Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-19 Excretory Products and Their Elimination
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-19 Excretory Products and Their Elimination
Uploaded by
RamachandranPerumalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-19 Excretory Products and Their Elimination
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-19 Excretory Products and Their Elimination
Uploaded by
RamachandranPerumalCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology)
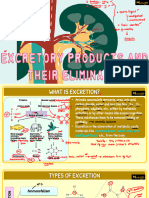
CHAPTER-19 EXCRETORY PRODUCTS AND THEIR ELIMINATION
Elimination of metabolic wastes products from the animal body to regulate the composition
of body fluids and tissues is called excretion. These wastes products includes ammonia, uric
acid, urea, carbon dioxide and ions like Na+, K+, Cl- and phosphates and sulphate.
Ammonia is the most toxic and uric acid is the least toxic. The process of removing ammonia
is called ammonotelism and organisms that excrete ammonia are called ammonotelic
(bony fishes, aquatic amphibians and insects).
The organism that release urea as nitrogenous wastes are called ureotelic (mammals,
terrestrial amphibians). The organism that excretes uric acids are called urecotelic
(reptiles, birds and land snails).
Animals
Excretory organs
Flat worms, some annelids and cephalochordates.
Protonephridia or flame cells.
Earthworms and annelids
Nephridia
Insects including cockroaches
Malpighian tubules
Mammals
Kidney
Human Excretory System
Human excretory system consists of
A pair of kidneys
i.
ii.
A pair of ureters
iii.
A urinary bladder
iv.
A urethra
Kidneys are reddish brown bean shaped structure
situated between last thoracic and lumber vertebra.
Each with a notch on its inner side called hilum
through which ureter, blood vessels and nerves
enter.
Inside the hilum has broad funnel shaped space called
renal pelvis with projection called calyces.
Inside the kidney are two zone- outer cortex and inner
medulla. Medulla is divided into medullary pyramids
projecting into calyx.
Cortex extends between medullary pyramids as renal
column called Columns of Bertini.
The functional unit of kidney is nephron. Each kidney contains about one million nephrons.
Each nephron had two parts- the glomerulus and renal tubules. Glomerulus is the tuft of
capillaries formed by afferent arteriole. Blood from glomerulus is carried away by efferent
arteriole.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Renal tubules starts with Bowmans
capsule continue with tubular parts
divided into Proximal Convoluted
tubules, Henles loop and Distal
Convoluted tubule.
The malpighian tubules, PCT and DCT of
nephron are situated in cortical region
where as loops of Hanles into medulla.
Juxtamedullary Nephrons
Cortical Nephrons
i. Loop of Henles is short and extend only a. Loop of Henles are very long and
a little into medulla.
extend deep into medulla.
ii. The glomeruli lie close to the inner b.The glomeruli lie in the outer cortex.
margin of the cortex.
Urine formation
1st step
Glomerular filtration.
Filtration of blood by glomerules.
2nd step
Reabsorption
Reabsorption by renal tubules.
Secretion
3rd step Tubular cells secretes H+,K+ ammonai into filtrate.
Glomerular capillaries blood pressure cause filtration of blood through 3 layers
(endothelium of glomerular blood vessels, epithelium of Bowmans capsule and basement
layer between two membranes as ultra-filtration.
The amount of filtrate formed by kidneys per minute is called glomerular filtration rate
(GFR) which is 125 ml/minute.
Glomerular Filtration rate is controlled by carried out by Juxta glomerular apparatus
(JGA).
99% of filtrate has been reabsorbed by renal tubules called reabsorption.
Function of Tubules
I.
Proximal Convoluted Tubules (PCT) - all the important nutrients, 70-80% electrolytes
and water are reabsorbed.
II.
Henles Loop- maintains high osmolarity of medullary institutional fluid.
III.
Distal Convoluted Tubules (DCT) conditional reabsorption of Na+ and water. Maintain
pH and sodium- potassium balance.
IV.
