Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Curve Elements
Curve Elements
Uploaded by
rbhavishCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Curve Elements
Curve Elements
Uploaded by
rbhavishCopyright:
Available Formats
Curve elements: angle of deflection, intersection point (IP), angle of deviation, tangent distance,
tangent point (TP),long chord, running chainage, standard chord, sub chords.
Describe the method of setting out circular curves by tape only.
Method offsets from long chord, offsets from the tangent, offset from chords produced
Practical test
Describe the method of setting out using one theodolite and a tape (deflection angle) and tabulate the
setting out data for use on site.
Explain various methods of overcoming obstacles when setting out a curve, including the use of coordinates.
Methods: obstacles where IP/ TP are inaccessible, where features prevent direct measurement of
points on the curve itself
Class test
Identify the various elements and purpose of a transition curve.
Elements: super elevation, length of curve, shift, tangent length, offsets
Explain the use of Global Positioning Systems (GPS) for surveying and setting out.
Explain the use of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) for updating plans and identifying
developments in relation to existing features.
Explain the use of the following:
EDM
Theodolite
Total station.
Rotating laser for alignment and to control reduce level of exacation.
Pipe laser
Curve elements: angle of deflection, intersection point (IP), angle of deviation, tangent distance,
tangent point (TP),long chord, running chainage, standard chord, sub chords.
Describe the method of setting out circular curves by tape only.
Method offsets from long chord, offsets from the tangent, offset from chords produced
Practical test
Describe the method of setting out using one theodolite and a tape (deflection angle) and tabulate the
setting out data for use on site.
Explain various methods of overcoming obstacles when setting out a curve, including the use of coordinates.
Methods: obstacles where IP/ TP are inaccessible, where features prevent direct measurement of
points on the curve itself
Class test
Identify the various elements and purpose of a transition curve.
Elements: super elevation, length of curve, shift, tangent length, offsets
Explain the use of Global Positioning Systems (GPS) for surveying and setting out.
Explain the use of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) for updating plans and identifying
developments in relation to existing features.
Explain the use of the following:
EDM
Theodolite
Total station.
Rotating laser for alignment and to control reduce level of exacation.
Pipe laser
Curve elements: angle of deflection, intersection point (IP), angle of deviation, tangent distance,
tangent point (TP),long chord, running chainage, standard chord, sub chords.
Describe the method of setting out circular curves by tape only.
Method offsets from long chord, offsets from the tangent, offset from chords produced
Practical test
Describe the method of setting out using one theodolite and a tape (deflection angle) and tabulate the
setting out data for use on site.
Explain various methods of overcoming obstacles when setting out a curve, including the use of coordinates.
Methods: obstacles where IP/ TP are inaccessible, where features prevent direct measurement of
points on the curve itself
Class test
Identify the various elements and purpose of a transition curve.
Elements: super elevation, length of curve, shift, tangent length, offsets
Explain the use of Global Positioning Systems (GPS) for surveying and setting out.
Explain the use of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) for updating plans and identifying
developments in relation to existing features.
Explain the use of the following:
EDM
Theodolite
Total station.
Rotating laser for alignment and to control reduce level of exacation.
Pipe laser
Curve elements: angle of deflection, intersection point (IP), angle of deviation, tangent distance,
tangent point (TP),long chord, running chainage, standard chord, sub chords.
Describe the method of setting out circular curves by tape only.
Method offsets from long chord, offsets from the tangent, offset from chords produced
Practical test
Describe the method of setting out using one theodolite and a tape (deflection angle) and tabulate the
setting out data for use on site.
Explain various methods of overcoming obstacles when setting out a curve, including the use of coordinates.
Methods: obstacles where IP/ TP are inaccessible, where features prevent direct measurement of
points on the curve itself
Class test
Identify the various elements and purpose of a transition curve.
Elements: super elevation, length of curve, shift, tangent length, offsets
Explain the use of Global Positioning Systems (GPS) for surveying and setting out.
Explain the use of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) for updating plans and identifying
developments in relation to existing features.
Explain the use of the following:
EDM
Theodolite
Total station.
Rotating laser for alignment and to control reduce level of exacation.
Pipe laser
Curve elements: angle of deflection, intersection point (IP), angle of deviation, tangent distance,
tangent point (TP),long chord, running chainage, standard chord, sub chords.
Describe the method of setting out circular curves by tape only.
Method offsets from long chord, offsets from the tangent, offset from chords produced
Practical test
Describe the method of setting out using one theodolite and a tape (deflection angle) and tabulate the
setting out data for use on site.
