Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Upload 1
Upload 1
Uploaded by
DD97Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Upload 1
Upload 1
Uploaded by
DD97Copyright:
Available Formats
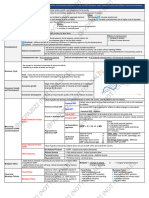
Macroeconomic Objectives
UNEMPLOYMENT
UNEMPLOYME
NT
Types and Causes
Note that some level of unN will always be present in an
economy at the level we know as full employment. This
natural rate of unN is also known as equilibrium unN.
Below are the four main types of unN you should be
aware of.
Frictional
Structural
Arises when people are in
Arises due to
between jobs exists even
1. Changes in the structure
when the economy is at full of the economy
employment.
2. Mismatch between
1. Imperfect labour market
skill/location of the labour
operations
force and those required
2. Immobility of workers
for new jobs
- Changes in pattern of
demand/supply
Classical
1. Monopoly power causing
wages to be above market
clearing level
- Role of unions
Demand-deficient
(cyclical)
Involuntary unemployment
1. Due to lack of AD for
goods
2. Associated with
transitions of the economy
through the business cycle
Policy Options
Expansionary demand
management policies
Generally only works for
demand-deficient unN as
these policies increase AD
Fiscal policy
G on supply-side policies
AD
Income tax more
incentive to be employed
Monetary policy
i/r Im AD
[xcrp to increase demand
for exports or to decrease
amount of foreign labour] weak
Conflicts
Supply-side policies
increase the productive
capacity of the economy
Improving employability:
through education,
retraining etc. (e.g. WDA
in Singapore)
Improving incentives for
people to search and
accept N (e.g. through
tax/benefit reforms)
Sustaining EG in the LR
constantly creates new
jobs
In general solving demand-deficient unN would have
demand-pull inflationary pressures demand and costs
pressures.
Also, a low rate of unemployment may result in a
current account deficit.
Consequences
runShort
Internal
Ye < Y f
unN output, G, NY all
unN SOL
Loss of potential output that could have been produce
if unemployed were employed less goods for
consumption
Long run
SOL for unemployed forced to consumer less due to
lower YD
Loss of output and profits:
unN limits the outward shift of the PPC
Structural unN inward shift of the PPC due to quantity
of labour falling
Deskilling skills becoming obsolete
PEG is affected in the LR PPC moves out less quickly
Lower PEG
unN dissavings S supply of loanable funds
i/r Im K stock PEG (outward shift of
PPC limited)
External
Decreased FDI
unN FDI
Especially in the case of structural unN labour force is
deskilled, companies tend to pull out
[unN M CP, current account ] this point is
rather weak
Income redistribution
The Y-gap worsens as structural/seasonal unN tends to
happen to people from lower Y groups
Fiscal costs to governments
In welfare states, G as unN benefits are paid out.
Tax revenues both directly (as zero Y earners do not
pay income tax) and indirectly (zero Y earners consume
less and thus pay less taxes on C).
Inefficiency as an economy is producing within the PPC
Negative social effects like strikes, crimes and suicide.