Collecting Duct- large amount of water is reabsorbed to produce concentrated urine.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Mechanism of concentration of urine- The
flow of filtrate in two limbs Henles loop is
in opposite direction to form counter
current. The flow of blood in two limbs of
vasa recta increase the osmalarity towards
the inner medullary interstitutium in the
inner medulla.
The transport of substance facilitated by
special arrangement of Henles loop and
vasa recta is called counter current
mechanism.
Regulation of kidney functionFunctioning of kidney is monitored by
hormonal
feedback
mechanism
of
hypothalamus and JGA. Change in blood
volume, body fluid and ion concentration activates the osmorecptors in the body that
stimulate the hypothalamus to release ADH or vasopressin hormones. The ADH facilitates
water absorption in tubules.
Decrease in glomerular blood pressure activate JG cells to release renin which converts
angiotensinogen to angiotensin I and II that increase the glomerular blood pressure and
release of aldosterone that increase absorption of Na+ ions and water.
Micturition The process of expulsion of urine from the urinary bladder is called micturition.
The neural mechanism that causes it is called micturition reflex. Urine formed in nephron is
stored in urinary bladder till a voluntary signal is received by CNS. The stretch receptors
present in wall of urinary bladder is received by CNS to initiate contraction of smooth
muscles of bladder to relax the urethral sphincter to release urine.
Lungs, liver and skin also play important role in process of excretion. Lungs remove CO2 and
water, liver eliminates bile containing substances and sweat and sebaceous glands in skin
which removes, NaCl, uria and lactic acid and sterol, hydrocarbons and waxes.
Disorders of Excretory System
Uremia- there is high concentration of non-protein nitrogen (urea, uric acid, creatinine).
Urea can be removed by hemodialysis.
Renal failure- also known as kidney failure which glomerular filtration is ceased and both
kidney stops working. Kidney transplant is the ultimate method in correction of acute
kidney failure.
Renal Calculi- formation of stone or insoluble mass of crystalized salts formed within the
kidney.
Glomerulonephritis ( Brights Disease)- inflammation of glomeruli of kidney due to
entry of protein or red blood corpuscles in to filtrate due to injury.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
You might also like
- Chapter 2 Living Things in Ecosystems PDFDocument12 pagesChapter 2 Living Things in Ecosystems PDFJohn Rey BuntagNo ratings yet
- CPEA BookReportsandWritingPortfoliosabridgedforwebDocument19 pagesCPEA BookReportsandWritingPortfoliosabridgedforwebShertal RegisNo ratings yet
- Pig Kidney DissectionDocument5 pagesPig Kidney DissectionroseNo ratings yet
- 85100-172 ERBE en Units and Modules Chapter Catalog D080643Document16 pages85100-172 ERBE en Units and Modules Chapter Catalog D080643Mazhar HanifNo ratings yet
- 2.2 - Recording and Reporting Based On FHSIS-noemi August25Document40 pages2.2 - Recording and Reporting Based On FHSIS-noemi August25Izæya80% (5)
- Map H SC HallwayDocument2 pagesMap H SC Hallwaysosomopadede0% (1)
- Ch-8 Excretion in Animals & PlantsDocument4 pagesCh-8 Excretion in Animals & PlantsRonnith NandyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Form 4Document127 pagesChapter 7 Form 4kulic82100% (1)
- Unit 1Document20 pagesUnit 1Sareeta PradhanNo ratings yet
- HSB Unit Test 2Document11 pagesHSB Unit Test 2Jessica Kinney0% (1)
- HSB Skeletal NotesDocument2 pagesHSB Skeletal NotesArvin SinghNo ratings yet
- HSB - Lesson A1Document31 pagesHSB - Lesson A1Osmany MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Conclusion ParagraphDocument7 pagesConclusion Paragraphapi-334926654No ratings yet
- Biology Teachers' Manual PDFDocument72 pagesBiology Teachers' Manual PDFAndrewNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument16 pagesExcretionNor Baizura Binti AzizNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 3 - Comparative Study of Mammalian Skeleton ProceduresDocument9 pagesPractical No. 3 - Comparative Study of Mammalian Skeleton ProceduresSana cheema100% (1)