Explain various methods of overcoming obstacles when setting out a curve, including the use of coordinates.
Methods: obstacles where IP/ TP are inaccessible, where features prevent direct measurement of
points on the curve itself
Class test
Identify the various elements and purpose of a transition curve.
Elements: super elevation, length of curve, shift, tangent length, offsets
Explain the use of Global Positioning Systems (GPS) for surveying and setting out.
Explain the use of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) for updating plans and identifying
developments in relation to existing features.
Explain the use of the following:
EDM
Theodolite
Total station.
Rotating laser for alignment and to control reduce level of exacation.
Pipe laser
Curve elements: angle of deflection, intersection point (IP), angle of deviation, tangent distance,
tangent point (TP),long chord, running chainage, standard chord, sub chords.
Describe the method of setting out circular curves by tape only.
Method offsets from long chord, offsets from the tangent, offset from chords produced
Practical test
Describe the method of setting out using one theodolite and a tape (deflection angle) and tabulate the
setting out data for use on site.
Explain various methods of overcoming obstacles when setting out a curve, including the use of coordinates.
Methods: obstacles where IP/ TP are inaccessible, where features prevent direct measurement of
points on the curve itself
Class test
Identify the various elements and purpose of a transition curve.
Elements: super elevation, length of curve, shift, tangent length, offsets
Explain the use of Global Positioning Systems (GPS) for surveying and setting out.
Explain the use of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) for updating plans and identifying
developments in relation to existing features.
Explain the use of the following:
EDM
Theodolite
Total station.
Rotating laser for alignment and to control reduce level of exacation.
Pipe laser
Curve elements: angle of deflection, intersection point (IP), angle of deviation, tangent distance,
tangent point (TP),long chord, running chainage, standard chord, sub chords.
Describe the method of setting out circular curves by tape only.
Method offsets from long chord, offsets from the tangent, offset from chords produced
Practical test
Describe the method of setting out using one theodolite and a tape (deflection angle) and tabulate the
setting out data for use on site.
Explain various methods of overcoming obstacles when setting out a curve, including the use of coordinates.
Methods: obstacles where IP/ TP are inaccessible, where features prevent direct measurement of
points on the curve itself
Class test
Identify the various elements and purpose of a transition curve.
Elements: super elevation, length of curve, shift, tangent length, offsets
Explain the use of Global Positioning Systems (GPS) for surveying and setting out.
Explain the use of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) for updating plans and identifying
developments in relation to existing features.
Explain the use of the following:
EDM
Theodolite
Total station.
Rotating laser for alignment and to control reduce level of exacation.
Pipe laser
Curve elements: angle of deflection, intersection point (IP), angle of deviation, tangent distance,
tangent point (TP),long chord, running chainage, standard chord, sub chords.
Describe the method of setting out circular curves by tape only.
Method offsets from long chord, offsets from the tangent, offset from chords produced
Practical test
Describe the method of setting out using one theodolite and a tape (deflection angle) and tabulate the
setting out data for use on site.
Explain various methods of overcoming obstacles when setting out a curve, including the use of coordinates.
Methods: obstacles where IP/ TP are inaccessible, where features prevent direct measurement of
points on the curve itself
Class test
Identify the various elements and purpose of a transition curve.
Elements: super elevation, length of curve, shift, tangent length, offsets
Explain the use of Global Positioning Systems (GPS) for surveying and setting out.
Explain the use of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) for updating plans and identifying
developments in relation to existing features.
Explain the use of the following:
EDM
Theodolite
Total station.
Rotating laser for alignment and to control reduce level of exacation.
Pipe laser
Curve elements: angle of deflection, intersection point (IP), angle of deviation, tangent distance,
tangent point (TP),long chord, running chainage, standard chord, sub chords.
Describe the method of setting out circular curves by tape only.
Method offsets from long chord, offsets from the tangent, offset from chords produced
Practical test
Describe the method of setting out using one theodolite and a tape (deflection angle) and tabulate the
setting out data for use on site.
Explain various methods of overcoming obstacles when setting out a curve, including the use of coordinates.
Methods: obstacles where IP/ TP are inaccessible, where features prevent direct measurement of
points on the curve itself
Class test
Identify the various elements and purpose of a transition curve.
Elements: super elevation, length of curve, shift, tangent length, offsets
Explain the use of Global Positioning Systems (GPS) for surveying and setting out.
Explain the use of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) for updating plans and identifying
developments in relation to existing features.
Explain the use of the following:
EDM
Theodolite
Total station.
Rotating laser for alignment and to control reduce level of exacation.
