Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Muscles of The Pharynx
Muscles of The Pharynx
Uploaded by
jasonCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- RFP Cut Code HAM Reference - Current EditionDocument46 pagesRFP Cut Code HAM Reference - Current EditionWarrenNo ratings yet
- Lumbosacral PlexusDocument3 pagesLumbosacral Plexusgehaoi4No ratings yet
- Cervical MusculatureDocument3 pagesCervical Musculaturesimone dumbrellNo ratings yet
- NCP For Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP For Impaired Gas ExchangeSweetie Star94% (16)
- Ancient Animal Wisdom Booklet PDFDocument44 pagesAncient Animal Wisdom Booklet PDFLorena Bruno100% (1)
- 6 Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem SensoriDocument59 pages6 Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem Sensoridenis marselaNo ratings yet
- Masha and The BearDocument11 pagesMasha and The BearAgienkz ZahatsNo ratings yet
- Upper Paleolithic Cave Art Final DraftDocument22 pagesUpper Paleolithic Cave Art Final DraftNishiNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Muscles OnlyDocument7 pagesUpper Limb Muscles OnlyGwen EnriquezNo ratings yet
- ALL Clinicals of Upper LimbDocument28 pagesALL Clinicals of Upper LimbБайден ТрампNo ratings yet
- Table A - TMJ and Infratemporal FossaDocument9 pagesTable A - TMJ and Infratemporal Fossaapi-422030113No ratings yet
- Popliteal Fossa: By: Dr. Sana KashifDocument18 pagesPopliteal Fossa: By: Dr. Sana KashifUSAMA AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Nerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesNerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries: Learning ObjectivesUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb NotesDocument14 pagesUpper Limb NotesSwasChanCNo ratings yet
- The Osteology of The Lower LimbDocument4 pagesThe Osteology of The Lower LimbAldi PrawidyaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lower LimbDocument4 pagesAnatomy Lower Limbch yaqoobNo ratings yet
- Musculosk UL5 Muscles 3Document94 pagesMusculosk UL5 Muscles 3Zaid HamdanNo ratings yet
- Study Sheet - Gross Anatomy Lower - ExtremityDocument12 pagesStudy Sheet - Gross Anatomy Lower - ExtremityMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- A Sole 16 12 14Document51 pagesA Sole 16 12 14Mariam AymanNo ratings yet
- Circumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus DorsiDocument4 pagesCircumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus Dorsispeedy.catNo ratings yet
- Blue Boxes Lower LimbDocument4 pagesBlue Boxes Lower LimbZllison Mae Teodoro MangabatNo ratings yet
- Axilla and Brachial PlexusDocument22 pagesAxilla and Brachial Plexusromaisa akhtarNo ratings yet
- Elbow Complex (Kinesiology)Document2 pagesElbow Complex (Kinesiology)Kimmybee Garcia50% (2)
- Thorax AllDocument174 pagesThorax Allravindra sharmaNo ratings yet
- Neck Triangles (Regional Anatomy) Anterior Triangle Borders Arteries Veins Nerves MiscDocument6 pagesNeck Triangles (Regional Anatomy) Anterior Triangle Borders Arteries Veins Nerves Misczara_emmeNo ratings yet
- Back Anatomy TableDocument7 pagesBack Anatomy TableJeffrey XieNo ratings yet
- Subclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)Document6 pagesSubclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)馮素琴No ratings yet
- Hip Joint: Important PointsDocument4 pagesHip Joint: Important PointsNamrah AfzalNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall.Document48 pagesThoracic Wall.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Joints of Lower LimbDocument7 pagesJoints of Lower LimbjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Nerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries, S-Ii-Lm-0120Document5 pagesNerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries, S-Ii-Lm-0120Shab GeNo ratings yet
- XX Vascular Supply of Lower Limb - PPTDocument15 pagesXX Vascular Supply of Lower Limb - PPTAlistair WalkerNo ratings yet
- Back Pain: Group 4Document71 pagesBack Pain: Group 4Cesar Guico Jr.No ratings yet
- High Yield GROSS AnatomyDocument11 pagesHigh Yield GROSS AnatomyKhalilKhaliNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Lower LimbDocument15 pagesBones of The Lower Limbyachiru121No ratings yet
- Muscles in The Posterior Scapula Muscle Proximal Attachment Distal Attachment Nervous Supply FunctionDocument37 pagesMuscles in The Posterior Scapula Muscle Proximal Attachment Distal Attachment Nervous Supply FunctionMicky TsuiNo ratings yet
- Joints of The Head and Trunk - 2015-RuanDocument30 pagesJoints of The Head and Trunk - 2015-RuanKw ChanNo ratings yet
- Anterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossaDocument24 pagesAnterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossaSky StoneNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb, Pectoral RegionDocument24 pagesUpper Limb, Pectoral Regiongtaha80No ratings yet
- Lumbar Plexus (Grays Anatomy)Document12 pagesLumbar Plexus (Grays Anatomy)Joemar ReveloNo ratings yet
- Popliteal Fossa and LegDocument40 pagesPopliteal Fossa and LegRaj Shekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Gluteal RegionDocument34 pagesGluteal Regionlion2chNo ratings yet
- Table of Head and Neck MusclesDocument5 pagesTable of Head and Neck MusclesAnubhuti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Blood Suppply of Lower LimbDocument8 pagesBlood Suppply of Lower LimbCamille Magdirila100% (2)
- Anatomy, Lecture 4, Thoracic Wall (2) (Slides)Document23 pagesAnatomy, Lecture 4, Thoracic Wall (2) (Slides)Ali Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- 16-Clinical Anatomy of The Upper LimbDocument27 pages16-Clinical Anatomy of The Upper LimbAlapati Vinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb 0809 PDFDocument59 pagesUpper Limb 0809 PDFasdaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The BackDocument2 pagesMuscles of The BackavrilaNo ratings yet
- Triangles of Neck (Anatomy)Document36 pagesTriangles of Neck (Anatomy)Dr Tahira Nihal100% (1)
- 3-Inguinal Canal PDFDocument58 pages3-Inguinal Canal PDFN A0% (1)
- Topographical Anatomy of The Lower Limb - Listed AlphabeticallyDocument3 pagesTopographical Anatomy of The Lower Limb - Listed AlphabeticallySaba Adde Duhera-HamidovicNo ratings yet
- Joints of Lower Limb 2017Document77 pagesJoints of Lower Limb 2017yasrul izadNo ratings yet
- Osteology of The Upper Limb LectureDocument40 pagesOsteology of The Upper Limb LectureFavour OnyeaboNo ratings yet
- Upper ADocument4 pagesUpper ARati SutariaNo ratings yet
- UE DermatomesDocument1 pageUE DermatomesmdmdegNo ratings yet
- Foot and Ankle Bones and JointsDocument43 pagesFoot and Ankle Bones and Jointshannah murphyNo ratings yet
- Adductor Canal LatestDocument18 pagesAdductor Canal LatestSaish100% (1)
- Dermatomes and Myotomes and Its Clinical Special Test in Upper Limb and Lower LimbDocument42 pagesDermatomes and Myotomes and Its Clinical Special Test in Upper Limb and Lower LimbkkaammiillaahhNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics Anatomia 1 PDFDocument11 pagesMnemonics Anatomia 1 PDFRocio SandersNo ratings yet
- Joint of Lower LimbDocument16 pagesJoint of Lower LimbZA ID100% (1)
- Radial and Median NervesDocument33 pagesRadial and Median NervesveegeerNo ratings yet
- Table of Lower Limb MusclesDocument5 pagesTable of Lower Limb MusclesJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb AnatomyDocument33 pagesLower Limb AnatomyfefioktaviaNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy of Posterior Compartment of The ThighDocument20 pagesGross Anatomy of Posterior Compartment of The ThighOnah ArinzeNo ratings yet
- Pharynx: Upper Part: Widest - 3.5 CM, Non-Collapsible Middle Part: Narrow Lower End: Narrowest Part of GITDocument5 pagesPharynx: Upper Part: Widest - 3.5 CM, Non-Collapsible Middle Part: Narrow Lower End: Narrowest Part of GITdrpnnreddyNo ratings yet
- Pharynx: DR - Wardiansah, M.BiomedDocument38 pagesPharynx: DR - Wardiansah, M.BiomedZen AhmadNo ratings yet
- 12-Cranial CavityDocument3 pages12-Cranial Cavityapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 2004Document5 pages2004api-3757921No ratings yet
- 14-Nasal & SinusesDocument1 page14-Nasal & Sinusesapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 11-CNS & BrainDocument6 pages11-CNS & Brainapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 10 InfratemporalDocument8 pages10 Infratemporalapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 9 FaceDocument6 pages9 Faceapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 8-Neck Muscles ChartDocument1 page8-Neck Muscles Chartapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 8 NeckDocument1 page8 Neckapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 6-Spinal CordDocument4 pages6-Spinal Cordapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 7 AutonomicDocument4 pages7 Autonomicapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 5 JointsDocument2 pages5 Jointsapi-3757921100% (2)
- 4 SkullDocument1 page4 Skullapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 3 AbdomenDocument7 pages3 Abdomenapi-3757921100% (1)
- 2 ThoraxDocument7 pages2 Thoraxapi-3757921No ratings yet
- Manhattan Sentence CorrectionDocument125 pagesManhattan Sentence Correctionapi-3736636100% (8)
- 20-Lymphatics ChartDocument1 page20-Lymphatics Chartapi-3757921No ratings yet
- Transportation in Animals and PlantsDocument2 pagesTransportation in Animals and PlantsHimanshi JainNo ratings yet
- GynaecologyDocument466 pagesGynaecologymyselfrakesh57No ratings yet
- Reading Class - Tongue TwistersDocument5 pagesReading Class - Tongue TwistersKeyla RamosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Parotid GlandDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The Parotid GlandHossam NawaraNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2352409X20304636 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S2352409X20304636 MainpjNo ratings yet
- Jabberwocky: by Lewis CarrollDocument4 pagesJabberwocky: by Lewis CarrollJames Tweedie100% (1)
- The Deep Sea AnglerfishDocument2 pagesThe Deep Sea AnglerfishKhagangrad 'No ratings yet
- IOT Based Pet Feeder Automation SystemDocument4 pagesIOT Based Pet Feeder Automation SystemRizyn ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Gabriel Ernest Notes (Litcharts)Document5 pagesGabriel Ernest Notes (Litcharts)NiidiiNo ratings yet
- DR Norris - Good Trasfusion Practice PDFDocument27 pagesDR Norris - Good Trasfusion Practice PDFvasu_5iveNo ratings yet
- RBCDocument3 pagesRBCMalkish RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal PAT B.Inggris Kelas 5Document2 pagesContoh Soal PAT B.Inggris Kelas 5neneng faidah100% (3)
- Exploring Animal HabitatsDocument3 pagesExploring Animal Habitatshi.printbeeNo ratings yet
- The Ballad of East and West - KiplingDocument3 pagesThe Ballad of East and West - Kiplingnicoler111No ratings yet
- Quiz End Rhyme or Internal RhymeDocument1 pageQuiz End Rhyme or Internal RhymeAnonymous pHooz5aH6V100% (2)
- Overlord Volume 01 Chapter 2Document50 pagesOverlord Volume 01 Chapter 2bob bobNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document3 pagesQuiz 2Hustice FreedNo ratings yet
- MTS Answer KeyDocument28 pagesMTS Answer KeyZoeyspecialNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 169752Document18 pagesG.R. No. 169752Ria CuaNo ratings yet
- 8 SubjectVerbAgreementDocument40 pages8 SubjectVerbAgreementThe chair jimin falls fromNo ratings yet
- GK SSC Vol 1Document7 pagesGK SSC Vol 1Vinay CkmNo ratings yet
- Standards For Blood Banks and Transfusion Services Standards For Blood Banks and Transfusion ServicesDocument5 pagesStandards For Blood Banks and Transfusion Services Standards For Blood Banks and Transfusion Serviceslaexm95No ratings yet
- Grade 5 - Unit 2 - Living Thing - AnimalsDocument16 pagesGrade 5 - Unit 2 - Living Thing - AnimalsкатяNo ratings yet
- Immersion TablesDocument4 pagesImmersion TablesGoppino8850% (2)
Muscles of The Pharynx
Muscles of The Pharynx
Uploaded by
jasonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Muscles of The Pharynx
Muscles of The Pharynx
Uploaded by
jasonCopyright:
Available Formats
~ ~ ~ PHARYNX ~ ~ ~
Dr. Baker
All MOTOR inneveration to pharynx muscles is by
Ann Nguyen -- NYUCD 2008
Pharyngeal Plexus (cranial-XI
with-- X)
D1traveling
Anatomy Notes
Spring '05
EXCEPT: Stylopharyngeus (IX)
Tensor Palatini (V3)
Cricopharyngeus (Recurrent Laryngeal)
- a common passageway for food and air, but structurally belongs to the GI tract
- air proceeds anteriorly down the larynx trachea bronchial tree
- food proceeds posteriorly down the esophagus
- posterior communication w/ nasal cavity (above) & oral cavity (below)
EXCEPT: Nasopharynx above the Eustachian Tube
(Pharyngeal branches of V2 traveling thru
Palatovaginal & Vomerovaginal Canals)
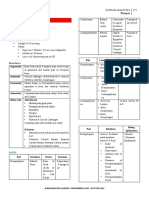
MUSCLES OF THE PHARYNX
Constrictor Muscles
Superior Constrictor
- Pterygopharyngeus
- Buccopharyngeus
- Mylopharyngeus
- Glosspharyngeus
Middle Constrictor
- Ceratopharyngeus
- Chondropharyngeus
Inferior Constrictor
- Thyropharyngeus
- Cricopharyngeus
Longitudinal Muscles
All SENSORY inneveration to pharynx mucosa is by
Pharyngeal Plexus (IX traveling with X)
Origin
Insertion
Pharyngeal Raphe
Greater Hyoid Horn
Lesser Hyoid Horn
Thyroid Cartilage
Cricoid Cartilage
Accessory (XI)
traveling with
Vagus (X)
Styloid Process
(medial aspect)
Constrictor muscles
Thyroid Cartilage (posterior)
Lateral Glossoepiglottic Fold
Palatopharyngeus
Hard Palate
(posterior edge)
Pharyngobasilar Fascia
Thyroid Cartilage (posterior)
pharyngeal wall
Eustachian Tube
(medial cartilaginous part)
pharyngeal wall
Origin
Insertion
Eustachian Tube
(medial cartilaginous part)
Tensor Veli Palatini
Eustachian Tube (lateral)
Scaphoid Fossa (M-Pt Plate base)
Sphenoid Spine
Action
Palatine Crest Aponeurosis
Innervation
Glossopharyngeal
(IX)
elevates
pharynx & larynx
during swallowing
Accessory (XI)
traveling with
Vagus (X)
