Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DrugApprovalProcess Infographic
DrugApprovalProcess Infographic
Uploaded by
Susan ZhouCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DrugApprovalProcess Infographic
DrugApprovalProcess Infographic
Uploaded by
Susan ZhouCopyright:
Available Formats
U.S.
Food and Drug Administration
What is a drug as defined by the FDA?
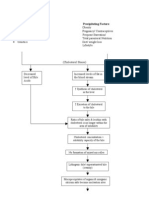
Drug Approval Process
A drug is any product that is intended for use in the diagnosis, cure mitigation, treatment , or
prevention of disease; and that tis intended to affect the structure or any function of the body.
Drug Sponsors Clinical Studies/Trials
Drug Sponsors Discovery and Screening Phase
2
IND Application
Drug Developed
Drug sponsor develops a
new drug compound and
seeks to have it approved
by FDA for sale in the
United States.
SE
D RE ARCH
AN
ER FOR D
NT
RU
CE
FDAs Center for Drug
Evaluation and Research
(CDER) evaluates new drugs
before they can be sold.
The centers evaluation not only prevents quackery, but also
provides doctors and patients the information they need to
use medicines wisely. CDER ensures that drugs, both
brand-name and generic, are effective and their health
benefits outweigh their known risks.
Sponsor must test new
drug on animals for
toxicity. Multiple species
are used to gather basic
information on the safety
and efficacy of the
compound being
investigated/researched.
The sponsor submits an
Investigational New Drug
(IND) application to FDA
based on the results from
intial testing that include,
the drugs composition and
manufacturing, and
develops a plan for testing
the drug on humans.
Animals Tested
LUATIO
EVA
N
P
H
A
S
E
P
H
A
S
E
20 - 80
The typical number of healthy volunteers used in Phase 1; this phase
emphasizes safety. The goal here in this phase is to determine what the
drug's most frequent side effects are and, often, how the drug is
metabolized and excreted.
100s
The typical number of patients used in Phase 2; this phase emphasizes
effectiveness. This goal is to obtain preliminary data on whether the drug works
in people who have a certain disease or condition. For controlled trials, patients
receiving the drug are compared with similar patients receiving a different
treatment--usually a placebo, or a different drug. Safety continues to be
evaluated, and short-term side effects are studied.
At the end of Phase 2, FDA and sponsors discuss how large-scale studies in Phase 3 will be done.
DRUG
SPONSOR
IND REVIEW
FDA reviews the IND to assure
that the proposed studies,
generally referred to as clinical
trials, do not place human
subjects at unreasonable risk of
harm. FDA also verifies that
there are adequate informed
consent and human subject
protection.
P
H
A
S
E
1000s
The typical number of patients used in Phase 3. These studies gather more
information about safety and effectiveness, study different populations and
different dosages, and uses the drug in combination with other drugs.
Page 1
What other drug products are regulated by FDA?
Who reviews new drug submissions?
Drugs include more than just medicines. For example,
fluoride toothpastes, antiperspirants (not deodorant),
dandruff shampoos, and sunscreens are all considered drugs.
A team of CDER physicians, statisticians, chemists, pharmacologists, and other
scientists review the drug sponsors data and proposed labeling of drugs.
FDAs New Drug Application (NDA)Review
FDAs Post-Approval Risk Assessment Systems
FASTER APPROVALS
Drug Labeling
10
FDA reviews the drugs professional labeling
and assures appropriate information is
communicated to health care professionals
and consumers.
Application Reviewed
DAY
60
8-9
11
Facility Inspection
FDA inspects the facilities where
the drug will be manufactured.
After an NDA is received, FDA has 60
days to decide whether to file it so it can
be reviewed. If FDA files the NDA, the
FDA Review team is assigned to evaluate
the sponsors research on the drugs
safety and effectiveness.
The Accelerated Approval program allows
earlier approval of drugs that treat serious
diseases and that fill an unmet medical
need. The approval is faster because FDA
can base the drugs effectiveness on a
surrogate endpoint, such as a blood test
or X-ray result, rather than waiting for
results from a clinical trial.
The Fast Track program helps reduce the
time for FDAs review of products that treat
serious or life-threatening diseases and
those that have the potential to address an
unmet medical need. Drug sponsors can
submit portions of an application as the
information becomes available (rolling
submission) instead of having to wait
until all information is available.
7
6
DRUG
SPONSOR
Review Meeting
FDA meets with a drug sponsor prior to
submission of a New Drug Application.
Because it's not possible to predict all of a drug's effects during clinical
trials, monitoring safety issues after drugs get on the market is critical. The
role of FDAs post-marketing safety system is to detect serious unexpected
adverse events and take definitive action when needed.
Once FDA approves a drug, the
post-marketing monitoring stage begins.
The sponsor (typically the manufacturer)
is required to submit periodic safety
updates to FDA.
www.fda.gov/medwatch
(800) FDA-1088 (322-1088) phone
(800) FDA-0178 (322-0178) fax
NDA Application
The drug sponsor formally asks FDA to approve
a drug for marketing in the United States by
submitting an NDA. An NDA includes all animal
and human data and analyses of the data, as
well as information about how the drug
behaves in the body and how it is
manufactured.
P
H
A
S
E
12
Drug Approval
FDA reviewers will approve
the application or issue a
response letter.
FDAs MedWatch voluntary system makes it
easier for physicians and consumers to report
adverse events. Usually, when important new
risks are uncovered, the risks are added to the
drug's labeling and the public is informed of
the new information through letters, public
health advisories, and other education. In
some cases, the use of the drug must be
substantially limited. And in rare cases, the
drug needs to be withdrawn from the market.