You might also like
- MacroDocument6 pagesMacrocorvids75% (4)
- GP - Essay Questions Collection From Past PrelimsDocument8 pagesGP - Essay Questions Collection From Past Prelimshelixate100% (16)
- Physics EquationsDocument5 pagesPhysics Equationsanon-992211100% (64)
- Chemistry - Overview of Aliphatic Organic ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistry - Overview of Aliphatic Organic Chemistryhelixate100% (5)
- Chemistry - Organic Chemistry Reaction SchemeDocument19 pagesChemistry - Organic Chemistry Reaction Schemehelixate94% (16)
- BEC Notes Chapter 2Document7 pagesBEC Notes Chapter 2cpacfa100% (10)
- Macroeconomics 1 Cheatsheet For MBA StudentsDocument4 pagesMacroeconomics 1 Cheatsheet For MBA StudentsDikshit KashyapNo ratings yet
- Ap Macroeconomic Models and Graphs Study GuideDocument23 pagesAp Macroeconomic Models and Graphs Study Guideapi-243723152100% (1)
- H2 Chemistry DefinitionsDocument2 pagesH2 Chemistry DefinitionsEugene TayNo ratings yet
- GCE A Level Essay Questions by Year (1995-2006)Document12 pagesGCE A Level Essay Questions by Year (1995-2006)helixate86% (7)
- Ms20 - MacroeconomicsDocument2 pagesMs20 - MacroeconomicsSeokjin KimNo ratings yet
- F2F W10 - ReviewDocument9 pagesF2F W10 - Reviews3976142No ratings yet
- Econ Review ProjectDocument5 pagesEcon Review ProjectNing GuangNo ratings yet
- AP Macro Cram Chart 2021Document1 pageAP Macro Cram Chart 2021weronikaNo ratings yet
- Types of Unemployment A) Seasonal UnemploymentDocument6 pagesTypes of Unemployment A) Seasonal Unemploymentabadi gebruNo ratings yet
- Economics Reviewer - 3.3 MacroEconomic ObjectivesDocument16 pagesEconomics Reviewer - 3.3 MacroEconomic ObjectivesCK OngNo ratings yet
- Econs Monetary Policy TableDocument11 pagesEcons Monetary Policy Tableregine sunNo ratings yet
- Acroeconomic IMS: U NY SDocument11 pagesAcroeconomic IMS: U NY SHitisha agrawalNo ratings yet
- Reading 11 - Understanding Business CyclesDocument33 pagesReading 11 - Understanding Business CyclesAllen AravindanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Macro Economics: 1. Business CycleDocument9 pagesChapter Three: Macro Economics: 1. Business CycleTewodros TadesseNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Objectives - Low Inflation Rate - HandoutDocument48 pagesMacroeconomic Objectives - Low Inflation Rate - Handoutdenny_sitorusNo ratings yet
- 44-45. Demand and Supply Side Causes of Unemployment 2Document12 pages44-45. Demand and Supply Side Causes of Unemployment 2ryan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document13 pagesChapter 9ffffffNo ratings yet
- Sessions 6,7,8 - Demand Supply - Keynesian ModelDocument143 pagesSessions 6,7,8 - Demand Supply - Keynesian ModelAbhay SahuNo ratings yet
- SRJC JC2 H1 Econs / 2018 / Workbook - Economic GrowthDocument25 pagesSRJC JC2 H1 Econs / 2018 / Workbook - Economic GrowthXian LongNo ratings yet
- 總體經濟學 12Document63 pages總體經濟學 12王佑丞No ratings yet
- Recession and Our RoleDocument35 pagesRecession and Our RoleRegina Sharon PalletiNo ratings yet
- Economics Duran and LachicaDocument1 pageEconomics Duran and LachicaAaron Daniel DuranNo ratings yet
- New Pol Econ - Chapter 2Document8 pagesNew Pol Econ - Chapter 2Maureen OlvisNo ratings yet
- 08 Business Cycles, Unemployment, InflationDocument3 pages08 Business Cycles, Unemployment, Inflationcatherine tucayNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Aggregate Supply & DemandDocument102 pagesModule 5 Aggregate Supply & DemandPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Ammu Inflation & Unemployment English NotesDocument5 pagesAmmu Inflation & Unemployment English NotesAnimated TamashaNo ratings yet
- l1 Ec Rsheets b2Document1 pagel1 Ec Rsheets b2eloise.vernierNo ratings yet
- End Term Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesEnd Term Cheat SheetnupurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document32 pagesChapter 14bhavesh TanwaniNo ratings yet
- Ec Mo InflationDocument2 pagesEc Mo InflationRellop NayNo ratings yet
- JP Mac MicDocument43 pagesJP Mac MicJP MishraNo ratings yet
- Keynesian vs. Classical Income ModelDocument70 pagesKeynesian vs. Classical Income ModelNitish KhatanaNo ratings yet
