Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Algebra Renz
Uploaded by
micahnollaseOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Algebra Renz
Uploaded by
micahnollaseCopyright:
Available Formats
Renz Marie R.
Nollase III- Saturn February 24,2010
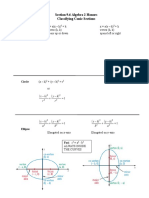
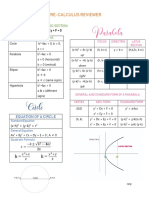
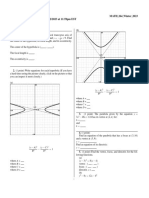
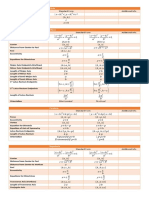
Conic Sections
CIRCLE ELLIPSE PARABOLA HYPERBOLA
The set of all points (x, y) The set of all points (x, y) in The set of all points (x, y) to
The set of all points (x, y)
in a plane whose distance the plane whose distance from which the absolute value of
in a plane whose distance
from two fixed points in the a fixed point called focus is the difference between two
from a fixed point called
Definition plane called foci gives a equal to the distance from the fixed points called foci is
center is constant.
constant sum. fixed line called directrix. constant.
C(0,0) Upward:
x-axis: x2 = 4cy
Center x-axis
x2 / a2 + y2 / b2 = 1 Downward:
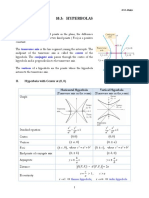
C(0,0) x2 / a2 - y2 / b2 = 1
at the x2 = -4cy
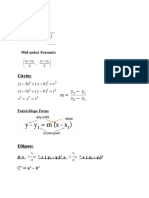
x2 + y2 = r2
Origin where a > b Left:
y-axis
(0,0) y-axis: y2 = -4cy
y2 / b2 - x2 / a2 = 1
x2 / a2 + y2 / b2 = 1 Right:
where b > a y2 = 4cy
Equation
Downward:
C(h,k)
(x-h)2 = -4c(y-k) x-axis
(x-h) /a + (y-k)2/b2 = 1
2 2
Left: (x-h)2/a2 - (y-k)2/b2 = 1
C(h, k)
Center (y-k)2 = -4c(x-h)
(x-h)2+(y-k)2 = r2 Where a > b
at (h.k) (x-h)2/a2 + (y-k)2/b2 = 1
Right: y-axis
(y-k)2 = 4c(x-h) (y-k) /b - (x-h)2/a2 = 1
2 2
Where b > a
Upward:
(x-h)2 =4c(y-k)
C(0,0):
Upward (0,c)
Downward (0,-c)
Left (-c,0)
P.A. x-axis: (±c,0) Right (c,0) C(0,0) :
Focus N/A (+c, 0)
P.A. y-axis: (0, ±c) C(h,k): (0, +c)
Upward (h,k+c)
Downward (h,k-c)
Left (h-c,k)
Right (h+c,k)
C(0,0):
x-axis: (±a ,0)
P.A. x-axis: (±a,0) (0,0)
Vertex N/A
P.A. y-axis: (0, ±b) (h,k)
y-axis: (0, ±b)
C(h,k):
(±h, ±k)
P.A. x-axis: 2b2/a x-axis: 2b2/a
Latus Rectum N/A
P.A. y-axis: 2a2/b
LR = 4c
y-axis: 2a2/b
e=c/b
Eccentricity: e=0
e=c/a
e=1 N/A
C(0,0):
Upward: y = -c
Directrix N/A N/A Downward: y=c N/A
Left: x=c
Right: x = -c
P.A. x-axis: 2a
Major axis N/A
P.A. y-axis: 2b
N/A N/A
P.A. x-axis: 2b
Minor axis N/A
P.A: y-axis: 2a
N/A N/A
Equations of y = ± (b/a)x
N/A N/A N/A
Asymptotes: x = ± (b/a)y
You might also like
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- 1 Parabolas 2 Circles 3 Ellipses 4 Hyperbolas 5 ExerciesDocument6 pages1 Parabolas 2 Circles 3 Ellipses 4 Hyperbolas 5 ExerciesKyle VuNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Ax + by + C 0 y MX + B, y - y M (YDocument12 pagesMathematics: Ax + by + C 0 y MX + B, y - y M (Yvzimak2355No ratings yet
- PRECALCULUS FORMULAS DetailedDocument2 pagesPRECALCULUS FORMULAS DetailedJessa Mae Dechavez DumalagNo ratings yet
- 9.6 Notes To Start ChapterDocument5 pages9.6 Notes To Start ChapterTeresa OrpenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Circles: Finding The Equation of The CircleDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Circles: Finding The Equation of The CircleLumpa RamosNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola: A. Standard Equation & Definition (S)Document12 pagesHyperbola: A. Standard Equation & Definition (S)Er. Narender SinghNo ratings yet
