Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank - Electrochemistry: Ω M Si Ohm Cm CGS
Uploaded by
Anaghesh MuruliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank - Electrochemistry: Ω M Si Ohm Cm CGS
Uploaded by
Anaghesh MuruliCopyright:
Available Formats
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank Electrochemistry
Note: Question which are highlighted with yellow colour are important
I
One mark Questions
1.
What is an electrochemical cell?
Ans: Electrochemical cell is a device in which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy
2.
What is an electrolytic cell?
Ans: In an electrolytic cell electrical energy is converted into chemical energy. Electrical energy
from an external source causes a non-spontaneous chemical reaction to occur
3.
Define one Faraday
Ans: One Faraday is the quantity of electricity which liberates 1 gm equivalent mass of the
substance during electrolysis
4.
What is the emf of SHE
Ans: Emf of SHE is zero volts
5.
Mention the unit of specific conductance
Ans: Unit of specific conductance K is Sm-1 or Mhom-1 or -1m-1 SI or Ohm-1Cm-1 CGS
6.
What is the unit for molar conductance
Ans: The unit for molar conductance m is Sm2 mol 1 or mhom2 mol-1 or -1m2 mol-1 (SI Units) or
Ohm-1 cm2 mol-1 CGS
7.
Define electrode potential
Ans: Electrode potential E is the potential developed when the metal electrode is in
equilibrium with its own ions in solution of unit molar concentration at 298K
8.
Define standard electrode potential
Ans: Standard electrode potential E is the potential developed between the metal electrode
and its metal ions at unit concentration when they are at equilibrium at 298 K and 1 atm
pressure
9.
What are the products of electrolysis of CuSO4 soln. using Cu electrodes?
Ans: Cu will be dissolved from anode and the same amount of Cu will be deposited on the
cathode (basis for electro refining of Cu )
10. Define emf or cell potential
Ans: It is the difference between potential of two electrodes of a cell
emf Ecathode Eanode
11. Define molar conductance
Ans: Molar conductance m is the conductance due to all the ions produced from one mole of
the electrolyte at a given concentration
12. Give the relationship between molar conductance and specific conductivity
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank Electrochemistry
Ans: m K
1000
C
Where K Specific conductivity
C molar concentration
13. Write Nernst equn. for a cell
Ans: E E 0
0.059
log M n
n
Where E electrode potential
E 0 standard electrode potential
n valency of metal ion
M n Conc. of metal ion
14. What is Faradays constant?
Ans: Charge on one mole of electrons is Faradays constant, F and it is 96500C mol 1
15. E of Cu 0.34V and E of Zn 0.76V which of the two is stronger reducing agent?
Ans: E of Zn is lesser than E of Cu and it is above Cu in electrochemical series. The standard
reduction potential of Zn is lesser than Cu Zn is the stronger reducing agent than Cu
16. Out of Zn and Sn which one protects Fe better even after cracks develop in layer why?
Ans: Zn protects better than Sn because its oxidation potential greater than Sn . The oxidation
potential of Sn is less than that of Fe
17. Why Zn reacts with dil. H 2 SO4 to give H 2 g but Cu does not?
Ans: Zn has higher oxidation potential then Hydrogen and Cu has lower oxidation potential
than hydrogen
18. What is a primary cell?
Ans: A primary cell is a cell in which electrical energy is produced by reaction occurring in the
cell. It cannot be recharged e.g. Daniel cell, dry cell
19. Why does a dry cell become dead even if it is not used?
Ans: The acidic NH 4Cl corrodes the Zinc container and makes the dry cell dead
20. Name any 2 metals that can be used for cathodic protection of Fe
Ans: Zinc and Magnesium & Al
21. How can reduction potential of an electrode be increased?
Ans: Reduction potential of an electrode can be increased by increasing the concentration of the
ions
22. Name electrolyte used in fuel cell
Ans: Concentrated aqueous potassium hydroxide KOH Soln
23. Why does a cell stop working after some time?
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank Electrochemistry
Ans: With time electrolytic soln. s undergo change in concentrations which change their electrode
potentials. When the electrode potentials of the two half-cells become equal, the cell stops
working
24. Can E cell or rG of cell reaction become equal to Zero?
Ans: No if that happens the reaction will become non feasible
25. Under what condition is E cell 0 or G 0 ?
Ans: At chemical equilibrium in the cell E cell 0 or G 0
26. Why is alternating current used for measuring resistance of an electrolytic solutions?
Ans: Alternating current is used in electrolysis so that concentration of ions in the soln. remains
constant
27. Electrical potential of galvanic cell 1.1V . If an opposing potential of 1.1V is applied to the cell
what will happen to cell reaction and current flowing in cell?
