Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Differences between TDMA, CDMA, and FDMA
Uploaded by
Karthik Mohan KOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Differences between TDMA, CDMA, and FDMA
Uploaded by
Karthik Mohan KCopyright:
Available Formats
Differences between TDMA, CDMA, and FDMA
With acknowledgement and appreciation to My Lord on Yahoo Answers
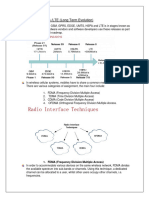
TDMA
Time division multiple access (TDMA) is a channel access method for shared medium (usually
radio) networks. It allows several users to share the same frequency channel by dividing the
signal into different timeslots. The users transmit in rapid succession, one after the other, each
using his own timeslot. This allows multiple stations to share the same transmission medium
(e.g. radio frequency channel) while using only the part of its bandwidth they require. TDMA is
used in the digital 2G cellular systems such as Global System for Mobile Communications
(GSM), IS-136, Personal Digital Cellular (PDC) and iDEN, and in the Digital Enhanced Cordless
Telecommunications (DECT) standard for portable phones. It is also used extensively in satellite
systems, and combat-net radio systems.
TDMA is a type of Time-division multiplexing, with the special point that instead of having one
transmitter connected to one receiver, there are multiple transmitters. In the case of the uplink
from a mobile phone to a base station this becomes particularly difficult because the mobile
phone can move around and vary the timing advance required to make its transmission match
the gap in transmission from its peers
CDMA
Code division multiple access (CDMA) is a form of multiplexing and a method of multiple access
that divides up a radio channel not by time (as in time division multiple access), nor by
frequency (as in frequency-division multiple access), but instead by using different pseudorandom code sequences for each user. CDMA is a form of "spread-spectrum" signaling, since
the modulated coded signal has a much higher bandwidth than the data being communicated.
CDMA also refers to digital cellular telephony systems that make use of this multiple access
scheme, such as those pioneered by QUALCOMM, and W-CDMA by the International
Telecommunication Union or ITU.
CDMA has been used in many communications and navigation systems, including the Global
Positioning System and in the OmniTRACS satellite system for transportation logistics
FDMA
Frequency Division Multiple Access or FDMA is an access technology that is used by radio
systems to share the radio spectrum. The terminology multiple access implies the sharing of
the resource amongst users, and the frequency division describes how the sharing is done: by
allocating users with different carrier frequencies of the radio spectrum.
This technique relies upon sharing of the available radio spectrum by the communications
signals that must pass through that spectrum. The terminology multiple access indicates how
the radio spectrum resource is intended to be used: by enabling more than one communications
signal to pass within a particular band; and the frequency division indicates how the sharing is
accomplished: by allocating individual frequencies for each communications signal within the
band.
In an FDMA scheme, the given Radio Frequency (RF) bandwidth is divided into adjacent
frequency segments. Each segment is provided with bandwidth to enable an associated
communications signal to pass through a transmission environment with an acceptable level of
interference from communications signals in adjacent frequency segments
You might also like
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 4th Lecture Access TechniquesDocument2 pages4th Lecture Access TechniquesAyesha NawazNo ratings yet
- Frequency Reuse: Channel Access MethodDocument6 pagesFrequency Reuse: Channel Access MethodBassy KaserNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE ACCESS TECHNIQUESDocument25 pagesMULTIPLE ACCESS TECHNIQUESDilpalNo ratings yet
- Time Division Muliple AccessDocument4 pagesTime Division Muliple AccessAbhishek RanaNo ratings yet
- Frequency-Division Multiple AccessDocument2 pagesFrequency-Division Multiple Accessnimer sheikhNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Report On CDMA TechnologyDocument9 pagesIndustrial Training Report On CDMA TechnologyDeepakGujraniya100% (6)
- Fdmatdmacdma 181225151208Document43 pagesFdmatdmacdma 181225151208Nada A. AminNo ratings yet
- Access Methods For Mobile Networks - ShavaneDocument2 pagesAccess Methods For Mobile Networks - ShavaneDrumz Staff50% (2)