- 3 MathematicsDocument12 pages3 MathematicsHugoSalidoNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS (ANALYTIC GEOMETRY) EQUATIONSDocument4 pagesMATHEMATICS (ANALYTIC GEOMETRY) EQUATIONSJhun Michael LocusNo ratings yet
- Shortcuts For Ellipses and HyperBolaDocument3 pagesShortcuts For Ellipses and HyperBolaChristian Simon D. SOLINAPNo ratings yet
- First NoteDocument3 pagesFirst NoteBlake WuutsinNo ratings yet
- Section ConicDocument22 pagesSection ConicRishab Kumar100% (1)
- MA2104 CheatSheet PDFDocument2 pagesMA2104 CheatSheet PDFRobert FisherNo ratings yet
- 1 4-EllipseDocument22 pages1 4-EllipseRayner RamiroNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola TheoryDocument30 pagesHyperbola TheorypadmaNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola: 1. Standard EquationDocument2 pagesHyperbola: 1. Standard EquationAkshit RajputNo ratings yet
- M49 AQuadratic SkillsDocument2 pagesM49 AQuadratic SkillsMohamed Sufian DamanhuriNo ratings yet
- N HSD ZL2 M9 Kgoc KEX8 MFMDocument39 pagesN HSD ZL2 M9 Kgoc KEX8 MFMRamcharan ShortsNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola Learning Objectives:: Ax Cy F 0 X A y B CX Ay F 0 y A X B Ax Cy DX+ Ey + F 0 X H) A y K) B y K) A X H) BDocument8 pagesHyperbola Learning Objectives:: Ax Cy F 0 X A y B CX Ay F 0 y A X B Ax Cy DX+ Ey + F 0 X H) A y K) B y K) A X H) BBilly Jasper DomingoNo ratings yet
- Ellipse - Short Notes - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024Document2 pagesEllipse - Short Notes - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024dushyantsiwach3263No ratings yet
- Understanding ellipsesDocument11 pagesUnderstanding ellipsesNova ChipsNo ratings yet
- 7.4 Ellipses: The Plural of Focus'Document11 pages7.4 Ellipses: The Plural of Focus'Nova ChipsNo ratings yet
- 1stQtr Pre Calculus ReviewerDocument3 pages1stQtr Pre Calculus ReviewerGanyu da SecretaryNo ratings yet
- The ParabolaDocument1 pageThe ParabolaShiella Mae A. JimenezNo ratings yet
- Section 9.2 HyperbolasDocument20 pagesSection 9.2 HyperbolasNoemi Rosario Sanchez0% (1)
- EllpiseDocument4 pagesEllpiseKirbyUSA TorresNo ratings yet
- Deriving Hyperbola EquationDocument1 pageDeriving Hyperbola EquationPrakriti SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 10.3: Hyperbolas: I. DefinitionsDocument2 pages10.3: Hyperbolas: I. Definitionsmohammed aliNo ratings yet
- Circle: 2.1 General FormDocument102 pagesCircle: 2.1 General FormShaima Ahmed100% (1)
- Parabola: B y A XDocument3 pagesParabola: B y A XharshanandiniNo ratings yet
- Parabola: Definitions of Various Important TermsDocument11 pagesParabola: Definitions of Various Important Termsno nameNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoryDocument44 pagesCircle TheoryINDIE EXORTIC GamingNo ratings yet
- DGT Circle and ConicsDocument52 pagesDGT Circle and ConicsHozaifa HamimNo ratings yet
- Mech2407: Multivariable Calculus & Partial Differential EquationsDocument8 pagesMech2407: Multivariable Calculus & Partial Differential EquationsLouis BrightonNo ratings yet
- 7bea3804 Ea3e 5b8Document2 pages7bea3804 Ea3e 5b8HeLio 007No ratings yet
- Conic Sections Circle: X H (H, K)Document4 pagesConic Sections Circle: X H (H, K)JadeChristynLeonorNo ratings yet
- Handout 2 PDFDocument2 pagesHandout 2 PDFstlonginus1942No ratings yet
- Formula Sheet: Point-Slope FormDocument3 pagesFormula Sheet: Point-Slope Formapi-237235863No ratings yet