- Circle Theorems: by Jay MadelaineDocument6 pagesCircle Theorems: by Jay MadelaineJayNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch20 Locomotion and Movement PDFDocument3 pages11 Biology Notes ch20 Locomotion and Movement PDFRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- Transport Systems in Plants: Stem Structure Root StructureDocument12 pagesTransport Systems in Plants: Stem Structure Root StructureJonathon HayesNo ratings yet
- 2-D Vector Ops SummaryDocument2 pages2-D Vector Ops SummaryClark Neily, Jr.No ratings yet
- Full Sugested Lesson Plan On Introduction To Integrated Science Form 1 Lesson 1 6Document17 pagesFull Sugested Lesson Plan On Introduction To Integrated Science Form 1 Lesson 1 6maazure francis100% (1)
- CAPE Chemistry FormulaeDocument9 pagesCAPE Chemistry FormulaeAmateurVoice LeelaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle NotesDocument36 pagesCell Organelle NotesChoebe Khaye Shoebe100% (1)
- CSEC Biology - Vegetative ReproductionDocument1 pageCSEC Biology - Vegetative ReproductionTamicka BonnickNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument28 pagesBalancing Chemical EquationsHaniel GalzoteNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 The Special SensesDocument8 pagesUnit 14 The Special SensesJess LNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument13 pagesReproduction in Flowering PlantsMaogageoffreyNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatDocument7 pagesCell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatSpongie BobNo ratings yet
- CXC Physics Notes Section ADocument13 pagesCXC Physics Notes Section ARoyson HendersonNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - Class Notes - Warrior-Life Processes (Samridhi Mam) WarriorDocument162 pagesLife Processes - Class Notes - Warrior-Life Processes (Samridhi Mam) Warriorsiddhesht104No ratings yet
- HSB - Inheritance and GenesDocument16 pagesHSB - Inheritance and GenesJalisaNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and Circulation by Dr. Sunita SaxenaDocument71 pagesBody Fluids and Circulation by Dr. Sunita SaxenaDivya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Study NotesDocument61 pagesAdd Maths Study NotesElisha James100% (1)
- Collins - Concise Revision Course For CSEC Human and Social Biology-Pages-156-162,169-171Document10 pagesCollins - Concise Revision Course For CSEC Human and Social Biology-Pages-156-162,169-171Nekia MillerNo ratings yet
- 2021 Jan CSEC Math Paper2Document34 pages2021 Jan CSEC Math Paper2Marie HenryNo ratings yet
- Circulatory and Respiratory ReviewDocument5 pagesCirculatory and Respiratory ReviewNur ShaNo ratings yet
- Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksDocument5 pagesPortal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksHasharaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology June 2012 P032Document14 pagesCSEC Biology June 2012 P032Terence JamesNo ratings yet
- Some CXC Math MC Questions PDFDocument17 pagesSome CXC Math MC Questions PDFnaseeb100% (1)
- CSEC Biology June 2013 P032Document10 pagesCSEC Biology June 2013 P032Terence JamesNo ratings yet
- The 7 Characteristics That Distinguish Living Things From Non-Living Objects AreDocument34 pagesThe 7 Characteristics That Distinguish Living Things From Non-Living Objects AreTonique GordonNo ratings yet
- July 9... CXC BiologyDocument58 pagesJuly 9... CXC BiologyShantay BurtonNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson Plan Dengue Jigsaw-2Document5 pagesScience Lesson Plan Dengue Jigsaw-2Devi RambaranNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules: One Mark QuestionsDocument11 pagesAtoms and Molecules: One Mark QuestionsSrividhya ManikandanNo ratings yet
- Dichotomous KeysDocument8 pagesDichotomous KeysTal4shinNo ratings yet
- Ch8 Cabook PDFDocument7 pagesCh8 Cabook PDFThiruvenkata ManiNo ratings yet