- BSU Electronics Engineering Department Report on Multiple Access Channeling ProtocolsDocument6 pagesBSU Electronics Engineering Department Report on Multiple Access Channeling ProtocolsJames Rannel BayonaNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document12 pagesGroup 2Tolu AyanaNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE ACCESS TECHNIQUES FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONDocument6 pagesMULTIPLE ACCESS TECHNIQUES FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONAwais ShoukatNo ratings yet
- Multiple Access TDMADocument5 pagesMultiple Access TDMAJasman SinghNo ratings yet
- CD MaDocument28 pagesCD MaParminder SinghNo ratings yet
- TDMA Network Using Serial CommunicationDocument59 pagesTDMA Network Using Serial CommunicationMaheshwar KumarNo ratings yet
- Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Is A Digital Cellular Technology Used For Mobile Communication. CDMA Is The Base On Which Access Methods SuchDocument25 pagesCode Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Is A Digital Cellular Technology Used For Mobile Communication. CDMA Is The Base On Which Access Methods SuchChristopher AiyapiNo ratings yet
- CDMA - Quick Guide - TutorialspointDocument32 pagesCDMA - Quick Guide - Tutorialspointhadeer.hNo ratings yet
- Multiple Access MethodsDocument5 pagesMultiple Access Methodsgeorgeng90No ratings yet
- CD MaDocument8 pagesCD MaDheeraj BahadurNo ratings yet
- LTEDocument6 pagesLTEDereje FelekeNo ratings yet
- LTEDocument6 pagesLTEDereje FelekeNo ratings yet
- Frequency Division Multiple AccessDocument2 pagesFrequency Division Multiple AccessRahul Raman SinghNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Strategy For Multiuser Detection in CdmaDocument40 pagesAn Efficient Strategy For Multiuser Detection in CdmaNiveli NaiviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document33 pagesChapter 4Behailu AsmareNo ratings yet
- Multiple Access TechniquesDocument5 pagesMultiple Access TechniquesSameerUsmaniNo ratings yet
- CDMADocument59 pagesCDMAAmit NainNo ratings yet
- CDMADocument41 pagesCDMAdasdawtNo ratings yet
- Multiple Input-Multiple Output Ofdm SystemsDocument36 pagesMultiple Input-Multiple Output Ofdm SystemsLoukya KuttiNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Multiple Access TechniquesDocument9 pages1.2 Multiple Access TechniquesAkash RaoNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing ReportDocument21 pagesMobile Computing Reportakshata_pinks3No ratings yet
- Mobile), Is A Standard Set Developed by The ETSI (European TelecommunicationsDocument1 pageMobile), Is A Standard Set Developed by The ETSI (European TelecommunicationsSaeed AalamNo ratings yet
- Advanced Communication Systems Module 6Document56 pagesAdvanced Communication Systems Module 6Arjun S KumarNo ratings yet
- GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)Document4 pagesGSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)vedhajuvalNo ratings yet
- Multiple Access Techniques (CDMA, TDMA, FDMA) : Reported byDocument7 pagesMultiple Access Techniques (CDMA, TDMA, FDMA) : Reported byXzxz WahshNo ratings yet
- TDMA(1)Document5 pagesTDMA(1)امجد حاتم عبد المنعمNo ratings yet
- UNIT-IV MULTIPLE DIVISION ACCESS TECHNIQUESDocument16 pagesUNIT-IV MULTIPLE DIVISION ACCESS TECHNIQUESTharun kondaNo ratings yet
- Multiple AccessDocument7 pagesMultiple AccessJaddie LorzanoNo ratings yet
- Cdma Deepak Final 1Document83 pagesCdma Deepak Final 1deepak18mNo ratings yet
- CDMADocument38 pagesCDMAneerNo ratings yet
- CDMA Quick GuideDocument29 pagesCDMA Quick GuideHashem AllahamNo ratings yet
- FDMA vs. TDMA vs. CDMADocument3 pagesFDMA vs. TDMA vs. CDMAMojes KoliNo ratings yet
- ##Multiple Access:: Duplexer Is Used Inside Each Subscriber Unit and Base Station To Allow Simultaneous RadioDocument5 pages##Multiple Access:: Duplexer Is Used Inside Each Subscriber Unit and Base Station To Allow Simultaneous RadioTozammel Hossain TusharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Multiple Access TechniquesDocument30 pagesChapter 8 - Multiple Access TechniquesDr. Mudita JunejaNo ratings yet
- Assignment #3Document2 pagesAssignment #3Ian James CalanzaNo ratings yet
- Code Division Multiple AccessDocument2 pagesCode Division Multiple AccessArindam MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Difference Between OFDM and OFDMADocument4 pagesDifference Between OFDM and OFDMAskshna100% (1)
- CDMADocument2 pagesCDMARewaa MaherNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Cdma TechnologyDocument102 pagesA Project Report On Cdma Technologyanujag007100% (2)
- Multiple Access Techniques ExplainedDocument5 pagesMultiple Access Techniques ExplainedPulkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Comparison Among Different Multiple Access Techniques Used in Cellular Network 2Document2 pagesComparison Among Different Multiple Access Techniques Used in Cellular Network 2asdsNo ratings yet
- Wireless Mobile CommunicationDocument6 pagesWireless Mobile Communicationduyttcute1989No ratings yet