Pipe laser
Curve elements: angle of deflection, intersection point (IP), angle of deviation, tangent distance,
tangent point (TP),long chord, running chainage, standard chord, sub chords.
Describe the method of setting out circular curves by tape only.
Method offsets from long chord, offsets from the tangent, offset from chords produced
Practical test
Describe the method of setting out using one theodolite and a tape (deflection angle) and tabulate the
setting out data for use on site.
Explain various methods of overcoming obstacles when setting out a curve, including the use of coordinates.
Methods: obstacles where IP/ TP are inaccessible, where features prevent direct measurement of
points on the curve itself
Class test
Identify the various elements and purpose of a transition curve.
Elements: super elevation, length of curve, shift, tangent length, offsets
Explain the use of Global Positioning Systems (GPS) for surveying and setting out.
Explain the use of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) for updating plans and identifying
developments in relation to existing features.
Explain the use of the following:
EDM
Theodolite
Total station.
Rotating laser for alignment and to control reduce level of exacation.
Pipe laser
Curve elements: angle of deflection, intersection point (IP), angle of deviation, tangent distance,
tangent point (TP),long chord, running chainage, standard chord, sub chords.
Describe the method of setting out circular curves by tape only.
Method offsets from long chord, offsets from the tangent, offset from chords produced
Practical test
Describe the method of setting out using one theodolite and a tape (deflection angle) and tabulate the
setting out data for use on site.
Explain various methods of overcoming obstacles when setting out a curve, including the use of coordinates.
Methods: obstacles where IP/ TP are inaccessible, where features prevent direct measurement of
points on the curve itself
Class test
Identify the various elements and purpose of a transition curve.
Elements: super elevation, length of curve, shift, tangent length, offsets
Explain the use of Global Positioning Systems (GPS) for surveying and setting out.
Explain the use of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) for updating plans and identifying
developments in relation to existing features.
Explain the use of the following:
EDM
Theodolite
Total station.
Rotating laser for alignment and to control reduce level of exacation.
Pipe laser
Curve elements: angle of deflection, intersection point (IP), angle of deviation, tangent distance,
tangent point (TP),long chord, running chainage, standard chord, sub chords.
Describe the method of setting out circular curves by tape only.
Method offsets from long chord, offsets from the tangent, offset from chords produced
Practical test
Describe the method of setting out using one theodolite and a tape (deflection angle) and tabulate the
setting out data for use on site.
Explain various methods of overcoming obstacles when setting out a curve, including the use of coordinates.
Methods: obstacles where IP/ TP are inaccessible, where features prevent direct measurement of
points on the curve itself
Class test
Identify the various elements and purpose of a transition curve.
Elements: super elevation, length of curve, shift, tangent length, offsets
Explain the use of Global Positioning Systems (GPS) for surveying and setting out.
Explain the use of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) for updating plans and identifying
developments in relation to existing features.
Explain the use of the following:
EDM
Theodolite
Total station.
Rotating laser for alignment and to control reduce level of exacation.
Pipe laser
You might also like
- Advance Surveying 9045 PDFDocument6 pagesAdvance Surveying 9045 PDFSheezan Khan100% (2)
- 2nd Semster - Lec04 - Introduction To Total Station PDFDocument13 pages2nd Semster - Lec04 - Introduction To Total Station PDFDakheel malekoNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Our Camp InstructorDocument35 pagesAcknowledgement: Our Camp InstructorPrashant ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Topo Practica 2Document8 pagesTopo Practica 2Brandon J. LovoNo ratings yet
- RACHO - Discussion and ConclusionDocument3 pagesRACHO - Discussion and ConclusionWei Shen56% (9)
- GMAT1110 SummaryDocument13 pagesGMAT1110 SummaryBenjamin BrownNo ratings yet
- Modern Survey Unit-4Document61 pagesModern Survey Unit-4KIRAN KUMAR100% (2)
- Tacheometry ReportDocument7 pagesTacheometry ReportMohd Zamzuri100% (1)
