Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atq1 31.1
Uploaded by
Clarence Pardiñas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
99 views2 pagesATQ1_31.1
Original Title
ATQ1_31.1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentATQ1_31.1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
99 views2 pagesAtq1 31.1
Uploaded by
Clarence PardiñasATQ1_31.1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Clarence C.
Pardias
2013-02355
Chem 31.1
ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS (SOLUBILITY OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS)
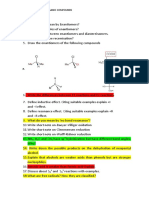
1. For solutes that are dissolved because of intermolecular attractions with the
solvent, state the intermolecular forces of attraction involved.
Acetone- its primary IMFA is dipole-dipole forces and it happens when polar
molecules are attracted to one another.
Ethanol- its hydroxyl group is able to take part in hydrogen bonding.
Sucrose- the IMFA present is dipole-dipole forces because of its polarity.
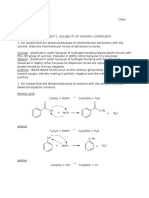
2. For solutes that are dissolved because of reaction with the solvent, write the
balanced equation involved.
Benzoic Acid
C7 H 6 O2+ NaOH C7 H 5 O2 Na+ H 2 O
Phenol
C6 H 6 O+ NaOH C6 H 5 ONa+ H 2 O
Aniline
++Cl
C6 H 5 NH 2 + HCl C 6 H 5 NH 3
Benzyl alcohol
++ H SO 4
C7 H 8 O+ H 2 SO 4 C 7 H 9 O
Benzaldehyde
C7 H 6 O+ H 2 SO4 C 7 H 8 O+SO 4
3. On the basis of solubility behavior, determine the best solvent to differentiate
the following pairs of compounds:
a. CH3COOH and CH3(CH2)5COOH - water
b. CH3CH2OCH2CH3 and CH3CH2OH - water
c. Toluene and benzaldehyde concentrated H2SO4
d. Tert-butyl chloride and tert-butanol water
Reference:
McMurry, J. (2010). Foundations of Organic Chemistry. 7th Edition. 2011. Cengage Learning Asia Pte. Ltd. Singapore.
You might also like
- Chem 31 AtqE1Document3 pagesChem 31 AtqE1Anonymous GO6JVW9WudNo ratings yet
- MODULE: Intermolecular Forces (IMF) and Acid Base Reactions LESSON 1: Intermolecular ForcesDocument8 pagesMODULE: Intermolecular Forces (IMF) and Acid Base Reactions LESSON 1: Intermolecular ForcesApple Mae Tol VictorianoNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 7Document31 pagesStudy Guide 7Dominador RomuloNo ratings yet
- LAS 3 - Solution ProcessDocument2 pagesLAS 3 - Solution ProcessDaniella Izabelle SaguinNo ratings yet
- Acid Base EquilibriumDocument21 pagesAcid Base Equilibriumkaushik247No ratings yet
- E1 AtqDocument2 pagesE1 AtqDorothy Joy YtacNo ratings yet
- Chap4asid BesDocument46 pagesChap4asid BesWan Azzura Wan IsmailNo ratings yet
- AcidBaseEquilibrium PDFDocument21 pagesAcidBaseEquilibrium PDFSylvinceterNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 Exp 1Document2 pagesChem 31.1 Exp 1qwertyuasiopNo ratings yet
- Lab 3: Solubility of Organic Compounds: ObjectivesDocument12 pagesLab 3: Solubility of Organic Compounds: ObjectivesJAN CAMILLE OLIVARESNo ratings yet
- 2 - Solubility of Organic CompoundsDocument4 pages2 - Solubility of Organic CompoundsJade AsparinNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Reactions in Aqueous Solution: SolutionsDocument24 pagesChapter Four: Reactions in Aqueous Solution: SolutionsPaulAngeloPascuaNo ratings yet
- Reference Chemistry For Pharmacy StudentsDocument62 pagesReference Chemistry For Pharmacy StudentsCORONA PUBGNo ratings yet
- Experiment1: Solubility of Organic CompoundsDocument1 pageExperiment1: Solubility of Organic CompoundsprimacrosseNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Beirut Arab University Faculty of Science Debbieh CampusDocument74 pagesSolutions: Beirut Arab University Faculty of Science Debbieh CampusMoh AmmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 IM Chang 11eDocument6 pagesChapter 4 IM Chang 11eSelma MeloNo ratings yet
- Solubility Behavior of Organic CompoundsDocument2 pagesSolubility Behavior of Organic CompoundsDione Gale NavalNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Series 5: Answer Any 3 Questions From 1 To 6. (2 Score Each)Document6 pagesWorksheet Series 5: Answer Any 3 Questions From 1 To 6. (2 Score Each)AswithNo ratings yet
- Solutions and Colloids PDFDocument19 pagesSolutions and Colloids PDFAhmet AlbayrakNo ratings yet
- Experiment 24 Qualitative Analysis I: GoalDocument9 pagesExperiment 24 Qualitative Analysis I: GoalggmmnmcncnnmNo ratings yet
- Ch13 Lecture 6e Final3Document90 pagesCh13 Lecture 6e Final3Jovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry The Central Science, 15th Global Edition in SI Units (Theodore L. Brown, Eugene H. LeMay Etc.)Document51 pagesChemistry The Central Science, 15th Global Edition in SI Units (Theodore L. Brown, Eugene H. LeMay Etc.)kelebogileseakgweNo ratings yet