Action
approximates the soft
palate to the tongue
to seal off
nsaopharynx during
swallowing
Posterior Nasal Spine
Levator Veli Palatini
Recurrent
Laryngeal
this part does NOT meet at Raphe
Stylopharyngeus
Musculus Uvulae
sequential peristaltic
squeezing of the
pharynx during
swallowing to move
food downward
Hamulus
Pterygomandibular Raphe
Mylohyoid Line of Mandible
Tongue
Insertion
Associated Muscles
Innervation
Pharyngeal Tubercle (occipital)
Origin
Salpingopharyngeus
Action
Innervation
Accessory (XI)
traveling with
Vagus (X)
elevate soft palate to
seal off nasopharynx
during swallowing
tenses soft palate to
seal off nasopharynx
during swallowing
root of V3
Compiled for you by:
Ann Nguyen -- NYUCD 2008
D1 Anatomy Notes -- Spring '05
BONY SKULL ATTACHMENTS of some pharyngeal muscles
Ann Nguyen -- NYUCD 2008
D1 Anatomy Notes -- Spring '05
- Pharyngeal Raphe = pharyngeal tubercle (11)
- Stylopharyngeus = medial aspect of the styloid process (22)
- Palatopharyngeus = posterior edge of the hard palate (10)
- Muscular Uvulae = posterior nasal spine (8)
- Levator Palatini = petrous portion by the opening of the carotid canal (4)
- Tensor Palatini = scaphoid fossa (27)
SPECIAL NOTES about some pharyngeal muscles
Tensor Palatini = uses the Hamulus to change its direction of pull
Superior Constrictor = shares a common attachment w/ the
Buccinator to the Pterygomandibular Raphe
Cricopharyngeus (Inferior Constrictor)
- does NOT insert into the Midline Raphe
- is NOT innervated by Pharyngeal Plexus
- innervated possibly by Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve
- is in a constant state of contraction
- to prevent air from going into the esophagus stomach
Stylopharyngeus
- runs b/t the Superior & Middle Constrictors
- is NOT innervated by Pharyngeal Plexus
- innervated by Glossopharyngeal (IX)
Palatopharyngeal Sphincter
- a tiny fiber from the Superior Constrictor
- acts as an accessory swallowing muscle to seal off the nasopharynx from oropharynx
Passavants Ridge
- created by the Palatopharyngeal Sphincter only during swallowing
- moves inferiorly as a stripping wave
Dehiscence of Killian
- the gap between Thyropharyngeus and the Cricopharyngeus portions of the Inferior Constrictor
Area of Lamiar
- the triangular-shaped blending of the Cricopharyngeus muscle to the Esophagus below
both areas have
potential for
herniation
Compiled for you by:
Ann Nguyen -- NYUCD 2008
D1 Anatomy Notes -- Spring '05
LAYERS OF THE PHARYNX
(1) Areolar Coat
- outermost layer that is continuous w/ the buccinators fascia
- therefore AKA: Buccopharyngeal Fascia
- contains plexus of veins & nerves
Retropharyngeal Space is located between the Buccopharyngeal & Prevertebral Fascia, and communicates w/ mediastinum
(2) Muscular Coat
- outer semicircular layer = constrictor muscles: Superior, Middle, Inferior (stacked on top of e/o like cups)
- inner longitudinal layer = longitudinal muscles: Stylopharyngeus, Palatopharyngeus, Salpinogpharyngeus
(3) Submucosa
- a tough fibrous coat that anchors the pharynx to the base of the skull
- U-shaped attachment involves the medial pterygoid plate, carotid canal, pharyngeal tubercle (occipital bone)
- therefore AKA: Basilarpharyngeal Fascia
(4) Mucosa = the internal lining of the pharynx
MUSCULAR GAPS OF THE PHARYNX
GAP 1 = b/t skull base and superior border of the Superior Constrictor muscle
Eustachian Tube
Tensor & Levator Palatini muscles
Ascending Palatine Artery
GAP 2 = b/t Superior & Middle Constrictor muscles
Stylopharyngeus muscle
Glosspharyngeal Nerve (IX)
Lingual Nerve (V3)
GAP 3 = b/t Middle & Inferior Constrictor muscles
Superior Laryngeal Artery
(from the Superior Thyroid artery off the External Carotid artery)
Internal Laryngeal Nerve
(from the Superior Laryngeal nerve off the Vagus)
- supplies sensory to larynx ABOVE VOCAL CORDS
By the way: BELOW vocal cords is innervated by Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve (directly off the Vagus)
GAP 4 = b/t Inferior Constrictor (Cricopharyngeus) & esophagus
Inferior Laryngeal Artery
(from the Inferior Thyroid artery off the Thyrocervical Trunk off the Subclavian)
Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve
(from directly off the Vagus)
- supplies motor to ALL LARYNX MUSCLES EXCEPT CRICOTHYROID
- supplies sensory to larynx BELOW VOCAL CORDS
By the way: Cricothyroid muscle is innervated by External Laryngeal nerve
(from the Superior Laryngeal nerve directly off the Vagus nerve)
SWALLOWING MECHANISM
Step 1 (voluntary)
Tongue = pushes food posteriorly into the oropharynx
Step 2 (involuntary)
Tensor & Levator Palatini muscles
- tenses & elevates the soft palate