- Economic Assignment 2Document7 pagesEconomic Assignment 2Prateek_Ghai_303No ratings yet
- Laws of Demand and Supply: 4 Phases of The Business CycleDocument3 pagesLaws of Demand and Supply: 4 Phases of The Business CyclejazNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics AS-AD ModelDocument3 pagesMacroeconomics AS-AD ModelMija DiroNo ratings yet
- Copia de Principles of Economics, Chapter 21 SummaryDocument3 pagesCopia de Principles of Economics, Chapter 21 SummaryMariaDeLosAngelesPachecoRuizNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Aims and Issues Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesMacroeconomic Aims and Issues Cheat SheetAjathShatruRajuNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand (AD) : AD and AS OnlineDocument52 pagesAggregate Demand (AD) : AD and AS OnlineM Shubaan Nachiappan(Student)No ratings yet
- India's Slowdown: What It Is and What Can Be DoneDocument6 pagesIndia's Slowdown: What It Is and What Can Be DonePrisha BhatiNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Supply Side PoliciesDocument1 pageAdvantages of Supply Side PoliciesGupi PalNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document43 pagesUnit 3PARVEENNo ratings yet
- ECON1102 Macroeconomics 1 CheatsheetDocument2 pagesECON1102 Macroeconomics 1 CheatsheetCarla MissionaNo ratings yet
- Injections and WithdrawalsDocument2 pagesInjections and WithdrawalsDynafrom100% (3)
- Total (GDP, GNP, GNI) Number of Population: Measures of Economic ActivityDocument9 pagesTotal (GDP, GNP, GNI) Number of Population: Measures of Economic ActivityjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Thiếu Hụt Ngân Sách Nhà NướcDocument71 pagesThiếu Hụt Ngân Sách Nhà Nướccocghe2No ratings yet
- Semester III Business Economics Module 2Document37 pagesSemester III Business Economics Module 2dharmojiraotyNo ratings yet
- 7 As-AdDocument34 pages7 As-AdThảo Vân Nguyễn ThịNo ratings yet
- Lecture2020 SSP 9757Document30 pagesLecture2020 SSP 9757Sebastian ZhangNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Fighting RecessionDocument42 pagesWeek 2 Fighting Recessiondaisyruyu2001No ratings yet
- 7 - Aggregate Demand and Supply - Student (Compatibility Mode)Document21 pages7 - Aggregate Demand and Supply - Student (Compatibility Mode)Hà Trang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- FDNECON NotesDocument4 pagesFDNECON Notesneo leeNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics A2 UpdatedDocument51 pagesMacroeconomics A2 UpdatedmatthewvanherzeeleNo ratings yet
- 5 Inflation Unemployment BCDocument39 pages5 Inflation Unemployment BCSara BatoolNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 - The MacroeconomyDocument10 pagesUnit 9 - The MacroeconomyNaomiNo ratings yet
- IG Business Chapter 24Document34 pagesIG Business Chapter 24JoyceeNo ratings yet
- OP Jindal Lecture Series Overview by RaguramJi RajanDocument18 pagesOP Jindal Lecture Series Overview by RaguramJi RajanAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Session 17 - Fiscal PolicyDocument54 pagesSession 17 - Fiscal PolicyLakshmi Harshitha mNo ratings yet
- Session 3 & 4 Aggregate Demand and Multiplier ModelDocument64 pagesSession 3 & 4 Aggregate Demand and Multiplier ModelPrateek BabbewalaNo ratings yet
- Open MacroDocument12 pagesOpen MacroLoliNo ratings yet
- Profit Maximisation at MR MC: An Open Source Education ProjectDocument6 pagesProfit Maximisation at MR MC: An Open Source Education ProjecthelixateNo ratings yet
- Math - Series & SequencesDocument4 pagesMath - Series & Sequenceshelixate100% (3)
- Math - Complex Numbers RefresherDocument5 pagesMath - Complex Numbers Refresherhelixate100% (2)
- Economics - Market StructuresDocument5 pagesEconomics - Market Structureshelixate67% (3)
- GP - Types of AqDocument18 pagesGP - Types of Aqhelixate100% (4)
- Chemistry Cheat Sheet - Physical and Chemical PropertiesDocument5 pagesChemistry Cheat Sheet - Physical and Chemical PropertiesEdward LeeNo ratings yet
- Physics - DefinitionsDocument2 pagesPhysics - Definitionshelixate100% (1)
- Chemistry - Organic Chemistry MechanismsDocument2 pagesChemistry - Organic Chemistry Mechanismshelixate100% (3)