- Surveying PDFDocument1 pageSurveying PDFMariam KariamNo ratings yet
- Total StationDocument128 pagesTotal StationVivek Ingle100% (2)
- GATE Architecture and Planning Climatology and Building Services and Infrastructure SyllabusDocument98 pagesGATE Architecture and Planning Climatology and Building Services and Infrastructure SyllabusGATE AR97No ratings yet
- Practical 5: Instruments and Accessories Required: Total Station, Leveling Staff EtcDocument9 pagesPractical 5: Instruments and Accessories Required: Total Station, Leveling Staff EtcVasilisaNo ratings yet
- Theodolite and TS Survey LectureDocument15 pagesTheodolite and TS Survey LectureJoseph ZotooNo ratings yet
- Rekomendasi Pemakaian:: Manfaat Total StationDocument2 pagesRekomendasi Pemakaian:: Manfaat Total StationNandy Bosky HattaNo ratings yet
- Exp.8 Total Station-IntroductionDocument4 pagesExp.8 Total Station-IntroductionSaurabhChoudhary67% (3)
- Total StationDocument47 pagesTotal StationYogendra PatilNo ratings yet
- What Are Instru-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesWhat Are Instru-WPS OfficealjonNo ratings yet
- 4-Theodolite & Total Station-2011 PDFDocument68 pages4-Theodolite & Total Station-2011 PDFPratik Babu GhimireNo ratings yet
- Surveying & GeomaticsDocument315 pagesSurveying & GeomaticsSahil Singh100% (2)
- Report Standart TraverseDocument25 pagesReport Standart TraverseAmirul Yaakub57% (7)
- SurveyingDocument54 pagesSurveyingWhy MeNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 2 TheodoliteDocument23 pagesLECTURE 2 TheodoliteKanika AdvaniNo ratings yet
- DRAFTSMAN Syllabus EnglishDocument5 pagesDRAFTSMAN Syllabus Englishஅருண்குமார் அமைப்பியல்No ratings yet
- Surveying & Geomatics Syllabus 2019Document3 pagesSurveying & Geomatics Syllabus 2019ashrafNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Setting Out SurveyDocument33 pagesTopic 6 Setting Out SurveyDebra DeirdreNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document6 pagesLab 1Muhammad IsmailNo ratings yet
- Total Station PDFDocument47 pagesTotal Station PDFkkrao100% (1)
- Vertical Lane Line Detection Technology Based On Hough TransformDocument7 pagesVertical Lane Line Detection Technology Based On Hough Transformpepethefrogg45No ratings yet
- Tacheometry Report 1Document13 pagesTacheometry Report 1Munirah Hassan77% (13)
- Lab.1 of Survey On Total StationDocument5 pagesLab.1 of Survey On Total StationMuhammad IsmailNo ratings yet
- Surveying - IIDocument7 pagesSurveying - IISagar MandaleekaNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering Department of Infrastructure and Geomatic EngineeringDocument9 pagesFaculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering Department of Infrastructure and Geomatic EngineeringFatin HazwaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 Total StationDocument40 pagesChapter 09 Total StationSuhasini PranayNo ratings yet
- Informe de Equipos de Laboratorio de Topografia: Integrantes: Herrera Huanca HilbertDocument15 pagesInforme de Equipos de Laboratorio de Topografia: Integrantes: Herrera Huanca HilbertKEYLA CHAMBA RIVERANo ratings yet
- Tacheometry Survey of DetailingDocument2 pagesTacheometry Survey of DetailingSuman JyotiNo ratings yet
- Shaft Orbit Identification For Rotating Machinery Based On Statistical Fuzzy Vector Chain Code and Support Vector MachineDocument12 pagesShaft Orbit Identification For Rotating Machinery Based On Statistical Fuzzy Vector Chain Code and Support Vector Machine권용수No ratings yet
- Job # 6. Study of Total StationDocument4 pagesJob # 6. Study of Total StationWaqas ArshadNo ratings yet
- Total Station and Its Application To Civil EngineeringDocument10 pagesTotal Station and Its Application To Civil EngineeringVB100% (4)
- 1 - Introduction To Total StationDocument32 pages1 - Introduction To Total StationSandeepNo ratings yet
- CET308Document5 pagesCET308Deepak VargheseNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ii A Field Report On TraversingDocument18 pagesChapter Ii A Field Report On TraversingMandisa ZibulaNo ratings yet
- SURVEYOR SyllabusDocument18 pagesSURVEYOR Syllabusakash nair100% (1)
- Ella FW 1Document16 pagesElla FW 1Carmela EllaNo ratings yet
- l4 Control Survey TraverseDocument23 pagesl4 Control Survey TraverseSerinaaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Surveying Instrument Use and Surveying FieldworksDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Surveying Instrument Use and Surveying FieldworksaljonNo ratings yet
