Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shark Respiration: Izmania Shaharani 3415122174
Shark Respiration: Izmania Shaharani 3415122174
Uploaded by
sharanianiaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Shark Respiration: Izmania Shaharani 3415122174
Shark Respiration: Izmania Shaharani 3415122174
Uploaded by
sharanianiaCopyright:
Available Formats
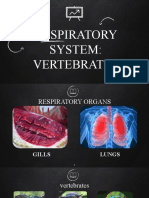
Shark Respiration
Izmania Shaharani
3415122174
Cartilaginous fishes:
5 naked gill slits
Anterior & posterior walls of the 1st 4 gill chambers have a gill surface
(demibranch). Posterior wall of last (5th) chamber has no demibranch.
Interbranchial septum lies between 2 demibranchs of a gill arch
Gill rakers protrude from gill cartilage & guard entrance into gill chamber
2 demibranchs + septum & associated cartilage, blood vessels, muscles, & nerves =
holobranch
The
respiratory system of
sharks is markedly different
from that of bony fishes.
Where bony fishes usually
have five gilled arches and
only one external gill
opening, sharks may have as
many as seven openings, but
the most common number is
five. Also, where the gill
arches of bony fishes are
protected by anopercle, or
plate, the gills of sharks are
not.
Sharks generally inhale most of the
necessary water through their mouths, but
they are also able to inhale water by way of
spiracles, which are opening located close
to the gills. When resting, sharks propel
water over their gills using the muscles of
their jaws and pharynx. Oxygen from the
incoming water is absorbed into the blood
system by way of the gill filaments. Water
exits through the gill slits .(Davies, 1964).
You might also like
- By 256 Lab Exam 1 StudyguideDocument22 pagesBy 256 Lab Exam 1 StudyguideshealynrcobbNo ratings yet
- 2Document6 pages2jessito2100% (1)
- External Anatomy of Vertebrates Class AgnathaDocument9 pagesExternal Anatomy of Vertebrates Class AgnathaJerico YoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory - VertebratesDocument53 pagesRespiratory - VertebratesEiann Jasper LongcayanaNo ratings yet
- History: For Other Uses of "Gill", SeeDocument6 pagesHistory: For Other Uses of "Gill", SeeWira SentanuNo ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy of Respiratory SystemDocument129 pagesComparative Anatomy of Respiratory Systemgerman guazaNo ratings yet
- CH 30 Notes FishDocument48 pagesCH 30 Notes Fishapi-244168124No ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Phylum - ChordataDocument11 pagesAnimal Kingdom Phylum - ChordatamalavikaNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom ChordataDocument10 pagesAnimal Kingdom ChordataRaichal P BijuNo ratings yet
- Accessory Respiratory Organ - FishDocument27 pagesAccessory Respiratory Organ - Fishkaushik mallick100% (1)
- Respiratory System: Lecture Six Assit - Lect.Maha MustafaDocument8 pagesRespiratory System: Lecture Six Assit - Lect.Maha Mustafanareman hassanNo ratings yet
- Phylum EchinodermataDocument88 pagesPhylum EchinodermataIkki PhoenixNo ratings yet
- Phylum ChordataDocument18 pagesPhylum Chordatasehrish100% (1)
- 3a - Module 3 Biodiversity Animalia Part 3b 2020Document66 pages3a - Module 3 Biodiversity Animalia Part 3b 2020Hailey McLeanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy SharkDocument32 pagesAnatomy SharkKanwal RashidNo ratings yet
- Phylum Mollusca: Mantle-Is A Dorsal Glandular Fold of The Body Wall. It Is Thick and Muscular and Encloses MantleDocument5 pagesPhylum Mollusca: Mantle-Is A Dorsal Glandular Fold of The Body Wall. It Is Thick and Muscular and Encloses MantleFrenzes PadabocNo ratings yet
- Chondrichthyes Dan OsteichthyesDocument34 pagesChondrichthyes Dan Osteichthyesfajar okta widaraNo ratings yet
- Anatomia e Fisiologia de PeixesDocument17 pagesAnatomia e Fisiologia de PeixesLuiz Vítor Oliveira VidalNo ratings yet
- SZL102 Topic Five Class Osteichthyes-1Document5 pagesSZL102 Topic Five Class Osteichthyes-1jenkionyangoNo ratings yet
- Phylum EchinodermataDocument23 pagesPhylum EchinodermataIsaacNo ratings yet
- BIOL330 Lab 2 - Lab ManualDocument7 pagesBIOL330 Lab 2 - Lab ManualOliverNo ratings yet
- Phylum MolluscaDocument50 pagesPhylum MolluscaIsaacNo ratings yet
- AEB 302 Lecture NoteDocument92 pagesAEB 302 Lecture Notemisakisuki7No ratings yet
- Evolution of KidneyDocument127 pagesEvolution of Kidneyanon_9692255300% (1)
- Urogenital System: By:Mariska Fitri Silvia (1710422003) Salsabila Luqyana (1710422023)Document26 pagesUrogenital System: By:Mariska Fitri Silvia (1710422003) Salsabila Luqyana (1710422023)Salsabila LuqyanaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Anotomy of Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesComparative Anotomy of Respiratory SystemNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- 1 - External Anatomy and TaxonomyDocument8 pages1 - External Anatomy and TaxonomyJuan David Quintero MonsalveNo ratings yet
