Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antenna
Antenna
Uploaded by
Syed Abdullah RizviCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antenna
Antenna
Uploaded by
Syed Abdullah RizviCopyright:
Available Formats
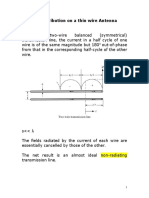
The main function of antenna is to match impedance of the medium with the cable/waveguide
impedance. Hence antenna is impedance transforming device.
Near field Region: The distance up to 2*Square (D)/Lambda is called near field region. Here D
is the antenna diameter and Lambda is wavelength of free space. This region is further divided
into two parts. The region up to 3*Lambda is called reactive or evanescent region, here wave is
of non-propagating type. The region above 3*Lambda is called radiating region or Fresnel
region.
Far field Region: The distance beyond limit of near field region is called far field region. This
region is also called as Fraunhofer region. In these region power radiated from antenna decays
inverse of square of distance.
Types:
There are two main types: non-directional antenna and directional antenna.
Non-directional antenna radiates energy in all the direction, which is also called as isotropic
antenna. In fact there is nothing like ideal isotropic antenna, each antenna will have some
directivity. Simple half wave dipole falls in this category. It is also called as Hertz antenna. This
antenna has omni-directional radiation pattern in one direction. It has figure eight shape radiation
pattern in the other two dimensions.
Directional antenna transmits/receives energy to/from particular direction. Parabolic antenna,
horn antenna falls in this category. This parabolic reflective antenna is widely used in microwave
and satellite applications. They focus energy in particular direction
Buliding loss -15 to -20db
You might also like
- Dipole AntennaDocument19 pagesDipole AntennaSherry Sher100% (1)
- Basic Antenna Theory and ConceptsDocument37 pagesBasic Antenna Theory and ConceptsRajat KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- Antenna - Module 1 - Part2Document3 pagesAntenna - Module 1 - Part2Anilakumari CANo ratings yet
- Properties of An AntennaDocument21 pagesProperties of An AntennaShankar BettadapuraNo ratings yet
- First Module Part 1Document53 pagesFirst Module Part 1hrithikNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Fundamental Parameters of Antenna PDFDocument88 pagesChapter Two Fundamental Parameters of Antenna PDFAmare Kassaw100% (1)
- Lectrure 2.basic Antenna ParametersDocument60 pagesLectrure 2.basic Antenna ParametersR Gowri ManohariNo ratings yet
- Types of AntennaDocument8 pagesTypes of AntennaHoney SkNo ratings yet
- Antenna TheoryDocument65 pagesAntenna TheoryÅpûrbǻ ßìswåsNo ratings yet
- Lecturer IIDocument78 pagesLecturer IIAhmed WasiuNo ratings yet
- Antenna Lecture1Document63 pagesAntenna Lecture1Jhanzeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Antenna - NotesDocument36 pagesAntenna - NotesRaj sambhavNo ratings yet
- Ame Unit 1Document91 pagesAme Unit 1Kamesh0% (1)
- AWP NotesDocument137 pagesAWP NotesSebastin SureshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Antenna FundamentalsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Antenna FundamentalsجعفرالشموسيNo ratings yet
- AntennaDocument8 pagesAntennaKimberly Joy FerrerNo ratings yet
- Microwave AntennasDocument78 pagesMicrowave AntennasPadmavathy VelayudhamNo ratings yet
- Antenna Qution AnswerDocument18 pagesAntenna Qution AnswerankitsprajapatiNo ratings yet
- Antenna & Wave Propagation: by Sir Qasim Ali ShahDocument11 pagesAntenna & Wave Propagation: by Sir Qasim Ali ShahFarooq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit3-Antenna and Microwave SystemDocument111 pagesUnit3-Antenna and Microwave SystemRahul RNo ratings yet
- 3 2 AntennasDocument23 pages3 2 AntennasKAWA CONTENT TEAMNo ratings yet
- Microwave AntennaDocument78 pagesMicrowave AntennaadilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Fundamental Parameters of AntennaDocument73 pagesChapter 01 Fundamental Parameters of AntennaEngr Nuzhat LashariNo ratings yet