- Scheme - e Fourth Semester - Ce, CS, CR, CVDocument34 pagesScheme - e Fourth Semester - Ce, CS, CR, CVprafullaNo ratings yet
- Study of Techeometry SurveyDocument6 pagesStudy of Techeometry SurveyAQIB IMRANNo ratings yet
- Total StationDocument12 pagesTotal StationLic Torres JimenezNo ratings yet
- Tachoemetry ReportDocument12 pagesTachoemetry ReportAin Sherin0% (1)
- Stadia TacheometryDocument13 pagesStadia Tacheometryadolfomc200150% (2)
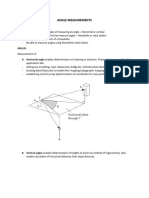
- Angle MeasurementsDocument12 pagesAngle Measurementsabdulgenius123No ratings yet
- Total StationDocument2 pagesTotal StationHimanshu KatyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document30 pagesChapter 1aljonNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Survey EquipmentDocument11 pagesChapter - 3 Survey Equipmentabdulgenius123No ratings yet
- Traversing: Types, Purpose, Procedure, ErrorsDocument10 pagesTraversing: Types, Purpose, Procedure, ErrorsIrwan Pratama100% (1)
- Geomatic Engineering: Lab ReportDocument8 pagesGeomatic Engineering: Lab ReportHati Saya50% (2)
- Theoretical method to increase the speed of continuous mapping in a three-dimensional laser scanning system using servomotors controlFrom EverandTheoretical method to increase the speed of continuous mapping in a three-dimensional laser scanning system using servomotors controlNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Dimensioning and Tolerancing for Design, Manufacturing and Inspection: A Handbook for Geometrical Product Specification Using ISO and ASME StandardsFrom EverandGeometrical Dimensioning and Tolerancing for Design, Manufacturing and Inspection: A Handbook for Geometrical Product Specification Using ISO and ASME StandardsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Engineering Surveying: Theory and Examination Problems for StudentsFrom EverandEngineering Surveying: Theory and Examination Problems for StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (24)
- Plumbing and Drainage1Document1 pagePlumbing and Drainage1rbhavishNo ratings yet
- Outdoor Living Area Design1Document1 pageOutdoor Living Area Design1rbhavishNo ratings yet
- Advantages Disadvantages SmartDocument6 pagesAdvantages Disadvantages SmartrbhavishNo ratings yet
- Building Materials and Finishes1Document1 pageBuilding Materials and Finishes1rbhavishNo ratings yet
- Green Construction ScribdDocument1 pageGreen Construction ScribdrbhavishNo ratings yet
- Vacancies Exist at Air CanadaDocument2 pagesVacancies Exist at Air CanadarbhavishNo ratings yet
- Conversion2016 PDFDocument1 pageConversion2016 PDFrbhavishNo ratings yet
- Physics of Remote SensingDocument1 pagePhysics of Remote SensingrbhavishNo ratings yet
- Interactions With The AtmosphereDocument3 pagesInteractions With The Atmosphererbhavish0% (1)
- The Construction of The Building in Reinforced Concrete As Per DrawingsDocument1 pageThe Construction of The Building in Reinforced Concrete As Per DrawingsrbhavishNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Solar Radiant EnergyDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of Solar Radiant EnergyrbhavishNo ratings yet
- WK Module 12 Structural Design and DETAILING (60 Hours, 4 Credits)Document3 pagesWK Module 12 Structural Design and DETAILING (60 Hours, 4 Credits)rbhavishNo ratings yet
- Government of Mauritius Ministry of Housing and Lands: November 2004Document45 pagesGovernment of Mauritius Ministry of Housing and Lands: November 2004rbhavishNo ratings yet
- Steel ConstructionDocument1 pageSteel ConstructionrbhavishNo ratings yet
- GIS Applications: Business Education Natural ResourcesDocument2 pagesGIS Applications: Business Education Natural ResourcesrbhavishNo ratings yet
- Steel Construction CheapDocument6 pagesSteel Construction CheaprbhavishNo ratings yet
- WK Module 12 Structural Design and DETAILING (60 Hours, 4 Credits)Document2 pagesWK Module 12 Structural Design and DETAILING (60 Hours, 4 Credits)rbhavishNo ratings yet
- Procurement Policy Office: Design-Build and Turnkey ContractsDocument2 pagesProcurement Policy Office: Design-Build and Turnkey ContractsrbhavishNo ratings yet
- How To Make A Fiberglass Subwoofer BoxDocument24 pagesHow To Make A Fiberglass Subwoofer BoxrbhavishNo ratings yet
- 1 A) .Determine The Support Reactions and The Forces in The Members BC, GC and GF of The Pin-Jointed Frames, Shown in Figure 1, Using The Method of Sections. (12 Marks)Document1 page1 A) .Determine The Support Reactions and The Forces in The Members BC, GC and GF of The Pin-Jointed Frames, Shown in Figure 1, Using The Method of Sections. (12 Marks)rbhavishNo ratings yet