Ans: The cell reaction stops ad no current flows through the cell
28. Mercury cell has a constant cell potential throughout life why?
Ans: Ions are not involved in the overall cell reaction of a mercury cell thus its cell potential is
always constant Electrolyte KOH is not consumed
29. What is fuel cell?
Ans: A fuel cell is a device in which heat produced by combustion of fuel like H 2 in presence of
O2 is converted into electrical energy
30. Name the electrolyte in Mercury cell
Ans: Electrolyte in mercury cell is moist Mercuric Oxide Hgo mixed with potassium hydroxide
KoH
31. Name 2 fuels that can be used instead of hydrogen in fuel cell
Ans: CH 4 (Methane) or CH 3OH (Methanol) are the other 2 fuels that can be used in a fuel cell
32. In an eqa. solun. how does specific conductivity of electrolyte change with addition of water?
Ans: Specific conductivity of electrolytic decreases on dilution due to decrease in number of ions
per unit volume
33. Write the reaction of an O2 H 2 fuel cell
Ans: 2H 2 g O2 g 2H 2Ol
34. Write cell notation of a galvanic cell in which the reaction is Cu 2 Ag 2 Ag Cu 2
|| Agaq | Ag s
Ans: Cu s | Cuaq
Cu anode, Ag cathode
35. E Zn2 Zn 0.76V What does sign means?
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank Electrochemistry
Ans: sign for Zn means the standard reduction potential is less and the standard oxidation
potential is high i.e., Zn will get oxidised when it is linked to SHE. Zn will undergo oxidation
easily
36. What is corrosion?
Ans: The gradual destruction of a metal by electrochemical attack of O2 , H 2O and acidic gases
present in air is called corrosion. Eg. Lusting of Iron
37. Write Debye-Huckel-onsager equation
Ans: em om A C
38. Name allotrope of carbon used for making electrodes
Ans: Graphite
39. How is emf of cell related to equilibrium constant of a cell reaction at 298K
Ans: E cell
0.0591
log K e
n
Where E cell = emf, K e equilibrium constant n No. of electrons lost or gained
40. Give relationship between free energy change and emf of cell
Ans: G nFE Cell where G free Energy change, F Faraday const. E emf of cell
potential n No. of lost or gained
Two Mark Questions
1.
State any two importance of Salt Bridge
Ans: Importance of Salt Bridge 1. Helps to maintain electrical neutrality of solution in the two half
cells. 2. Helps complete the external circuit and allows the current to flow without diffusion of
ions in solution
2.
Name the products of electrolysis of dil. H 2 SO4 with inert electrodes
Ans: H 2 will be liberated at cathode & O2 will be liberated at Anode
3.
When Iron nail is dipped in Copper Sulphate soln., Copper is deposited on it why?
Ans: Iron Fe is more electropositive than copper Cu Fe is above Cu in electrochemical series
3 Fe has lower reduction potential than Cu so Cu is displaced from CuSO4 solu. by Fe
CuSO4 Fe
FeSO4
Cu
Copper Sulphate
Ferrous sulphate reddish
blue
4.
pale green
Can you store CuSO4 in Iron vessel. Why
Ans: 1. No CuSO4 cannot be store in Fe vessel because Fe is more reactive than Cu
2. CuSO4 Fe FeSO4 Cu Fe will displace Cu from CuSO4
5.
Write the cell r n for Pb storage battery
4
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank Electrochemistry
Ans: Anode: Pb s SO42 PbSO4 s 2e
Cathode: PbO 2 s SO42 4H 2e PbSO4 s 2H 2O1
Overall cell r n . Pb s PbO2 s 2H 2 SO4aq 2PbSO4 s 2H 2O
6.
Why does Zn displace hydrogen from dil. H 2 SO4 while Ag does not
Ans: 1. Zn is above hydrogen where as Ag is below hydrogen in the electrochemical series.
2. The standard reduction potential of Zn is lower than that of Ag . Thus Zn will displace
hydrogen from dil. H 2 SO4
Zn H 2 SO4 ZnSO4 H 2
7.
Represent symbolically the lead storage battery
Ans: Pb | PbSO4 s | H 2 SO4 aq | PbSO4 s | PbO2 s | Pb
8.
What is an inert electrode? Give Eg.
Ans: 1. An inert electrode should not react with the solvent, should not oxidize and produce ions
in solutions
2. Eg. Platinum Pt electrode
9.