- to seal off the oropharynx from the nasopharynx
Muscular Uvulae muscle
- pushes back towards the oropharynxs posterior wall
- oropharynxs posterior wall pushes forward too
Palatopharyngel Sphincter forms the Passavants Ridge (occurs only during swallowing)
Longitudinal pharynx muscles
Suprahyoid muscles
elevates the larynx to prevent food going down the trachea
Step 3 (involuntary)
Constrictor pharynx muscles = sequentially contract in peristaltic waves to continue the food down into the esophagus
Step 4 (involuntary)
Esophagus = peristaltic squeezing to continue the food down into the stomach
Compiled for you by:
NASOPHARYNX
Ann Nguyen -- NYUCD 2008
D1 Anatomy Notes -- Spring '05
- superior portion of the pharynx located above the soft palate, at the level of C1 vertebrae
- anterior communication w/ nasal cavity thru the Choanae
- lined w/ respiratory epithelium (ciliated pseudostratified columnar)
- always remains open and never closes up
Eustachian / Pharyngotympanic Tube
- opening is located on nasopharynxs lateral wall and leads to Middle Ear potential for communicating infections
- opening is located at the level of Inferior Nasal Concha of the nasal cavity potential for communicating infections
Levator Palatini muscle = runs along the MEDIAL side of the Eustachian Tube
Tensor Palatini muscle = runs along the LATERAL side of the Eustachian Tube
Pharyngeal Tonsils (Adenoids)
- located on the nasopharynxs superior posterior wall
- extends laterally into the Pharyngeal Recess
Tubal Tonsils = located near the Torus Tubaris
Torus Tubaris
- caused by the cartilage of the Eustachian Tube projecting into the nasopharynxs lateral wall
- located above the Eustachian Tube
Salpingopharyngeal Fold
- caused by the underlying Salpingopharyngeus muscle covered w/ mucosa
- it is the narrowed continuation of the Torus Tubaris,
- runs posterior to the Eustachian Tube and down to the pharynx
Pharyngeal Recess
- posterior to the Salpingopharyngeal Fold
- Eustachian Tube can be opened thru here and internal carotid artery may be damaged in the process
Compiled for you by:
OROPHARYNX
Ann Nguyen -- NYUCD 2008
D1 Anatomy Notes -- Spring '05
- middle portion of the pharynx located below the soft palate, at the level of C2 C3 vertebrae
- soft palate at rest = anterior communication w/ the oral cavity thru the fauces
- soft palate tensed and raised = Tensor & Levator Palatini muscles seal off nasaopharynx from oropharynx
- boundary begins at the Palatoglossal Arch
anterior to this arch is the oral cavity
posterior to this arch is the oropharynx
Palatoglossal Arch (Anterior Pillar) = a fold created by the Palatoglossal Muscle, running from palate to tongue
Palatopharyngeal Arch (Posterior Pillar) = a fold created by the Palatopharyngeal Muscle, running from palate to pharynx
Fauces = Anterior Pillar + Posterior Pillar
Palatine Tonsils
- located in between the Anterior & Posterior Pillars
- large during childhood, but atrophies during adulthood
- when these get infected, this is what people mean by Tonsilitis
- lie on top of a neurovascular bed comprised of Tonsillar Branches arising off the following vessels
Glosspharyngeal Nerve (IX)
Ascending Pharyngeal Artery
(directly off the External Carotid)
Ascending Palatine Artery
(off the Facial artery from External Carotid)
Lesser Palatine Artery
(off the Maxillary artery from External Carotid)
Dorsal Lingual Artery
(off the Lingual Artery from External Carotid)
Lingual Tonsils
- located in the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
Ring of Waldeyer
- Pharyngeal + Palatine +Lingual + Tubal Tonsils collectively form a circle around the oral opening
Compiled for you by:
LARYNGOPHARYNX
Ann Nguyen -- NYUCD 2008
D1 Anatomy Notes -- Spring '05
- inferior portion of the pharynx located between Epiglottis Esophagus (at the level of C4 C6 vertebrae)
Epiglottis = leaf-shaped elastic cartilage that guards the opening to the larynx
3 Glossoepiglottic Folds
- 1 median fold + 2 lateral folds
- run anteriorly from the epiglottis to the posterior base of the tongue
2 Valleculae
- small depressions created by the glossoepiglottic folds
- located on both sides of the median fold, anterior to the epiglottis
- particles can get trapped here cough reflex
Piriform Recess
- a vertical gutter located in between the laryngopharynxs lateral wall and the lateral glossoepiglottic fold
- continues down the larynx and into the esophagus
- Internal Laryngeal Nerve runs through here
- particles can also get trapped here
Compiled for you by:
Ann Nguyen -- NYUCD 2008
Note what pierces the Superior
Constrictor:
D1 Anatomy
Notes -- Spring '05
Tonsillar Artery (Facial)
Paratonsillar Vein
ARTERIAL SUPPLY
From the Maxillary Artery
Greater Palatine
Lesser Palatine
= supplies hard palate
= supplies soft palate
From the Facial Artery
Tonsillar Artery
Ascending Palatine
= supplies palatine tonsils
= supplies Superior Constrictor
From the External Carotid Artery
Lingual
= supplies upper pharynx
Superior Thyroid
= supplies Inferior Constrictor
Ascending Pharyngeal
- Pharyngeal branch
= supplies pharynx
- Palatine branch
= supplies palate
VENOUS DRAINAGE
Pharyngeal Plexus [Pharyngeal Veins] Pterygoid Plexus
Internal Jugular Vein
External Palatine (Paratonsillar) Vein
- pierces Superior Constrictor
- drains palatine tonsils into Pterygoid Plexus
PHARYNGEAL PLEXUS (9, 10, 11)
Motor (11)
all muscles of the pharynx, larynx, soft palate
EXCEPT Stylopharyngeus (IX)
EXCEPT Tensor Palatini (V3)
EXCEPT Cricopharyngeus (Recurrent Laryngeal)
Sensory (9)
mucosa of the pharynx, soft palate, palatine tonsils
EXCEPT the nasopharynx above the level of Eustachian Tube (V2)
GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL (IX)
Motor
Stylopharyngeus muscle
General Sensory
pressure receptors in Carotid Sinus
mucosa of pharynx, soft palate, palatine tonsils
touch to posterior 1/3 tongue
Special Sensory
taste to posterior 1/3 tongue
taste to circumvallate papillae
Pre-gang. Parasymp.
Post-gang. Parasymp.
Tympanic Plexus = medial side of tympanic membrane
Lesser Petrosal Nerve = parotid gland
Eagle Syndrome
caused by an elongated styloid process or a calcified stylohyoid ligament
may press on the external wall of tonsillar bed pain travels through CN IX.
VAGUS (X)
Motor
muscles of the pharynx, larynx, soft palate
EXCEPT Stylopharyngeus (IX)
EXCEPT Tensor Palatini (V3)
General Sensory
chemoreceptors in Carotid Body
mucosa of pharynx, larynx
skin of posterior external ear & canal
Special Sensory
taste to oropharynx & epiglottis
Parasympathetic
abdominocardiothoracic viscera
MAXILLARY (V2)
General Sensory
AUTONOMIC
nasopharynx above the Eustachian Tube
post-ganglionic sympathetic fibers arise off the Internal Carotid Arterys plexus
Compiled for you by:
SENSORY INNERVATION TO THE PHARYNX
Ann Nguyen -- NYUCD 2008
D1 Anatomy Notes -- Spring '05
Compiled for you by:
You might also like
- RFP Cut Code HAM Reference - Current EditionDocument46 pagesRFP Cut Code HAM Reference - Current EditionWarrenNo ratings yet
- Lumbosacral PlexusDocument3 pagesLumbosacral Plexusgehaoi4No ratings yet
- Cervical MusculatureDocument3 pagesCervical Musculaturesimone dumbrellNo ratings yet
- NCP For Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP For Impaired Gas ExchangeSweetie Star94% (16)
- Ancient Animal Wisdom Booklet PDFDocument44 pagesAncient Animal Wisdom Booklet PDFLorena Bruno100% (1)
- 6 Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem SensoriDocument59 pages6 Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem Sensoridenis marselaNo ratings yet
- Masha and The BearDocument11 pagesMasha and The BearAgienkz ZahatsNo ratings yet
- Upper Paleolithic Cave Art Final DraftDocument22 pagesUpper Paleolithic Cave Art Final DraftNishiNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Muscles OnlyDocument7 pagesUpper Limb Muscles OnlyGwen EnriquezNo ratings yet
- ALL Clinicals of Upper LimbDocument28 pagesALL Clinicals of Upper LimbБайден ТрампNo ratings yet
- Table A - TMJ and Infratemporal FossaDocument9 pagesTable A - TMJ and Infratemporal Fossaapi-422030113No ratings yet
- Popliteal Fossa: By: Dr. Sana KashifDocument18 pagesPopliteal Fossa: By: Dr. Sana KashifUSAMA AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Nerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesNerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries: Learning ObjectivesUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb NotesDocument14 pagesUpper Limb NotesSwasChanCNo ratings yet
- The Osteology of The Lower LimbDocument4 pagesThe Osteology of The Lower LimbAldi PrawidyaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lower LimbDocument4 pagesAnatomy Lower Limbch yaqoobNo ratings yet
- Musculosk UL5 Muscles 3Document94 pagesMusculosk UL5 Muscles 3Zaid HamdanNo ratings yet
- Study Sheet - Gross Anatomy Lower - ExtremityDocument12 pagesStudy Sheet - Gross Anatomy Lower - ExtremityMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- A Sole 16 12 14Document51 pagesA Sole 16 12 14Mariam AymanNo ratings yet
- Circumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus DorsiDocument4 pagesCircumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus Dorsispeedy.catNo ratings yet
- Blue Boxes Lower LimbDocument4 pagesBlue Boxes Lower LimbZllison Mae Teodoro MangabatNo ratings yet