- Section 9.2 HyperbolasDocument20 pagesSection 9.2 HyperbolasRitu SinghNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Analytic Geometry 02 SolutionsDocument11 pages5.2 Analytic Geometry 02 SolutionsJM John Waps100% (2)
- Mathematics Formula: Topic Phase-2Document9 pagesMathematics Formula: Topic Phase-2testerNo ratings yet
- Anthony Vaccaro MATH 264 Winter 2023 Assignment Assignment 3 Due 02/12/2023 at 11:59pm ESTDocument3 pagesAnthony Vaccaro MATH 264 Winter 2023 Assignment Assignment 3 Due 02/12/2023 at 11:59pm ESTAnthony VaccaroNo ratings yet
- Section 9.2 HyperbolasDocument20 pagesSection 9.2 HyperbolasTrúc Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4Document3 pagesExercise 4ANo ratings yet
- Conicfm PDFDocument2 pagesConicfm PDFGlenn CalingasanNo ratings yet
- Ellipse: Engr. Diana Grace QuiñonesDocument33 pagesEllipse: Engr. Diana Grace QuiñonesRansu SenpaiNo ratings yet
- 9 Circle (@mrbeastjee)Document39 pages9 Circle (@mrbeastjee)I AM KIM TAEHYUNGNo ratings yet
- 9.5 HyperbolasDocument14 pages9.5 HyperbolasCNo ratings yet
- Conic Section - SummaryDocument16 pagesConic Section - Summarymehakgarg2k5No ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Roots of A Quadratic EquationDocument40 pagesQuadratic Equations: Roots of A Quadratic EquationAnshuman BhartiyaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Introduction To Analytic Geometry Review of Basic Analytic GeometryDocument3 pagesPre-Calculus Introduction To Analytic Geometry Review of Basic Analytic GeometryBea PrestoNo ratings yet
- ACTMathFormulaSheetFREE 1Document1 pageACTMathFormulaSheetFREE 1segun shonaNo ratings yet
- Comb W Book-2Parab Ellip HypDocument18 pagesComb W Book-2Parab Ellip Hypuser 12No ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document13 pagesLecture 8Solomon BinutuNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Parabola at VertexDocument1 pageParts of The Parabola at VertexFiedacan, Sherwin Jr.No ratings yet
- Jovic G. Rullepa: SST - Iii, Shs StemDocument36 pagesJovic G. Rullepa: SST - Iii, Shs StemMykhaela Louize GumbanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 309 - Conic Sections and Their Applications: 1. Solving Quadratic Equations NumericallyDocument10 pagesMathematics 309 - Conic Sections and Their Applications: 1. Solving Quadratic Equations NumericallySubhankar HowladerNo ratings yet
- Awesome Formula SheetDocument12 pagesAwesome Formula Sheetsurendranath jadhavNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections Formulas and PropertiesDocument2 pagesConic Sections Formulas and Propertiesgio tongolNo ratings yet
- 01 Pre-Calculus Shs Stem ReferenceDocument61 pages01 Pre-Calculus Shs Stem ReferenceHannah Tiama100% (1)
- Engineering Mathematics IDocument21 pagesEngineering Mathematics IPrabesh PokharelNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Quarter 1 - Module 4: Ellipses and HyperbolasDocument19 pagesPre-Calculus Quarter 1 - Module 4: Ellipses and HyperbolasAbby Gayle Nacino0% (1)
- Conic Section: Formulae & Important Notes: y Ax y Ax X by X byDocument3 pagesConic Section: Formulae & Important Notes: y Ax y Ax X by X byMuhammadShabbirNo ratings yet
- Precalcuus11 - Q1 - Mod1 - Analytic Geometry - Version1 PDFDocument119 pagesPrecalcuus11 - Q1 - Mod1 - Analytic Geometry - Version1 PDFGemmy Ronald Teves85% (13)
- Equation of Hyperbola Center at The HKDocument12 pagesEquation of Hyperbola Center at The HKMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- R - On Syzygies of Mori Fibre Spaces - HeDocument78 pagesR - On Syzygies of Mori Fibre Spaces - HeUnDueTreSberlaNo ratings yet
- Senior Inter Mathematics Model Paper - (IIB)Document2 pagesSenior Inter Mathematics Model Paper - (IIB)Lalam santhiNo ratings yet
- Exercise (6.6-6.7-6.9) Second Year StepDocument14 pagesExercise (6.6-6.7-6.9) Second Year StepAqeel AbbasNo ratings yet
- Geometry Chapter 6 Conic Sections and Circles Review QuestionsDocument6 pagesGeometry Chapter 6 Conic Sections and Circles Review Questionscreative mughalsNo ratings yet
- Stem Pre Calculus Module 1 Illustrating The Different Types of Conic SectionsDocument20 pagesStem Pre Calculus Module 1 Illustrating The Different Types of Conic SectionsInero PHNo ratings yet
- CONIC SECTIONSDocument2 pagesCONIC SECTIONSJohn Renzo ErfeloNo ratings yet
- Conic Section: Formulae & Important Notes: y Ax y Ax X by X byDocument3 pagesConic Section: Formulae & Important Notes: y Ax y Ax X by X byMd FahadNo ratings yet
- Qso25/1 Makematja Paprl Ii 2011'2012 Hours: Matrikulasi MalaysiaDocument8 pagesQso25/1 Makematja Paprl Ii 2011'2012 Hours: Matrikulasi Malaysiajokydin92No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document4 pagesChapter 5Aika DipasupilNo ratings yet
- Presentation Output: Learning Task 7: Photo Conic SectionsDocument28 pagesPresentation Output: Learning Task 7: Photo Conic Sectionsjaypee sarmientoNo ratings yet
- The Parabola: Graphing and Standard FormDocument8 pagesThe Parabola: Graphing and Standard FormHavy TjNo ratings yet
- Identify Parts of A Circle WorksheetDocument1 pageIdentify Parts of A Circle WorksheetRiesta tarianiNo ratings yet
- ParabolaDocument18 pagesParabolaanniaAx ఌNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Conic SectionsDocument1 pageCBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Conic SectionsRanjitha SabapathyNo ratings yet
- Model Paper-1: Maths-2BDocument10 pagesModel Paper-1: Maths-2BAdilNo ratings yet
- Parabola PDFDocument55 pagesParabola PDFrakesh12031965No ratings yet
- Supplementary Assessment Sheet (Sas) Topic: CIRCLES: Senior High School Department First Semester SY 2021 - 2022Document4 pagesSupplementary Assessment Sheet (Sas) Topic: CIRCLES: Senior High School Department First Semester SY 2021 - 2022John Asher Josh AguinilloNo ratings yet
- Ellipse-Jeemain Guru PDFDocument10 pagesEllipse-Jeemain Guru PDFRonnith NandyNo ratings yet
- PreCal Quarter 1 Module 1Document37 pagesPreCal Quarter 1 Module 1PRINCESS CLARIZZ JOY SALUDESNo ratings yet
- More Problems On Conic Sections: by CHED On August 12, 2017Document9 pagesMore Problems On Conic Sections: by CHED On August 12, 2017Patricia LlanaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus (Second Quarter)Document2 pagesPre-Calculus (Second Quarter)Christine MananghayaNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: AES Venue AddressDocument20 pagesFiitjee: AES Venue Addressarnavanand3009No ratings yet
- Important Maths Questions for TS Inter ExamsDocument6 pagesImportant Maths Questions for TS Inter ExamsKota ๖ۣۜRαkͥesͣhͫNo ratings yet
- Balanc Test Edisoni+TikuDocument3 pagesBalanc Test Edisoni+TikuTea MetaNo ratings yet