Which factors can increase the voltage of a cell having cell reaction of
2
Cu s 2 Ag aq Cuaq
2 Ag s
2
Ag
2.303RT
log 2
Ans: 1. Since E E
nF
Cu
2. By increasing the Ag 1 ion concentration and by increasing the temperature voltage of cell
can be increased
10. What is SHE?
Ans: 1. SHE (Standard Hydrogen Electrode) is a reference electrode
2. Electrode potential of SHE 0 volts (zero)
3. Standard reduction potential of any other electrode can be determined by coupling it with SHE
and measuring the cell potential
4. E values of electrodes are measured on a Hydrogen Scale
11. State difference between Primary Cell and Secondary cell
Ans: Primary cell are used once only & cannot be recharged
2. Cheap, compact and convenient
3. Once exhausted must be discarded
4. Used in flash light, transistors, hearing aids, calculators, electronic watches. Eg. Dry cell.
Secondary cells can be recharged and used again
2. Heavy, has corrosive H 2 SO4 which may spill
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank Electrochemistry
3. Once exhausted can be re used
4. Used in automobiles, watches, calculators
E.g. Lead storage Battery, NiCad cell
12. State Kohlrauschs law and give its formula
Ans: Kohlrauschs law of independent migration of ions states that the molar conductivity of an
electrolyte at infinite dilution can be expressed as the sum of contributions from its individual
ions (cations of anions)
2. m0 0 0
Molar conductivity at dilution - limiting molar conductivities of cation + anion
13. State 2 advantages of H 2 O2 fuel cell
Ans: 1. They have a very high efficiency of 70%
2. They do not cause any pollution
14. Give any 2 differences between strong & weak electrolyte
Ans: Strong electrolyte
1. Undergoes Total ionisation
2. Exists only as ions in solution
3. No equilibrium exists
Eg. Hcl , NaOH , NaCl
Weak Electrolyte
1. Undergoes partial ionisation
2. exists as ions and unionised molecules in solution
3. There is equilibrium between ions & unionised molecules
Eg: CH3COOH . NH 4OH , CH3COONH 4
15. Define Faradays I Law
Ans: The amount of substance deposited at an electrode is directly proportional to the quantity of
current passed through an electrolyte solution
m Q
m It
m ZIt
Q It
m mass, I current in amperes t time in second, Z ece or electro chemical equivalent
16. Define ece
Ans: From Faradays I law Z
m
if I 1 amp t 1 sec. then z m
It
2. ece 1 electro chemical equivalent) is the mass of substance deposited when 1 ampere of current
flows through electrolyte solution for one second
6
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank Electrochemistry
17. State differences between electrolytic cell and electro chemical cell
Ans: Electrolytic cell
1. Electrical energy is converted to chemical energy
2. Electrical energy is used to carry out electrolysis (Chemical r n )
3. Involves non-spontaneous redox r n
4. Positive terminal is anode & -ve terminal is cathode
Electrochemical cell
1. Chemical energy is converted to electrical energy
2. Chemical r n generates electricity
3. Involves spontaneous redox t n
4. Positive terminal is cathode & -ve terminal is anode
18. Can CuSO4 solution be stored in a Zn pot?
Ans: 1. No. CuSO4 solution cannot be stored in a Zn pot the E of Zn is less than E of Cu
2. Zn is stronger reducing agent than Cu Zn will lose e s to Cu 2 ions and redox r n . occurs
2
2
Zn s Cuaq
Znaq
Cu s
Two or Three Mark Questions
19. Write 2 disadvantage or demerits of SHE
Ans: 1. It is difficult to pass H 2 g at one atm pressure
2. difficult to control Pt poisoning
3. difficult to maintain concentration of HCl at 1M
4. SHE is not used for all oxidising substance
20. State Faradays II Law
Ans: 1. The mass of substances deposited or discharged is directly proportional to equivalent
mass of substances when the same quantity of current is passed through different electrolyte
connected in series for CuSO4 and AgNO3 in series
2.
Mass of Cu deposited Eq. mass of Cu
Mass of Ag deposited Eq. mass of Ag
21. Calculate limiting molar conductivity of CaSO4 when m of Ca 2 and SO42 are 119.0 and
160.0 S cm2 mol 1 respectively
Ans: From Kohlrausch law
m CaSO4 m Ca2 m mSO42
119.0 160.0
179.0 Scm2 mol-1
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank Electrochemistry
22. The SRP of Cu & Ag are 0.34V and 0.80V respectively. Construct a galvanic cell using these
electrodes and calculate its emf. Write cell notation and cell r n
Ans: SRP of Cu 0.34V Anode
SRP of Ag 0.80V Cathode
1 2 Anodic r n Cu 2e oCu 2
1 2 cathodic r n Ag 1 1e RAg
Overall cell r n Cu 0 Ag 1 1e R Ag 0
2
1
Cell notation Cu s Cuaq
Agaq
Ag
Emf E cathode E anode
0.80 0.34
E cell 0.46 V
Emf is spontaneous cell.
23. Specific conductance of 0.1 M NaCl solution at 298 K is 1.1 sm1 Calculate the molar
conductivity.
Ans: K 1.1 S m1 , C 0.1 mol L1
k
1000c
1.15m1
1000cLm3 x0.1molL1
Molar conductivity 1.1102 Sm2 mol 1
24. The 0 m of NaCl , LiBr LiCl are 126, 165 and 170 Sm2 mol 1 respectively calculate 0 m for NaBr
Ans: 0 m NaBr 0 Na 0 Br 0 Na 0Cl
0 Br 0 Li 0Cl
0m NaCl 0m LiBr 0m LiCl
126 165 170
0m NaBr 121 Sm2 mol 1
25. For a cell rxn. Involving two electron change, the standard emf of cell is 0.295V at 25C.
Calculate equilibrium constant for the rxn. At 25C.
Ans: For a cell rxn.
Data:
n 2es
E 0cell 0.295V
E 0cell
2.303RT
log Kc
nF
8
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank Electrochemistry
0.059
log Kc
n
log Kc
nE 0
2 x0.295
10
0.059
0.059
Kc anti log10 1010
27. Calculate quantity of current required to deposit 9g of Al.
Ans: Al 3 3e Al
One mole of Al 27 gm
27 g of Al deposited by 3F current
9 f of Al is deposited by
3
9
27
1 F or 96500C
28. Same quantity of current is passed through AgNo3 and Hcl solutions. 1.08g of Ag is deposited
at Ag cathode in first case. What volume of H 2 is evolved at STP in second case) (At mass of
Ag 108 )
Ans: From Faradays II law
Mass of AG deposited
Eq. Mass of Ag
Volume of H 2 liberated at STP Volume of H 2 corresponding to 1 eq. mass of H 2 at STP
1.08
108
VH 2 11200cc
VH 2
1.08 x11200
108
VH2 112CM 3
29. Same current is passed through Cu and Ag voltameters in series Anode of Cu Voltmeter was
found to weigh 0.08g less after electrolysis. What mass of Ag is deposited when At mass of Cu
and Ag are 63.5 and 107.8 respectively.
Ans: From Faradays II law
mass of Cu deposited Eq. mass of Cu
mass of Ag deposited Eq. mass of Ag
Eq. mass
At. mass
Valency
0.08 63.5 2
M Ag 107.8 1
M Ag
0.08 x107.8
0.271 g
31.75
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank Electrochemistry
Mass of Ag deposited 0.271 g.
30. Name the electrolyte used in dry cell
Ans: 1. A paste of NH 4Cl and ZnCl2 in the zinc cylinder and
2. paste of MnO2 and C surrounding the graphite rod.
31. Calculate equilibrium constant for the cell rxn. The standard cell emf is 1.56 V
Ans: E 0
1.56
0.059
log K
n
0.059
log Kc
2
log Kc
1.56 x2
52.79
0.059
Kc anti log 52.79 6.111052
e Ag s
32. Calculate the reduction potential for the following half-cell reaction at 298 K Agaq
Given Ag 0.1M and E 0 0.80V
Ans: According to Nernst equation
E E0
0.0591
1
log
n
n
Mnaq
Given E 0 0.80V , Ag 0.1 Mn 1
E 0.80
0.0591
1
log
1
0.1
E 0.80 0.0591 0.741 V
E 0.741 V
33. The cell rxn. is Mg s 2 Ag 0.0001M Mg 2 0.130M 2 Ag s if E 0 cell 3.17V Calculate it
Ecell
Ans: Cell Notation is
Mg Mg 2 0.130M Ag 0.0001M Ag
0
Ecell Ecell
3.17
Anode
0.0591
log
n
Cathode
0.130
0.591
log
2
2
0.001
Ecell 3.17
0.0591
0.130
log 8
2
10
3.17 0.02955log1.3 107
3.17 0.02955 7.1139
10
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank Electrochemistry
3.17 0.21
Ecell 2.96 V
34. Calculate standard free energy change for the rxn. in Daniel cell at 298 K when SRP of Zn and
Cu are 0.763V and 0.337V respectively.
Ans: Daniel cell Notation
2
2
Zn s Znaq
Cuaq
Cu s
Anode Zn, Cathode Cu
E 0cell E 0 Cathode E 0 anode
0.337 0.763
E 0cell 1.10V
Cell rxn. Zn Cu 2 Zn2 Cu
n 2
G0 nFE 0
2 96500 1.1
2123005 or 212.3 KJ
35. Distinguish between emf and potential difference.
Ans: emf
1. is difference in the electrode potentials when no current flows through cell.
2. is the maximum voltage which is got from cell.
3. is responsible for flow of steady current
4. It can be measured by a potentiometer
Potential difference
1. is the difference in electrode potentials when current is flowing in cell.
2. is less than the maximum voltage got from cell
3. is not responsible for flow of steady current.
4. It can be measured by a voltameter.
Four or Five Marks Questions
1.
Predict the products of electrolysis in (i) an aq. soln. of AgNo3 with Ag electrode (ii) Aq. Soln. of
AgNo3 with pt electrodes.
Ans: (i) In AgNo3aq with Ag electrodes
AgNo3 Agaq
No3aq
H 2Ol H aq OH ag
11
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank Electrochemistry
At Cathode: Ag aq
has less discharge potential than H aq
so Ag will be deposited at cathode
Agaq
1e Ag s
At Anode: A equivalent amount of Ag will be oxidised to Ag releasing es5
Ag s Agaq
1e
(ii) In AgNo3aq with pt electrodes
1
AgNo3 Agaq
NO3aq1
H 2Ol H aq OH aq
Pt electrodes are inert electrodes so they are not attacked by No31
1
Agaq
1e Ag s
At Anode: out of NO31 and OH ions only OH ions will be oxidised due to less discharge
potential No31 will remain in Solu.
OH aq
1e OH
4OH 2H 2Ol O2 g
O2 g is liberated at anode. Soln. becomes acidic due to presence of HNO3
2.
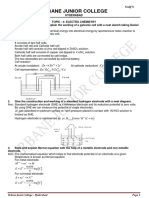
Describe Daniel Cell.
Ans: 1. Anodic half cell Zn electrode dipping in 1M ZnSo4 solu.
2. Cathodic half cell Cu electrode dipping in 1M CuSo4 solu.
3. The 2 soluns. Are connected by Salt Bridge a inverted U tube (glass) filled with agaragar+KCl or KNo3 or NH 4 No3 and connecting wires with voltameter.
4. Cell rxns.
1
anodic rxn Zn 2e Zn2
2
1
Cathodic rxn Cu 2 2e Cu 0
2
Overall cell rxn. Zn Cu 2 Zn2 Cu 0
5. Cell Notation Zn s ZnSO4 1M CuSO4 1M Cus
Current flow
6. Due to overall redox. rxn. A potential of 1.1 volts is developed which is the emf of Daniel cell.
12
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank Electrochemistry
3.
How is E 0 of Mg 2 mg determined.
Ans: 1. To determine E 0 of Mg 2 Mg electrochemical cell is set up.
2. Mg in 1M MgSo4 is coupled with SHE
3. Anodic
1
1
cell Mg electrode in 1 M .MgSo4 Cathodic
cell = SHE
2
2
4. The deflection of Voltameter placed in cell circuit is towards Mg which indicate direction of
current flow.
5. Cell Notation is
Mg s MgSo4 1M Hcl 1 M H 2 1atom Pt15
0
6. Reading given by Voltameter gives Ecell
0
0
0
Ecell
Ecathode
Eanode
E 0
H
H
1 2
E 0 Mg 2
E 0cell 0 E 0 Mg 2
4.
Mg
Mg
Give eqns. for recharging of Pb storage battery.
Ans: 1. During recharging Pb battery acts like an electrolytic cell.
2. Electrical energy is supplied from external source and electrode rxns. are reverse of
discharging.
13
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank Electrochemistry
2
PbSo4 s 2e Pb s SO4aq
2
PbSo4 s 2H 2 ol Pbo2 s SO4aq
4H aq
2e
2
2So4aq
Overall rxn. 2PbSo4 s 2H 2 ol Pb s PbO2 s 4H aq
3. Recharging is possible because PbSo4 s sticks to electrodes and it can lose or gain electrons
during recharging.
5.
Describe a Dry cell
Ans: 1. In a dry cell Anode Zn container,
Cathode = graphite rod and electrolyte =
paste of C Mno2 NH 4Cl ZnCl2
2. Cell Notation
2
Zn s Znaq
NH 4aq C s
3. Cell rxns.
At Anode Zn s 2e Zn2
2
Mn2O3 s 2 NH 4 aq
At Cathode 2 Mno2 s 2 NH 4aq Znaq
2
Overall rxn Zn s 2MnO2 s 2 NH 4aq Znaq MnO3 s 2 NH3aq H 2O
4. emf of dry cell = 1.5 V
6.
Explain electro chemical theory of corrosion.