- Axilla and Brachial PlexusDocument22 pagesAxilla and Brachial Plexusromaisa akhtarNo ratings yet
- Elbow Complex (Kinesiology)Document2 pagesElbow Complex (Kinesiology)Kimmybee Garcia50% (2)
- Thorax AllDocument174 pagesThorax Allravindra sharmaNo ratings yet
- Neck Triangles (Regional Anatomy) Anterior Triangle Borders Arteries Veins Nerves MiscDocument6 pagesNeck Triangles (Regional Anatomy) Anterior Triangle Borders Arteries Veins Nerves Misczara_emmeNo ratings yet
- Back Anatomy TableDocument7 pagesBack Anatomy TableJeffrey XieNo ratings yet
- Subclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)Document6 pagesSubclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)馮素琴No ratings yet
- Hip Joint: Important PointsDocument4 pagesHip Joint: Important PointsNamrah AfzalNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall.Document48 pagesThoracic Wall.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Joints of Lower LimbDocument7 pagesJoints of Lower LimbjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Nerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries, S-Ii-Lm-0120Document5 pagesNerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries, S-Ii-Lm-0120Shab GeNo ratings yet
- XX Vascular Supply of Lower Limb - PPTDocument15 pagesXX Vascular Supply of Lower Limb - PPTAlistair WalkerNo ratings yet
- Back Pain: Group 4Document71 pagesBack Pain: Group 4Cesar Guico Jr.No ratings yet
- High Yield GROSS AnatomyDocument11 pagesHigh Yield GROSS AnatomyKhalilKhaliNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Lower LimbDocument15 pagesBones of The Lower Limbyachiru121No ratings yet
- Muscles in The Posterior Scapula Muscle Proximal Attachment Distal Attachment Nervous Supply FunctionDocument37 pagesMuscles in The Posterior Scapula Muscle Proximal Attachment Distal Attachment Nervous Supply FunctionMicky TsuiNo ratings yet
- Joints of The Head and Trunk - 2015-RuanDocument30 pagesJoints of The Head and Trunk - 2015-RuanKw ChanNo ratings yet
- Anterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossaDocument24 pagesAnterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossaSky StoneNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb, Pectoral RegionDocument24 pagesUpper Limb, Pectoral Regiongtaha80No ratings yet
- Lumbar Plexus (Grays Anatomy)Document12 pagesLumbar Plexus (Grays Anatomy)Joemar ReveloNo ratings yet
- Popliteal Fossa and LegDocument40 pagesPopliteal Fossa and LegRaj Shekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Gluteal RegionDocument34 pagesGluteal Regionlion2chNo ratings yet
- Table of Head and Neck MusclesDocument5 pagesTable of Head and Neck MusclesAnubhuti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Blood Suppply of Lower LimbDocument8 pagesBlood Suppply of Lower LimbCamille Magdirila100% (2)
- Anatomy, Lecture 4, Thoracic Wall (2) (Slides)Document23 pagesAnatomy, Lecture 4, Thoracic Wall (2) (Slides)Ali Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- 16-Clinical Anatomy of The Upper LimbDocument27 pages16-Clinical Anatomy of The Upper LimbAlapati Vinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb 0809 PDFDocument59 pagesUpper Limb 0809 PDFasdaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The BackDocument2 pagesMuscles of The BackavrilaNo ratings yet
- Triangles of Neck (Anatomy)Document36 pagesTriangles of Neck (Anatomy)Dr Tahira Nihal100% (1)
- 3-Inguinal Canal PDFDocument58 pages3-Inguinal Canal PDFN A0% (1)
- Topographical Anatomy of The Lower Limb - Listed AlphabeticallyDocument3 pagesTopographical Anatomy of The Lower Limb - Listed AlphabeticallySaba Adde Duhera-HamidovicNo ratings yet
- Joints of Lower Limb 2017Document77 pagesJoints of Lower Limb 2017yasrul izadNo ratings yet
- Osteology of The Upper Limb LectureDocument40 pagesOsteology of The Upper Limb LectureFavour OnyeaboNo ratings yet
- Upper ADocument4 pagesUpper ARati SutariaNo ratings yet
- UE DermatomesDocument1 pageUE DermatomesmdmdegNo ratings yet
- Foot and Ankle Bones and JointsDocument43 pagesFoot and Ankle Bones and Jointshannah murphyNo ratings yet
- Adductor Canal LatestDocument18 pagesAdductor Canal LatestSaish100% (1)
- Dermatomes and Myotomes and Its Clinical Special Test in Upper Limb and Lower LimbDocument42 pagesDermatomes and Myotomes and Its Clinical Special Test in Upper Limb and Lower LimbkkaammiillaahhNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics Anatomia 1 PDFDocument11 pagesMnemonics Anatomia 1 PDFRocio SandersNo ratings yet
- Joint of Lower LimbDocument16 pagesJoint of Lower LimbZA ID100% (1)
- Radial and Median NervesDocument33 pagesRadial and Median NervesveegeerNo ratings yet