- WCDMA UMTS and CDMA 2000Document11 pagesWCDMA UMTS and CDMA 2000Dhanmeet KaurNo ratings yet
- CDMA TutorialDocument65 pagesCDMA Tutorialsamtec32No ratings yet
- Assignment#1 OF Mobile and ADHOC NetworksDocument13 pagesAssignment#1 OF Mobile and ADHOC NetworksRajesh RanaNo ratings yet
- 2G Cellular SystemsDocument5 pages2G Cellular SystemsVanagara BharatNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communications Multiple Access TechniquesDocument25 pagesSatellite Communications Multiple Access TechniquesRamacharyuluPattabhiGovardhanamNo ratings yet
- Analyses of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Schemes For Global Mobile Satellite Communications (GMSC)Document9 pagesAnalyses of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Schemes For Global Mobile Satellite Communications (GMSC)Nguyễn Văn TuấnNo ratings yet
- Code-Division Multiple AccessDocument11 pagesCode-Division Multiple AccessMr. Akhil WaliaNo ratings yet
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesFrom EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CH 9 Practice SolutionsDocument3 pagesCH 9 Practice SolutionsKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Exercises in Chapter 8: 1.szm, xr8-1.wf1 and Xr8-1.sas, RespectivelyDocument12 pagesSolutions To Exercises in Chapter 8: 1.szm, xr8-1.wf1 and Xr8-1.sas, RespectivelyKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- Turbo Coding and MAP Decoding: Intuitive Guide To Principles of Communications Charan LangtonDocument25 pagesTurbo Coding and MAP Decoding: Intuitive Guide To Principles of Communications Charan LangtonKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Practice SolutionsDocument3 pagesCH 7 Practice SolutionsKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Practice SolutionsDocument2 pagesCH 8 Practice SolutionsKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- 521484A Exercise5Document2 pages521484A Exercise5Karthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- AutocorrelationDocument9 pagesAutocorrelationCuong PolymeNo ratings yet
- Week6 PDFDocument20 pagesWeek6 PDFFetsum LakewNo ratings yet
- ECE531 Screencast Fisher InformationDocument7 pagesECE531 Screencast Fisher InformationKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- Noise Term FINALDocument30 pagesNoise Term FINALNaresh TeresNo ratings yet
- ECE531 Screencast 2.1: Introduction To The Cramer-Rao Lower Bound (CRLB)Document5 pagesECE531 Screencast 2.1: Introduction To The Cramer-Rao Lower Bound (CRLB)Karthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- TurboDocument10 pagesTurboAlireza MovahedianNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction, Channel Capacity PDFDocument22 pages1 - Introduction, Channel Capacity PDFKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- Null Atrix PDFDocument1 pageNull Atrix PDFKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- GMSKDocument11 pagesGMSKgoutam4321No ratings yet
- Null Space and Range Space PDFDocument7 pagesNull Space and Range Space PDFKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- Basics of Signals - Princeton UniversityDocument21 pagesBasics of Signals - Princeton Universityg5680No ratings yet
- Basics of Signals - Princeton UniversityDocument21 pagesBasics of Signals - Princeton Universityg5680No ratings yet
- Null Space and Range Space PDFDocument7 pagesNull Space and Range Space PDFKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- Basics of Signals - Princeton UniversityDocument21 pagesBasics of Signals - Princeton Universityg5680No ratings yet
- Python Numpy Tutorial (CS231n-Stanford)Document27 pagesPython Numpy Tutorial (CS231n-Stanford)Karthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- Eliminating CHN FB in Next Gen Cellular NWDocument14 pagesEliminating CHN FB in Next Gen Cellular NWKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- GSM and Lte Network ArchitectureDocument12 pagesGSM and Lte Network ArchitectureKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- ML, Bayesian and MAP PDFDocument63 pagesML, Bayesian and MAP PDFKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- ContohDocument7 pagesContohJiah Mohd DaudNo ratings yet
- 18 Kalman FilteringDocument25 pages18 Kalman FilteringKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- A Multipath Fading Channel Model Applied To Fast UMTS Link Simulation With Channel Estimation - Gelpi - 2003Document3 pagesA Multipath Fading Channel Model Applied To Fast UMTS Link Simulation With Channel Estimation - Gelpi - 2003Karthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- Bell Labs BLAST Architecture for MIMO Wireless SystemsDocument3 pagesBell Labs BLAST Architecture for MIMO Wireless SystemsKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet