Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Histograms: Histogram: A Graphical Display of Data Using Bars of Different Heights
Uploaded by
api-2909951880 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views5 pagesHistograms are a great way to show results of continuous data, such as: weight height how much time etc. But when the data is in categories (such as Country or Favorite movie), we should use a Bar Chart. A histogram is a graphical display of data using bars of different heights.
Original Description:
Original Title
histograms
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHistograms are a great way to show results of continuous data, such as: weight height how much time etc. But when the data is in categories (such as Country or Favorite movie), we should use a Bar Chart. A histogram is a graphical display of data using bars of different heights.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views5 pagesHistograms: Histogram: A Graphical Display of Data Using Bars of Different Heights
Uploaded by
api-290995188Histograms are a great way to show results of continuous data, such as: weight height how much time etc. But when the data is in categories (such as Country or Favorite movie), we should use a Bar Chart. A histogram is a graphical display of data using bars of different heights.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Histograms
Histogram: a graphical display of data using bars of different heights.
It is similar to a Bar Chart,
but a histogram groups
numbers into ranges
And you decide what ranges
to use!
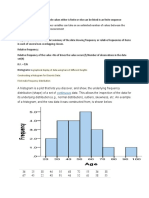
Example: Height of Orange Trees
You measure the height of every tree in the orchard in centimeters (cm)
The heights vary from 100 cm to 340 cm
You decide to put the results into groups of 50 cm:
The 100 to just below 150 cm range,
The 150 to just below 200 cm range,
etc...
So a tree that is 260 cm tall is added to the "250-300" range.
And here is the result:
You can see (for example) that there
are 30 trees from 150 cm to just below
200 cm tall
The horizontal axis is continuous like a number line:
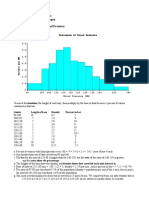
Example: How much is that puppy growing?
Each month you measure how much weight your pup has gained and get
these results:
0.5, 0.5, 0.3, 0.2, 1.6, 0, 0.1, 0.1, 0.6, 0.4
They vary from 0.2 (the pup lost weight that month) to 1.6
Put in order from lowest to highest weight gain:
0.2, 0, 0.1, 0.1, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.5, 0.6, 1.6
You decide to put the results into groups of 0.5:
The 0.5 to just below 0 range,
The 0 to just below 0.5 range,
etc...
And here is the result:
There are no values from 1 to just below 1.5,
but we still show the space:
The range of each bar is also called the Class Interval
In the example above each class interval is 0.5
Histograms are a great way to show results of continuous data, such as:
weight
height
how much time
etc.
But when the data is
in categories (such as
Country or Favorite Movie),
we should use a Bar Chart.
Frequency Histogram
A Frequency Histogram is a special histogram that uses vertical columns
to show frequencies (how many times each score occurs):
Here I have added up how often 1 occurs (2
times), how often 2 occurs (5 times), etc,
and shown them as a histogram.
You might also like
- Chapter 1 Fundamental Concepts SPSS - Descriptive StatisticsDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Fundamental Concepts SPSS - Descriptive StatisticsAvinash AmbatiNo ratings yet
- HistogramsDocument4 pagesHistogramsapi-233663523No ratings yet
- HistogramsDocument2 pagesHistogramsJay OllanoNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument8 pagesDescriptive StatisticsEa FatihahNo ratings yet
- HistogramDocument34 pagesHistogramመለክ ሓራNo ratings yet
- Statistics - 1: Presentation of DataDocument37 pagesStatistics - 1: Presentation of Datanpk007No ratings yet
- Grouped Data:: BA 302: Chapter-2 Instructions by Dr. Kishor Guru-GharanaDocument8 pagesGrouped Data:: BA 302: Chapter-2 Instructions by Dr. Kishor Guru-GharanaLou RawlsNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis-Univariate & BivariateDocument9 pagesData Analysis-Univariate & BivariateMeenakshi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Probability+&+Statistics FormulasDocument50 pagesProbability+&+Statistics Formulaschetandk47No ratings yet
- What Is StatisticsDocument6 pagesWhat Is StatisticsAdrian RaganitNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.2Document4 pagesUnit 1.2Akash kumarNo ratings yet
- MT1 - Text NotesDocument25 pagesMT1 - Text NotesMatthew StewartNo ratings yet
- Uncertainties and Error PropagationDocument28 pagesUncertainties and Error PropagationruukiNo ratings yet
- Growth Drive ReadDocument10 pagesGrowth Drive ReadFelix da SilvaNo ratings yet
- CH 1-Data Condensation and Graphical MethodsDocument16 pagesCH 1-Data Condensation and Graphical MethodsVishal Padhar100% (2)
- The Rows of A WorksheetDocument27 pagesThe Rows of A WorksheetKarey SmithNo ratings yet
- Stastical Data Analysis: A Lokeshwari 22N31E0014Document30 pagesStastical Data Analysis: A Lokeshwari 22N31E0014turpu poojithareddyNo ratings yet
- Frequency Distribution and Data: Types, Tables, and Graphs: What Is Descriptive Statistics?Document19 pagesFrequency Distribution and Data: Types, Tables, and Graphs: What Is Descriptive Statistics?Muhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Section 2: Descriptive Statistics Part 1: Organizing DataDocument59 pagesSection 2: Descriptive Statistics Part 1: Organizing DataTian ZeNo ratings yet
- Justin 0 VenkatDocument22 pagesJustin 0 Venkathackedgamers.925No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document34 pagesChapter 3varshinpouriNo ratings yet
- Bar Charts, HistogramsDocument4 pagesBar Charts, HistogramsczvzNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 MAS202Document43 pagesChapter2 MAS202Quỳnh VânNo ratings yet
- Using Excel 2010 To Process Data in PhysicsDocument6 pagesUsing Excel 2010 To Process Data in PhysicsNandita NawalNo ratings yet
- HW I ReviewDocument10 pagesHW I ReviewNuraeni ShqNo ratings yet
- STATS Sums For PracticeDocument9 pagesSTATS Sums For PracticePranav PasteNo ratings yet
- Statistics ReviewDocument62 pagesStatistics ReviewJohn_2998No ratings yet
- Statistics & ProbabilityDocument105 pagesStatistics & ProbabilityWilliNo ratings yet
- Basics StatisticsDocument11 pagesBasics StatisticsrssarmaNo ratings yet
- This Excel File Will Allow You To Do The Following Tests: Chi-Square Test T-Test Paired T-Test Regression Simpson's Diversity IndexDocument40 pagesThis Excel File Will Allow You To Do The Following Tests: Chi-Square Test T-Test Paired T-Test Regression Simpson's Diversity IndexDimitrios MilionisNo ratings yet
- Sta 103 L1 Upda2Document104 pagesSta 103 L1 Upda2Daniel olayioyeNo ratings yet
- PercentilesDocument6 pagesPercentilesanon_239619688No ratings yet
- Revit Family Formula Tips and TricksDocument14 pagesRevit Family Formula Tips and TricksDaniel VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Statistics Course in PsychologyDocument176 pagesStatistics Course in PsychologySpongeBobLongPantsNo ratings yet
- Topic 23 HistogramsDocument11 pagesTopic 23 HistogramszillxsNo ratings yet
- Sample DataDocument43 pagesSample DataQueenzel SaggotNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument6 pagesDescriptive StatisticsRuach Dak TangNo ratings yet
- Introductory Statistics (Chapter 2)Document3 pagesIntroductory Statistics (Chapter 2)Riezel PepitoNo ratings yet
- Family Tables in PRO-EDocument10 pagesFamily Tables in PRO-Eanon-76488580% (5)
- Lecture 101 PDF HistogramDocument7 pagesLecture 101 PDF Histogramcssuresh71No ratings yet
- 2020 - STATISTICS 1a - Form 4Document10 pages2020 - STATISTICS 1a - Form 4Jacob SeraphineNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Statistics-Frequency Distribution: WEEK # 06Document39 pagesFundamentals of Statistics-Frequency Distribution: WEEK # 06Sarmad Altaf Hafiz Altaf HussainNo ratings yet
- WWW Social Research Methods Net KB Statdesc PHPDocument87 pagesWWW Social Research Methods Net KB Statdesc PHPNexBengson100% (1)
- Descriptive Statistics: By: Margaretha Madha MelissaDocument38 pagesDescriptive Statistics: By: Margaretha Madha MelissaKristian Made SuhardanaNo ratings yet
- Introductory Statistics (Chapter 2)Document3 pagesIntroductory Statistics (Chapter 2)Riezel PepitoNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Frequency and Box Plots WITH GRATEFUL THANKS TO MR BARTONDocument10 pagesCumulative Frequency and Box Plots WITH GRATEFUL THANKS TO MR BARTONMathsArkAcademyNo ratings yet
- 4LAB2020Document5 pages4LAB2020Kyle FikaniNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument9 pagesMathematicsJoseph VijuNo ratings yet
- AS Level Physics Practical Paper 3Document9 pagesAS Level Physics Practical Paper 3Rupali Samriddhi InalaNo ratings yet
- Week 9 An Introduction To SPSS Descriptive StatisticsDocument54 pagesWeek 9 An Introduction To SPSS Descriptive StatisticsMariyam MoosaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument19 pagesDescriptive StatisticsFrancis NyekoNo ratings yet
- Spss SmallDocument7 pagesSpss SmallЕлена Рева-МихееваNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument105 pagesDescriptive StatisticsBenj Jamieson DuagNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Excel GraphsDocument25 pagesLab 5 Excel Graphspuneet singhalNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument5 pagesDescriptive StatisticsEmelson VertucioNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics Excel - StataDocument37 pagesDescriptive Statistics Excel - StataAnushrut MNo ratings yet
- Finding PercentagesDocument6 pagesFinding Percentagesarajamani78No ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument6 pagesNormal DistributionAjai Prasad NigamNo ratings yet
- Statistics (Part 1)Document15 pagesStatistics (Part 1)ABRIANNA HARRISNo ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument18 pagesRelations and Functionsapi-290995188No ratings yet
- Stats AsgnmtDocument1 pageStats Asgnmtapi-290995188No ratings yet
- Cumulative Tables and GraphsDocument4 pagesCumulative Tables and Graphsapi-290995188No ratings yet
- Mathematics May 2012Document12 pagesMathematics May 2012api-290995188No ratings yet
- Frequency DistributionDocument3 pagesFrequency Distributionapi-290995188No ratings yet
- Line GraphsDocument4 pagesLine Graphsapi-290995188No ratings yet
- Functions and RelationsDocument8 pagesFunctions and Relationsapi-290995188No ratings yet
- Mathematics May 2013 Csec CXCDocument13 pagesMathematics May 2013 Csec CXCJodikaye Davis0% (2)
- Functions 1Document2 pagesFunctions 1api-290995188No ratings yet