1 pageQB It4Nishant MayekarNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing Processes and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesAdditive Manufacturing Processes and ApplicationsNishant MayekarNo ratings yet
- Rapid Manufacturing Process OptimizationDocument30 pagesRapid Manufacturing Process OptimizationNishant MayekarNo ratings yet
- Mil - A - 8865BDocument13 pagesMil - A - 8865BLoc Das NeyfusNo ratings yet
- Propeller design with modified velocity for improved coolingDocument11 pagesPropeller design with modified velocity for improved coolingfelip987No ratings yet
- BGUQ - Uummannaq2Document1 pageBGUQ - Uummannaq2Adam MosseriNo ratings yet
- Project Presentation on Quadcopter DroneDocument17 pagesProject Presentation on Quadcopter DroneAkshay SinghalNo ratings yet
- The National Academies Press: Nextgen For Airports, Volume 5: Airport Planning and Development (2017)Document160 pagesThe National Academies Press: Nextgen For Airports, Volume 5: Airport Planning and Development (2017)ERRAMESH1989No ratings yet
- IOSA Standards Manual (ISM) Ed 13Document657 pagesIOSA Standards Manual (ISM) Ed 13Willy Suárez100% (7)
- Jeppview For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitDocument26 pagesJeppview For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitMichael ParkanskiNo ratings yet
- Ica RVSM - Ami-Iica-Lj-0432-CDocument35 pagesIca RVSM - Ami-Iica-Lj-0432-CLuciene Orecchio100% (1)
- Iata CRM TemDocument184 pagesIata CRM TemPILCOMOV10No ratings yet
- Thai Airways A380 Paper ModelDocument15 pagesThai Airways A380 Paper ModelAndriy Kovalyshyn100% (1)
- Piper Service Bulletin 528D Provides Guidance on Wing Lift Strut Inspection and ReplacementDocument6 pagesPiper Service Bulletin 528D Provides Guidance on Wing Lift Strut Inspection and ReplacementjulzzyNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation For Confined Rectangular Slot JetsDocument14 pagesNumerical Simulation For Confined Rectangular Slot JetsmrccahmedNo ratings yet
- Pipistrel Sinus 912 POHDocument102 pagesPipistrel Sinus 912 POHGourav DasNo ratings yet
- 15 - Landing GearDocument2 pages15 - Landing Gear郝帅No ratings yet
- Cambridge Ils/Dme/Ndb (L) RWY 23 Instrument Approach Chart - IcaoDocument1 pageCambridge Ils/Dme/Ndb (L) RWY 23 Instrument Approach Chart - IcaoAbdelhak MiohsineNo ratings yet
- 1 - HND QCF Propulsion Assignment 3 2011.2012Document6 pages1 - HND QCF Propulsion Assignment 3 2011.2012Muhammad HussainNo ratings yet
- 01-CPD-8, Civil Aviation Procedure Document On Airworthiness-MinDocument884 pages01-CPD-8, Civil Aviation Procedure Document On Airworthiness-Minnishat529100% (1)
- Unit test physics friction forces Newton's lawsDocument8 pagesUnit test physics friction forces Newton's lawsDa babyNo ratings yet
- University of Dayton Research Institute AnalysisDocument135 pagesUniversity of Dayton Research Institute AnalysisGFNo ratings yet
- Rotary Wing Aircraft Handbooks and History Volume 14 The Rotary Wing IndustryDocument73 pagesRotary Wing Aircraft Handbooks and History Volume 14 The Rotary Wing Industrypiolenc@archivale.com50% (2)
- 2020-02 - Proposal KODIAK SN 268 - AIMDocument5 pages2020-02 - Proposal KODIAK SN 268 - AIMАндрей100% (1)
- FBW Airliner Flying Hints and TipsDocument26 pagesFBW Airliner Flying Hints and Tipsfizo tizoNo ratings yet
- MMOPA Magazine Summer 2010Document56 pagesMMOPA Magazine Summer 2010Antonio Cesar de Sa LeitaoNo ratings yet
- Flight Itinerary 46836Document2 pagesFlight Itinerary 46836alwi nukmanNo ratings yet
- 2000 2 EngDocument21 pages2000 2 EngTateNo ratings yet
- Aviation History of Air BalloonsDocument18 pagesAviation History of Air BalloonsIbtisam AwanNo ratings yet
- FDTT (KD)Document11 pagesFDTT (KD)blip2604No ratings yet
- C152 Operating Manual Performance DataDocument11 pagesC152 Operating Manual Performance DataEmanuelNo ratings yet
- FG English Kisan Drone Operator AGRQ1006 V2.0Document153 pagesFG English Kisan Drone Operator AGRQ1006 V2.0prasenjit100% (1)
- Scale Aviation Modeller International - February 2020Document84 pagesScale Aviation Modeller International - February 2020Ron Lebert100% (2)
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesFrom EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsFrom EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersFrom EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Nutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeFrom EverandNutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeNo ratings yet
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesFrom EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemFrom EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsFrom EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNo ratings yet
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationFrom EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesFrom EverandHandbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeFrom EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyFrom EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesFrom EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- 3D Printing of Concrete: State of the Art and Challenges of the Digital Construction RevolutionFrom Everand3D Printing of Concrete: State of the Art and Challenges of the Digital Construction RevolutionArnaud PerrotNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Redefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesFrom EverandRedefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesNo ratings yet
- Safety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryFrom EverandSafety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementNo ratings yet
- Safety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaFrom EverandSafety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaNo ratings yet
- General Orders for Security Personnel: A Guide to Maintaining Discipline and ProfessionalismFrom EverandGeneral Orders for Security Personnel: A Guide to Maintaining Discipline and ProfessionalismNo ratings yet
- Autophagy in Health and DiseaseFrom EverandAutophagy in Health and DiseaseBeverly RothermelNo ratings yet
- Exercise, Sport, and Bioanalytical Chemistry: Principles and PracticeFrom EverandExercise, Sport, and Bioanalytical Chemistry: Principles and PracticeNo ratings yet