Ans: 1. During rusting oxidative degradation of Fe occurs due to environmental factors
2. In presence of impurities and moisture Fe in air develops many electrochemical cells on its
surface.
3. At anode 2Fe Fe2 4e
At cathode O2 4H 4e 2H 2O
Overall rxn. 2Fe O2 4H 2Fe2 2H 2O
4. Ferrous ion is oxidised to ferric ions which with moisture form hydrated Ferric oxide
Fe2O3 x H 2O Rust
4Fe2 O2 4H 2O 2Fe2O3 8H
Fe2O3 xH 2O Fe2O3 xH 2O
7.
0
025V and
Calculate emf of cell Cr Cr 3 1x103 M Ni 2 1x104 M Ni at 25 C if ENi
2
/ Ni
0
ECr
3 Cr 0.74V
Ans: Anode = Cr Cathode = Ni
0
0
Eanode
E 0 cell = Ecathode
0.25 0.74 0.49 V
14
PU12 Chemistry Question Bank Electrochemistry
8.
What are the precaution to be taken while measuring conductivity of solutions.
Ans: 1. Conductivity water must be used to make electytic solutions.
2. Platinised Pt electrodes are used to prevent polarisation effects.
3. DC should not be used since DC caused electrolysis and products of electrolysis will
accumulate at electrodes and change in electrolyte concentration will result in polarisation.
Therefore only AC should be used.
4. Since AC is used DC galvanometer cannot be used for Null point detection, So telephone head
is used as Null point detection.
5. Temperature must be kept constant throughout the experiment.
9.
The SRP of Al and Cu are 1.66 V and +0.34 V respectively. What will be the emf and of a cell
having those electrodes under standard conditions. Write cell reaction and cell notation.
Ans: SRP of Al = -1.66 V Anode
SRP of Cu = - 0.34 V Cathode
10. What is a. Over potential b. Products of electrolysis of aq. NaCl
Ans: a. Over potential some electrochemical process are thermodynamically feasible but
kinetically very slow. At lower potential (as voltage) process does not occur. An extra potential or
over voltage has to be applied for liberation of gasses products. Over voltage may that SEP has to
applied. The extra voltage needed for gases liberation is called over potential. For metals voltage
for deposition at cathode is = SEP
b. NaCl Na Cl , H 2O H OH
1
At Anode H 2O O2 2H 2e1 O2 g
2
At Cathode between Na H H has high SRP
2H 2O 2e R H 2 2OH
H 2 g is
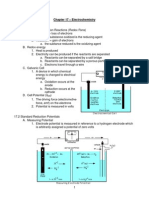
11. Describe working and construction of SHE
Ans: Standard hydrogen cathode is used as reference electrode. Its
electrode potential as 0.00 volts. Hydrogen electrode consists of
Platinum wire coated with finely divided platinum black. Which
forms the cathode which is dipped in HCl (1 M) solution. Pure
hydrogen gas at 1 atm per is bubbled through it. There exists an
equilibrium between H ions and H 2 gas. Platinum catalyses the
reaction.
2Heq
H g
2H 2e H 2 g
Is the reaction at positive electrode. (Cathode)
15
You might also like
- 1006 6T 132.7 HP PerkinsDocument2 pages1006 6T 132.7 HP PerkinsHendra100% (1)
- Investigational New Drug Application INDDocument3 pagesInvestigational New Drug Application INDAnaghesh MuruliNo ratings yet
- Delphi E3 Unit Injector PDFDocument2 pagesDelphi E3 Unit Injector PDFAlex Pakito100% (1)
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3Document16 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3Kingro SimNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Imp Ch3 1Document5 pages12 Chemistry Imp Ch3 1Sneha saviousNo ratings yet
- Questions - Answers Bank Class - Xii Subject - Chemistry UNIT-3 (Electrochemistry)Document6 pagesQuestions - Answers Bank Class - Xii Subject - Chemistry UNIT-3 (Electrochemistry)Abhay BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Vba For A ChapterDocument43 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Vba For A ChapterGaneshNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ElectrochemistryDocument14 pagesUnit 3 ElectrochemistrySuresh Dasaraddi100% (1)
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 02 PDFDocument9 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 02 PDFamanNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 02 PDFDocument9 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 02 PDFamanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemitry FinalDocument29 pagesElectrochemitry FinalGGEZNo ratings yet
- Notes Chem NewDocument17 pagesNotes Chem Newilias1973No ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument80 pagesElectrochemistryNitin NishantNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument12 pagesDepartment of Chemical EngineeringSheikh AliNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Project (Electochemistry)Document10 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Project (Electochemistry)Raghvendra Pandey0% (1)