- Table of Lower Limb MusclesDocument5 pagesTable of Lower Limb MusclesJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb AnatomyDocument33 pagesLower Limb AnatomyfefioktaviaNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy of Posterior Compartment of The ThighDocument20 pagesGross Anatomy of Posterior Compartment of The ThighOnah ArinzeNo ratings yet
- Pharynx: Upper Part: Widest - 3.5 CM, Non-Collapsible Middle Part: Narrow Lower End: Narrowest Part of GITDocument5 pagesPharynx: Upper Part: Widest - 3.5 CM, Non-Collapsible Middle Part: Narrow Lower End: Narrowest Part of GITdrpnnreddyNo ratings yet
- Pharynx: DR - Wardiansah, M.BiomedDocument38 pagesPharynx: DR - Wardiansah, M.BiomedZen AhmadNo ratings yet
- 12-Cranial CavityDocument3 pages12-Cranial Cavityapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 2004Document5 pages2004api-3757921No ratings yet
- 14-Nasal & SinusesDocument1 page14-Nasal & Sinusesapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 11-CNS & BrainDocument6 pages11-CNS & Brainapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 10 InfratemporalDocument8 pages10 Infratemporalapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 9 FaceDocument6 pages9 Faceapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 8-Neck Muscles ChartDocument1 page8-Neck Muscles Chartapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 8 NeckDocument1 page8 Neckapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 6-Spinal CordDocument4 pages6-Spinal Cordapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 7 AutonomicDocument4 pages7 Autonomicapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 5 JointsDocument2 pages5 Jointsapi-3757921100% (2)
- 4 SkullDocument1 page4 Skullapi-3757921No ratings yet
- 3 AbdomenDocument7 pages3 Abdomenapi-3757921100% (1)
- 2 ThoraxDocument7 pages2 Thoraxapi-3757921No ratings yet
- Manhattan Sentence CorrectionDocument125 pagesManhattan Sentence Correctionapi-3736636100% (8)
- 20-Lymphatics ChartDocument1 page20-Lymphatics Chartapi-3757921No ratings yet
- Transportation in Animals and PlantsDocument2 pagesTransportation in Animals and PlantsHimanshi JainNo ratings yet
- GynaecologyDocument466 pagesGynaecologymyselfrakesh57No ratings yet
- Reading Class - Tongue TwistersDocument5 pagesReading Class - Tongue TwistersKeyla RamosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Parotid GlandDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The Parotid GlandHossam NawaraNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2352409X20304636 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S2352409X20304636 MainpjNo ratings yet
- Jabberwocky: by Lewis CarrollDocument4 pagesJabberwocky: by Lewis CarrollJames Tweedie100% (1)
- The Deep Sea AnglerfishDocument2 pagesThe Deep Sea AnglerfishKhagangrad 'No ratings yet
- IOT Based Pet Feeder Automation SystemDocument4 pagesIOT Based Pet Feeder Automation SystemRizyn ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Gabriel Ernest Notes (Litcharts)Document5 pagesGabriel Ernest Notes (Litcharts)NiidiiNo ratings yet
- DR Norris - Good Trasfusion Practice PDFDocument27 pagesDR Norris - Good Trasfusion Practice PDFvasu_5iveNo ratings yet
- RBCDocument3 pagesRBCMalkish RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal PAT B.Inggris Kelas 5Document2 pagesContoh Soal PAT B.Inggris Kelas 5neneng faidah100% (3)
- Exploring Animal HabitatsDocument3 pagesExploring Animal Habitatshi.printbeeNo ratings yet
- The Ballad of East and West - KiplingDocument3 pagesThe Ballad of East and West - Kiplingnicoler111No ratings yet
- Quiz End Rhyme or Internal RhymeDocument1 pageQuiz End Rhyme or Internal RhymeAnonymous pHooz5aH6V100% (2)
- Overlord Volume 01 Chapter 2Document50 pagesOverlord Volume 01 Chapter 2bob bobNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document3 pagesQuiz 2Hustice FreedNo ratings yet
- MTS Answer KeyDocument28 pagesMTS Answer KeyZoeyspecialNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 169752Document18 pagesG.R. No. 169752Ria CuaNo ratings yet
- 8 SubjectVerbAgreementDocument40 pages8 SubjectVerbAgreementThe chair jimin falls fromNo ratings yet
- GK SSC Vol 1Document7 pagesGK SSC Vol 1Vinay CkmNo ratings yet
- Standards For Blood Banks and Transfusion Services Standards For Blood Banks and Transfusion ServicesDocument5 pagesStandards For Blood Banks and Transfusion Services Standards For Blood Banks and Transfusion Serviceslaexm95No ratings yet
- Grade 5 - Unit 2 - Living Thing - AnimalsDocument16 pagesGrade 5 - Unit 2 - Living Thing - AnimalsкатяNo ratings yet
- Immersion TablesDocument4 pagesImmersion TablesGoppino8850% (2)