- TetrapodDocument83 pagesTetrapodyafetNo ratings yet
- Amphibians: Introduction and EvolutionDocument5 pagesAmphibians: Introduction and Evolutionmurse101No ratings yet
- The Vertebrates: 500 Million Years AgoDocument100 pagesThe Vertebrates: 500 Million Years AgoShawa DabaNo ratings yet
- The Phylum Mollusca: A. AmphineuraDocument16 pagesThe Phylum Mollusca: A. AmphineuraCindy RahmahNo ratings yet
- E Paths Hal A File 801642487718Document27 pagesE Paths Hal A File 801642487718Aijaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Fish DissectionDocument3 pagesFish DissectionVanessa Carolina Martinez Ahumada100% (1)
- 2014 Chapter 25 PPTDocument37 pages2014 Chapter 25 PPTAgus WahyudiNo ratings yet
- ZLY 412 - LIFE OF CHORDATE - (PISCES) University of IlorinDocument26 pagesZLY 412 - LIFE OF CHORDATE - (PISCES) University of IlorinGaniu MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Animal Diversity II - Introduction (Protochordates) PDFDocument5 pagesAnimal Diversity II - Introduction (Protochordates) PDFinam ullahNo ratings yet
- General Description: PlanktonDocument5 pagesGeneral Description: PlanktonshahuNo ratings yet
- GastropodsDocument19 pagesGastropodsAnoushka RoyNo ratings yet
- Reptiles: History: Reptiles Originated Approximately 300 Million Years Ago During The CarboniferousDocument32 pagesReptiles: History: Reptiles Originated Approximately 300 Million Years Ago During The CarboniferousCreate VinayNo ratings yet
- Genbio 11 20Document2 pagesGenbio 11 20sophtzu9No ratings yet
- Lecture 1: SHARKS: Corresponding Reading Material Shark Section in Lab Manual Levinton: Chapter 8Document15 pagesLecture 1: SHARKS: Corresponding Reading Material Shark Section in Lab Manual Levinton: Chapter 8JelenaNo ratings yet
- Dogfish Shark Dissection:: Squalus Acanthius)Document34 pagesDogfish Shark Dissection:: Squalus Acanthius)Bio SciencesNo ratings yet
- PISCESDocument27 pagesPISCESHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. II Sem. (Zoology) : Primitive Characters of DipnoiDocument11 pagesM.Sc. II Sem. (Zoology) : Primitive Characters of DipnoirajuNo ratings yet
- Colegio de San Juan de LetranDocument71 pagesColegio de San Juan de Letranirish xNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science SHS 20.1 Gas Exchange in FishDocument18 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 20.1 Gas Exchange in FishjijiNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sambalpur: Science Project SESSION 2016-17 Topic-Fishes Pujarani Behera Ix - C 16 S.S.Bhoi SirDocument8 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sambalpur: Science Project SESSION 2016-17 Topic-Fishes Pujarani Behera Ix - C 16 S.S.Bhoi SirNiranjan BeheraNo ratings yet
- Phylum Echinodermata PresentationDocument38 pagesPhylum Echinodermata PresentationAliah CanalsNo ratings yet
- MolluscsDocument11 pagesMolluscsmakishtpNo ratings yet
- General Characteristic Features of Superclass PiscesDocument2 pagesGeneral Characteristic Features of Superclass PiscesSKNo ratings yet
- Ichthyology: Done by Ahlam Abbas Harasani Under Supervision Dr. Fayza Abdulrhman BawazeerDocument41 pagesIchthyology: Done by Ahlam Abbas Harasani Under Supervision Dr. Fayza Abdulrhman BawazeerDENNIS N. MUÑOZNo ratings yet
- Invertebrates Chordata VertebratesDocument62 pagesInvertebrates Chordata VertebratesDao Ming SiNo ratings yet
- Class OsteichthyesDocument13 pagesClass Osteichthyesedivisha100% (1)
- Animal Kingdom 13Document17 pagesAnimal Kingdom 13Vicky KinsNo ratings yet
- Hemichordata and Invert ChordatesDocument16 pagesHemichordata and Invert ChordatesLorie MinNo ratings yet
- Molluscs New Revised Ppt-1Document41 pagesMolluscs New Revised Ppt-1Issa Avena100% (2)
- Phylum Chordata: (Some Invertebrates and All Vertebrates)Document60 pagesPhylum Chordata: (Some Invertebrates and All Vertebrates)nightingale1995No ratings yet
- Comparative Vertebrate AnatomyDocument9 pagesComparative Vertebrate AnatomyJayson Tafalla LopezNo ratings yet
- Seahorses as Pets. Seahorse Complete Owners Manual. Seahorse care, health, tank, costs and feeding.From EverandSeahorses as Pets. Seahorse Complete Owners Manual. Seahorse care, health, tank, costs and feeding.No ratings yet
- Angler's Guide to Fishes of the Gulf of MexicoFrom EverandAngler's Guide to Fishes of the Gulf of MexicoRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1)