- ElectroDocument13 pagesElectrodulalsushant3No ratings yet
- 6 2020 06 14!03 08 19 PM PDFDocument13 pages6 2020 06 14!03 08 19 PM PDFraj kamal pandeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Introduction of ElectrochemistryDocument29 pagesChapter One: Introduction of ElectrochemistryBayan O. Abu SaadaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Questions AnswersDocument14 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Questions AnswersDivyansh Rana100% (1)
- Electochemistry PDFDocument29 pagesElectochemistry PDFAnshu KarmacharyaNo ratings yet
- Thermal & Chemical Effect of Current (Notes)Document8 pagesThermal & Chemical Effect of Current (Notes)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- 2marks QuestionDocument7 pages2marks QuestionjranjithsinghNo ratings yet
- Electro ChemistryDocument2 pagesElectro Chemistryradhikanaveen60No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - ElectrochemistryDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - ElectrochemistryMADHAVNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument4 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYSAIRAJ PRABHAKAR PAWARNo ratings yet
- Thermal & Chemical Effect of Current (Notes)Document8 pagesThermal & Chemical Effect of Current (Notes)devansh dewanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Neet - Chem-Electro-KerthanaDocument12 pagesElectrochemistry: Neet - Chem-Electro-KerthanaManickam GnanashekaranNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Key Concepts: RT C D E E NF A BDocument6 pagesElectrochemistry Key Concepts: RT C D E E NF A BRohit ReddyNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical-Cells Kec PDFDocument10 pagesElectrochemical-Cells Kec PDFsachinNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument17 pagesElectrochemistryAbhianv GuptaNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument58 pagesElectrochemistryWatan SahuNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument5 pagesElectrochemistrydanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry &batteries 2018Document52 pagesElectrochemistry &batteries 2018santhoshNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument18 pagesChemistry Projectom dahale92% (26)
- NotesDocument20 pagesNotesP I X Ξ LNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument20 pagesNotesP I X Ξ LNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Electrochemical CellsDocument16 pagesElectrochemistry: Electrochemical CellsRichie JacobNo ratings yet
- Fuel CellDocument27 pagesFuel CellGallium TNo ratings yet
- Engineering ChemistryDocument64 pagesEngineering ChemistryPRABHANJANNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Backbencher - ClubDocument16 pagesModule 1 Backbencher - ClubKUNALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - ElectrochemistryDocument38 pagesChapter 2 - Electrochemistrysoodritwik3No ratings yet
- Electrochemical Energy: Unit 2. Matter and Energy: CDocument43 pagesElectrochemical Energy: Unit 2. Matter and Energy: CMayNo ratings yet
- Chem InvestigatoryDocument3 pagesChem InvestigatoryManan SethiNo ratings yet
- University of The South Pacific EMFDocument6 pagesUniversity of The South Pacific EMFKartik PillayNo ratings yet
- My IpDocument12 pagesMy IpMSD PrajwalNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgment: Electrochemical CellDocument12 pagesAcknowledgment: Electrochemical CellMSD PrajwalNo ratings yet
- Chem 17Document9 pagesChem 17Adi SoNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM Q4 Module 6 PDFDocument17 pagesGEN CHEM Q4 Module 6 PDFAnthony CreationNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Gen Chem 2 q4Document17 pagesModule 6 Gen Chem 2 q4Hazel EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Class 12Document6 pagesElectrochemistry: Class 12manaviNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 3 ElectrochemistryDocument17 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 3 ElectrochemistryRavi Kumar50% (4)
- MODULE 2 ElectrochemistryDocument31 pagesMODULE 2 ElectrochemistryChristian Mark De JesusNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: ElectrochemistryDocument14 pagesUnit 5: ElectrochemistryOGEGA KERUBONo ratings yet