- (AT) Summary (Chapter 2)Document13 pages(AT) Summary (Chapter 2)Omar MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Small Antennas For High FrequenciesDocument29 pagesSmall Antennas For High FrequenciesNameNo ratings yet
- Near and Far FieldDocument12 pagesNear and Far Fieldchuck333No ratings yet
- AntennaDocument68 pagesAntennaFarra Ineza ZahariNo ratings yet
- AntennaDocument45 pagesAntennaIndraysh Vijay [EC - 76]No ratings yet
- Antenna AssignmentDocument8 pagesAntenna AssignmentShobuj100% (1)
- CH 2 PDFDocument57 pagesCH 2 PDFmuhmmad hassanNo ratings yet
- Thesis UpdatedDocument40 pagesThesis UpdatedcyberpunkNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2: Radiation Integrals and Auxiliary Potential FunctionsDocument15 pagesCHAPTER 2: Radiation Integrals and Auxiliary Potential FunctionsTibebu Xibe TeNo ratings yet
- Ch7 - 3 Antennas3Document20 pagesCh7 - 3 Antennas3MasterArvinNo ratings yet
- Small Antennas For High FrequenciesDocument23 pagesSmall Antennas For High FrequenciesGumaMohamedNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Fundamental Parameters of AntennaDocument84 pagesCH-2 Fundamental Parameters of AntennaAbenezer BedluNo ratings yet
- 11 Chapter IVDocument15 pages11 Chapter IVfanorkNo ratings yet
- EC6602 Uw 2Document451 pagesEC6602 Uw 2jenath1No ratings yet
- All About AntennasDocument6 pagesAll About AntennasgunjanNo ratings yet
- Antenna Measurement TheoryDocument21 pagesAntenna Measurement Theorybrahmamtech100% (1)
- Question Bank-Antenna Wave and PropogationDocument56 pagesQuestion Bank-Antenna Wave and Propogationabinayageetha33% (3)
- Antenna Material: Resistivity ResistanceDocument5 pagesAntenna Material: Resistivity ResistanceAbdul GhaniNo ratings yet
- Basics AntennasDocument196 pagesBasics Antennashappy girl100% (3)
- AntennaDocument129 pagesAntennaChonny Reyes E100% (1)
- Types of Antenna and Types of PropagationDocument22 pagesTypes of Antenna and Types of PropagationPaul PerezNo ratings yet
- Antenna A NotesDocument13 pagesAntenna A NotesspgmaniarunagiriNo ratings yet
- AMWE PPT Unit1 Topic2Document15 pagesAMWE PPT Unit1 Topic2Asan Mohideen KhansaduraiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 3 Study of HORN Antenna MeasurementsDocument7 pagesExperiment No. 3 Study of HORN Antenna MeasurementsAtharv NigamNo ratings yet
- 09 - Principle of AntennaDocument6 pages09 - Principle of AntennameghanaNo ratings yet
- WiFi Lab Notes 2022 PDFDocument10 pagesWiFi Lab Notes 2022 PDFSupr RayNo ratings yet
- LN - 10 - 50 - Radar MeteorologyDocument47 pagesLN - 10 - 50 - Radar MeteorologyPantulu MurtyNo ratings yet
- SECA1504Document71 pagesSECA1504SuganrajNo ratings yet
- Antenna: NLS FPTV UthmDocument28 pagesAntenna: NLS FPTV UthmMuhamad ReduanNo ratings yet
- AntennaDocument34 pagesAntennakarranNo ratings yet
- Antenna Theory LectureDocument18 pagesAntenna Theory LecturetleeanneraNo ratings yet
- Antennas 101 5ppDocument5 pagesAntennas 101 5ppj.emmett.dwyer1033No ratings yet
- BASICS OF - AntennasDocument193 pagesBASICS OF - AntennasAlas Mallari Donato100% (1)
- Antenna PrimerDocument102 pagesAntenna PrimerWaqar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Basic Antenna Theory and ConceptsDocument75 pagesBasic Antenna Theory and Conceptsvaldesc_tolNo ratings yet
- Pef & Allied Groups Panel - Pecelections 2015Document4 pagesPef & Allied Groups Panel - Pecelections 2015Syed Abdullah RizviNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Graduate ProgramsDocument6 pagesSample Test Graduate ProgramsSyed Abdullah RizviNo ratings yet
- Webinar 5 Part 1 LTE Optimization Rev13 PDFDocument178 pagesWebinar 5 Part 1 LTE Optimization Rev13 PDFEskiterio Ipora OporeNo ratings yet
- Code Division Mutiple AccessDocument36 pagesCode Division Mutiple AccessSyed Abdullah RizviNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5, Inside Digital DesignDocument33 pagesCHAPTER 5, Inside Digital DesignSyed Abdullah RizviNo ratings yet
- Flyball GovernorDocument5 pagesFlyball GovernorSyed Abdullah RizviNo ratings yet