- Alkanes Notes and Naming PDFDocument4 pagesAlkanes Notes and Naming PDFyad e baiza nawalNo ratings yet
- Notes Cells (Slides by Slidesgo)Document38 pagesNotes Cells (Slides by Slidesgo)salinaNo ratings yet
- Classification of OrganismsDocument5 pagesClassification of Organisms言爱邦No ratings yet
- CSEC Study Guide - March 22, 2011Document12 pagesCSEC Study Guide - March 22, 2011ChantelleMorrisonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Rectum and Anal Canal: The Rectum Is The Part of The Colon Between The Sigmoid ColonDocument25 pagesAnatomy of The Rectum and Anal Canal: The Rectum Is The Part of The Colon Between The Sigmoid ColonJoy GhoseNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living OrganismsDocument7 pagesClassification of Living OrganismsPralex PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Chap-20 - Locomotion & MovementDocument52 pagesChap-20 - Locomotion & MovementMittal SavaniNo ratings yet
- 14 Respiration in Plants-NotesDocument4 pages14 Respiration in Plants-NotesAnanth DharanidharanNo ratings yet
- Ecology Test For CSEC StudentsDocument3 pagesEcology Test For CSEC Studentsnehru09No ratings yet
- Science 8 PDFDocument172 pagesScience 8 PDFaftab khanNo ratings yet
- Caribbean Examinations Council Caribbean Secondary Certificate of Education Guidelines For On-Site Moderation SciencesDocument9 pagesCaribbean Examinations Council Caribbean Secondary Certificate of Education Guidelines For On-Site Moderation SciencesjokerNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology June 2014 P032Document12 pagesCSEC Biology June 2014 P032Terence JamesNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Water Cycle Work SheetDocument4 pagesCarbon and Water Cycle Work SheetRasha GhabbounNo ratings yet
- Major Classification of PlantsDocument19 pagesMajor Classification of PlantsJhoy Angeles PinlacNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument7 pagesExcretory Products and Their EliminationAjay JamwalNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch19 Excretory Products and Their Elimination 1Document4 pages11 Biology Notes ch19 Excretory Products and Their Elimination 1Sumanth SY 1119No ratings yet
- Vipin Sir Biology 19. Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument55 pagesVipin Sir Biology 19. Excretory Products and Their EliminationvanshpatelssisNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants PDFDocument23 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants PDFRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- NSO Class 9 Solved Sample Paper PDFDocument8 pagesNSO Class 9 Solved Sample Paper PDFRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- Microbes in Human Welfare PDFDocument12 pagesMicrobes in Human Welfare PDFRamachandranPerumal100% (1)
- NSEJS Solved Paper 2012 PDFDocument22 pagesNSEJS Solved Paper 2012 PDFRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument10 pagesBiotechnology and Its ApplicationsAlok YadavNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem PDFDocument17 pagesEcosystem PDFRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- 05principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument28 pages05principles of Inheritance and VariationAnonymous pMVR77x1No ratings yet
- Evolution PDFDocument17 pagesEvolution PDFRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Conservation PDFDocument12 pagesBiodiversity and Conservation PDFRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- 12 DVO Lens Formulee DerivationDocument109 pages12 DVO Lens Formulee DerivationRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- 13 DVO Measurement of Light VelocityDocument36 pages13 DVO Measurement of Light VelocityRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch20 Locomotion and Movement PDFDocument3 pages11 Biology Notes ch20 Locomotion and Movement PDFRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- 11 Consevation of MoventumDocument77 pages11 Consevation of MoventumRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch21 Neural Control and Coordination PDFDocument3 pages11 Biology Notes ch21 Neural Control and Coordination PDFRamachandranPerumal100% (1)