- Exam Mid HHHHDocument4 pagesExam Mid HHHHsafNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Lecture NotesDocument28 pagesElectrochemistry Lecture NotesRamesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl ElectroChemistry NotesDocument7 pagesZumdahl ElectroChemistry NotesMalletNjonkemNo ratings yet
- Sr-Chem QB 23-24 - UjcDocument42 pagesSr-Chem QB 23-24 - Ujcunitedrj.hgpNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Reference ElectrodesDocument26 pagesChapter Four Reference ElectrodesBayan O. Abu SaadaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Short NotesDocument5 pagesElectrochemistry Short Notestukutanigel423No ratings yet
- Chemistry Test - Chapter 1Document4 pagesChemistry Test - Chapter 1ameena-11173No ratings yet
- Chapter 1A - ElectrochemistryDocument15 pagesChapter 1A - Electrochemistryniyathi panickerNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstractAnaghesh MuruliNo ratings yet
- 1PU Maths QP Model 2013Document11 pages1PU Maths QP Model 2013Anaghesh MuruliNo ratings yet
- Biotech/Biotechnology Companies in BangaloreDocument14 pagesBiotech/Biotechnology Companies in BangaloreAnaghesh MuruliNo ratings yet
- Gravitation - 14.01 PU - 11: M M D FDocument55 pagesGravitation - 14.01 PU - 11: M M D FAnaghesh MuruliNo ratings yet
- DCFL Speaks: Issue: 16 DT: 16 January 2015Document2 pagesDCFL Speaks: Issue: 16 DT: 16 January 2015Anaghesh MuruliNo ratings yet
- Quality of LifeDocument18 pagesQuality of LifeAnaghesh MuruliNo ratings yet
- Early Phase Clinical ResearchDocument1 pageEarly Phase Clinical ResearchAnaghesh MuruliNo ratings yet
- Oracle Apps-OPM Sample ScriptsDocument19 pagesOracle Apps-OPM Sample ScriptsrradazaNo ratings yet
- 9.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2 InstructionsDocument6 pages9.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2 InstructionsRizky Hoki VoLtagerNo ratings yet
- Jan'22Document13 pagesJan'22eka putriNo ratings yet
- Industrial EthernetDocument3 pagesIndustrial EthernetkemeachakNo ratings yet
- MICOM P442 21 Outputs - Programmable Logic: Input-Opto CouplersDocument5 pagesMICOM P442 21 Outputs - Programmable Logic: Input-Opto CouplersAmal P RaviNo ratings yet
- Guide ResSimDocument21 pagesGuide ResSimrajesh005No ratings yet
- Se 95Document27 pagesSe 95Милен НиновNo ratings yet
- Air ConditionerDocument12 pagesAir Conditionerchris5gNo ratings yet
- Composites: Part A: Ping Zhang, Qiang Li, Yimin XuanDocument7 pagesComposites: Part A: Ping Zhang, Qiang Li, Yimin Xuaneid elsayedNo ratings yet
- Application Form To Register As A Structural Engineer and To Get Listed in The Directory of Structural EngineersDocument5 pagesApplication Form To Register As A Structural Engineer and To Get Listed in The Directory of Structural EngineersDilina HettiarachchiNo ratings yet
- Debugging Package For Motorola 68K Cisc Cpus User'S Manual (Part 1 of 2)Document280 pagesDebugging Package For Motorola 68K Cisc Cpus User'S Manual (Part 1 of 2)Raul BrunoNo ratings yet
- Readme SilentModeDocument2 pagesReadme SilentModeYasirAkdenizNo ratings yet
- Project Coordinator Business Analyst in Charlotte NC Resume Sean BrandonDocument4 pagesProject Coordinator Business Analyst in Charlotte NC Resume Sean BrandonSeanBrandonNo ratings yet
- Precast FlooringDocument20 pagesPrecast FlooringantonamxNo ratings yet
- R R RoadDocument10 pagesR R RoadvenugopalchintaNo ratings yet
- AS4041 ASME B31 - 3 Pipe Wall ThicknessDocument8 pagesAS4041 ASME B31 - 3 Pipe Wall Thicknesscutefrenzy100% (1)
- Person Responsible For Work CentreDocument5 pagesPerson Responsible For Work CentremanjunathaNo ratings yet
- EIM Load Explanation With An ExampleDocument54 pagesEIM Load Explanation With An ExampleDharani Prasad ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Per Spek TivaDocument17 pagesPer Spek TivaIvana MiloševićNo ratings yet
- The HengeDocument15 pagesThe HengeMirosław TyszkaNo ratings yet
- Cavity WallsDocument4 pagesCavity WallsEma MyzunNo ratings yet
- Pms Color ChartDocument20 pagesPms Color ChartAnaidNo ratings yet
- OMRON - Motion & DrivesDocument64 pagesOMRON - Motion & Drivestanto_deep_15No ratings yet
- Tesa 4204 pv0Document1 pageTesa 4204 pv0dianNo ratings yet
- Design of Free Standing WallsDocument12 pagesDesign of Free Standing Wallssaif.mulla0% (1)
- Excavator MacDocument1 pageExcavator MackarlrossmannNo ratings yet
- Manual Electrico Caravan 97 InglesDocument454 pagesManual Electrico Caravan 97 InglesGermán R VillelaNo ratings yet
- KULIAH4 EC3 Column-Kl PDFDocument27 pagesKULIAH4 EC3 Column-Kl PDFZazliana IzattiNo ratings yet