- 04 Types of Chemical Reactions & Solution Stoich PDFDocument16 pages04 Types of Chemical Reactions & Solution Stoich PDFaskamnNo ratings yet
- Ch04 LectureDocument96 pagesCh04 LectureTsaiBenyanNo ratings yet
- 125 A Mid 2 Chemistry-1Document24 pages125 A Mid 2 Chemistry-1syeda ruqaiyah ashfaqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument19 pagesChapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersNaina SinghNo ratings yet
- CH9 1 Solutions GOB Structures 5th EdDocument19 pagesCH9 1 Solutions GOB Structures 5th EdAlice C. RiveraNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Plustwo Most Important 137 Questions Answers 2023Document18 pagesHsslive Plustwo Most Important 137 Questions Answers 2023Janet RoyNo ratings yet
- 8 Chapter 12 1Document51 pages8 Chapter 12 1azizNo ratings yet
- 13-1 Compounds in Aqueous SolutionsDocument16 pages13-1 Compounds in Aqueous SolutionslutimoNo ratings yet
- Model Paper With SolutionsDocument16 pagesModel Paper With SolutionsHoly GhostNo ratings yet
- Advanced ChemistryDocument137 pagesAdvanced ChemistryMaheshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Lecture Notes: Solutions, Colloids, and SuspensionsDocument44 pagesChapter 7 Lecture Notes: Solutions, Colloids, and SuspensionstitusNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged 2Document41 pagesIlovepdf Merged 2api-533764142No ratings yet
- 2 ChemistryDocument7 pages2 ChemistryAlexandra EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AML NMAT ReviewerDocument14 pagesChemistry AML NMAT ReviewerXyla Jane DiodinaNo ratings yet
- Actinide SeparationDocument35 pagesActinide SeparationZain MSDNo ratings yet
- Reaction Mechanism DDocument36 pagesReaction Mechanism Dprajaktac506No ratings yet
- CBSE XII - Chemistry: Board Paper Solution - 2012Document12 pagesCBSE XII - Chemistry: Board Paper Solution - 2012rahulNo ratings yet
- Class 12 (Board Questions With Answers)Document5 pagesClass 12 (Board Questions With Answers)Mohanalakshmi ManoharNo ratings yet
- GENCHM280 SolutionDocument58 pagesGENCHM280 SolutionReysel MonteroNo ratings yet
- CHY103Document33 pagesCHY103sahar kabiriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10-11Document14 pagesChapter 10-11api-201479236No ratings yet
- Protocol LabDocument53 pagesProtocol LabKristine Marie SantosNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Aqueous SolutionDocument91 pagesModule 3 - Aqueous SolutionTrần Thu ThảoNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry 13th Edition Raymond Chang Jason OverbyDocument30 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry 13th Edition Raymond Chang Jason OverbyHeatherBowmaniotf100% (37)
- APCh 13 NotesDocument20 pagesAPCh 13 NotesmtannaganNo ratings yet
- Qn. No. Part - A MarksDocument13 pagesQn. No. Part - A MarkslingarajugowdaNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes & Haloarenes-2Document3 pagesHaloalkanes & Haloarenes-2kishoreNo ratings yet
- BLB 14e Ch04 Worked ExamplesDocument44 pagesBLB 14e Ch04 Worked ExamplesJay FortunadoNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Unit 11 Study Material em 215587Document9 pagesNamma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Unit 11 Study Material em 215587prathiksha6660No ratings yet
- Organic QuestionDocument3 pagesOrganic Questionsimran simranNo ratings yet
- Solution, Suspension, ColloidsDocument149 pagesSolution, Suspension, ColloidsApril Eballena100% (1)
- BLB chp4Document88 pagesBLB chp4Nora Zor-elNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 FG Post Lab Group 4 Expt. 2Document10 pagesChem 31.1 FG Post Lab Group 4 Expt. 2lazygemNo ratings yet
- CHM 222 Stoichiometry of Chemical PDFDocument44 pagesCHM 222 Stoichiometry of Chemical PDFGlory UsoroNo ratings yet
- Metathesis ReactionsDocument11 pagesMetathesis Reactionsfranciscrick69No ratings yet
- Lecture 04 1Document57 pagesLecture 04 1Daniel SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- 351expt 01 Solubility 230914 172803Document5 pages351expt 01 Solubility 230914 172803noNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Culture and Development: Renato ConstantinoDocument76 pagesSynthetic Culture and Development: Renato ConstantinoClarence PardiñasNo ratings yet
- 1 New Public ManagementDocument24 pages1 New Public ManagementClarence PardiñasNo ratings yet
- POLSC 11 Martial Law ReflectionDocument1 pagePOLSC 11 Martial Law ReflectionClarence PardiñasNo ratings yet
- POLSC 11 ReflectionDocument1 pagePOLSC 11 ReflectionClarence PardiñasNo ratings yet
- Eapp PropDocument13 pagesEapp PropClarence PardiñasNo ratings yet