- 6 Uniform Circular MotionDocument83 pages6 Uniform Circular MotionRamachandranPerumal0% (1)
- 10 Kinamatics of Rotation UCMDocument27 pages10 Kinamatics of Rotation UCMRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- SB2 1Document368 pagesSB2 1RamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- PhilHealth Circular 11 Series of 2011Document6 pagesPhilHealth Circular 11 Series of 2011Pia VSNo ratings yet
- Quick Start Oral ContraceptivesDocument2 pagesQuick Start Oral ContraceptivesAnna DangNo ratings yet
- Tamai Zone 1 Fingertip Amputation: Reconstruction Using A Digital Artery Flap Compared With Microsurgical ReplantationDocument7 pagesTamai Zone 1 Fingertip Amputation: Reconstruction Using A Digital Artery Flap Compared With Microsurgical ReplantationFeliciaDewiNo ratings yet
- I. Intrapartum Electronic Fetal Monitoring: Ob Rotation OsceDocument24 pagesI. Intrapartum Electronic Fetal Monitoring: Ob Rotation OsceAngelie Therese ChuaNo ratings yet
- Principal Veins and ArteriesDocument5 pagesPrincipal Veins and Arteriesrodz_verNo ratings yet
- NCCN Bone CancerDocument93 pagesNCCN Bone Canceraurika sinambelaNo ratings yet
- ESWTDocument16 pagesESWTPrahoveanu IoanaNo ratings yet
- Am I A Juvenile DelinquentDocument3 pagesAm I A Juvenile DelinquentJiffy MaghanoyNo ratings yet
- Completed Essential 3 E-Folio Nursing 402Document4 pagesCompleted Essential 3 E-Folio Nursing 402api-374818694No ratings yet
- Operating Manifold Services in Hospitals: A Costly Affair?: Kumar P, Gupta SK, Sharma DK, Batra RKDocument9 pagesOperating Manifold Services in Hospitals: A Costly Affair?: Kumar P, Gupta SK, Sharma DK, Batra RKPankaj Mittal100% (1)
- Textbook of Cardiovascular MedicineDocument3,088 pagesTextbook of Cardiovascular MedicineAndreea Alina Tanase100% (4)
- South Peace Division of Family Practice PresentationDocument15 pagesSouth Peace Division of Family Practice PresentationTom SummerNo ratings yet
- Health Camp ReportDocument8 pagesHealth Camp ReportDuduNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document14 pagesPaper 1Arnold Steven Villacrez ZeladaNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot: Anatomic Variants and Their Impact On Surgical ManagementDocument9 pagesTetralogy of Fallot: Anatomic Variants and Their Impact On Surgical ManagementRoberto AmayaNo ratings yet
- Practice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALDocument36 pagesPractice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALFilipino Nurses CentralNo ratings yet
- White Sleep: Noise and InductionDocument3 pagesWhite Sleep: Noise and InductionMariaNo ratings yet
- Down Syndrome - Wikipedia PDFDocument171 pagesDown Syndrome - Wikipedia PDFSanket TelangNo ratings yet
- HMB Nice GuidelinesDocument192 pagesHMB Nice Guidelineschar1356No ratings yet
- Rogelio Ramos Et, Al vs. Court of Appeals, Et. AlDocument4 pagesRogelio Ramos Et, Al vs. Court of Appeals, Et. AlKim BarriosNo ratings yet
- B. Locus of Power: Individual As A Client Atomistic ApproachDocument5 pagesB. Locus of Power: Individual As A Client Atomistic ApproachKris Elaine GayadNo ratings yet
- Mindray DP6600 Operation Manual Advanced PDFDocument113 pagesMindray DP6600 Operation Manual Advanced PDFGabriel Garcia100% (1)
- Anterior Shoulder InstabilityDocument19 pagesAnterior Shoulder InstabilitySiti Nur JannahNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka ObgynDocument1 pageDaftar Pustaka ObgynISMJNo ratings yet
- Hypnobirthing - The Mongan Method - Is A Unique Method of Relaxed, NaturalDocument3 pagesHypnobirthing - The Mongan Method - Is A Unique Method of Relaxed, NaturalZhaii Garcia MariacaNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLIGIST DOCkkkTORSDocument6 pagesENDOCRINOLIGIST DOCkkkTORSRanabir DebNo ratings yet
- Dice Hospital Rules v2.11-PnpDocument7 pagesDice Hospital Rules v2.11-PnpViktorNo ratings yet