Since the PDUFA was passed in 1992, more
than 1,000 drugs and biologics have come to
the market, including new medicines to treat
cancer, AIDS, cardiovascular disease, and
life-threatening infections.
PDUFA has enabled the Food and Drug Administration to bring access to new drugs as fast or faster
than anywhere in the world, all while maintaining the same thorough review process. Under PDUFA,
drug companies agree to pay fees that boost FDA resources, and FDA agrees to time frames for its
review of new drug applications.
Page 2
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Frca Final Guide PDFDocument8 pagesFrca Final Guide PDFSuhas KapseNo ratings yet
- Dialysis DrugsDocument56 pagesDialysis DrugsrxdocNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionKathleen Dimacali100% (2)
- 14.2 Checklist - Newborn ResuscitationDocument4 pages14.2 Checklist - Newborn ResuscitationSrishti Goel75% (4)
- AL Molecular Diagnostic Laboratory Inc.: Comments: Important NoticeDocument2 pagesAL Molecular Diagnostic Laboratory Inc.: Comments: Important NoticeMarco Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- BCS-Based Biowaivers: A Regulatory Tool For Streamlined Drug DevelopmentDocument1 pageBCS-Based Biowaivers: A Regulatory Tool For Streamlined Drug DevelopmentmagicianchemistNo ratings yet
- United States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0073806 A1Document30 pagesUnited States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0073806 A1magicianchemistNo ratings yet
- Clinical Microbiology Newsletter: Genexpert Testing: Applications For Clinical Microbiology, Part IDocument5 pagesClinical Microbiology Newsletter: Genexpert Testing: Applications For Clinical Microbiology, Part ImagicianchemistNo ratings yet
- Infra-Red Spectrum.: Principal Peaks at Wavenumbers 1709, 1435, 1226, 997 CM (KBR Pellet)Document1 pageInfra-Red Spectrum.: Principal Peaks at Wavenumbers 1709, 1435, 1226, 997 CM (KBR Pellet)magicianchemistNo ratings yet
- IodometryDocument2 pagesIodometrymagicianchemistNo ratings yet
- Postdoctoral Positions INDICASATDocument1 pagePostdoctoral Positions INDICASATmagicianchemistNo ratings yet
- MultinationalsDocument1 pageMultinationalsmagicianchemistNo ratings yet
- Ich Q2BDocument6 pagesIch Q2BmagicianchemistNo ratings yet
- GC Column Selection Guide SUPELCODocument24 pagesGC Column Selection Guide SUPELCOmagicianchemistNo ratings yet
- GC Liners InsertsDocument4 pagesGC Liners InsertsmagicianchemistNo ratings yet
- GC Column Selection Guide SUPELCODocument24 pagesGC Column Selection Guide SUPELCOmagicianchemistNo ratings yet
- F I DNotesDocument10 pagesF I DNotesmagicianchemistNo ratings yet
- Derivatives For HPLC AnalysisDocument68 pagesDerivatives For HPLC Analysismagicianchemist0% (1)
- Derivatización Por Dansyl o DabsylDocument13 pagesDerivatización Por Dansyl o DabsylmagicianchemistNo ratings yet
- Electron Capture Detector Is Used For Halogens (CL, F, BR, and I)Document7 pagesElectron Capture Detector Is Used For Halogens (CL, F, BR, and I)magicianchemistNo ratings yet
- Thermocouple S NotesDocument4 pagesThermocouple S NotesmagicianchemistNo ratings yet
- Flame Thermionic Detectors Are Used For Organic Nitrogen and Phosphorus CompoundsDocument9 pagesFlame Thermionic Detectors Are Used For Organic Nitrogen and Phosphorus CompoundsmagicianchemistNo ratings yet
- Platinum Sensors: Temperature Feedback To The Heater Control CircuitDocument4 pagesPlatinum Sensors: Temperature Feedback To The Heater Control CircuitmagicianchemistNo ratings yet
- Washington - Medical Apartheid Ch4Document8 pagesWashington - Medical Apartheid Ch4Kyung Hee YounNo ratings yet
- A Beautiful Mind (Movie Analysis) - GARBOSA, RMDocument2 pagesA Beautiful Mind (Movie Analysis) - GARBOSA, RMRej GarbosaNo ratings yet
- NCM119ClinicalLab Pediatric Ward Pneumonia Case Study Group 4Document40 pagesNCM119ClinicalLab Pediatric Ward Pneumonia Case Study Group 4Allysa MacalinoNo ratings yet
- Hernia: Information For PatientsDocument2 pagesHernia: Information For Patientsrianrifaldi123_98497No ratings yet
- Jordanian Medical LSKDocument96 pagesJordanian Medical LSKAlaor LopesNo ratings yet
- Platelet Rich Plasma (Hassett, Sheryl A, R.N.)Document2 pagesPlatelet Rich Plasma (Hassett, Sheryl A, R.N.)DariusNo ratings yet
- Lopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgDocument2 pagesLopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgAdrianne Bazo100% (2)
- Exercise For Sciatic Pain From Piriformis SyndromeDocument3 pagesExercise For Sciatic Pain From Piriformis SyndromeFaizul Haque100% (1)
- NablDocument46 pagesNablGupta AtulNo ratings yet
- CPT ChecklistDocument3 pagesCPT ChecklistMa. Angelica Alyssa RachoNo ratings yet
- Medication ErrorsDocument2 pagesMedication ErrorsFahad AlkenaniNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat Multiple StrengthDocument2 pagesDaftar Obat Multiple StrengthCharles Nong MakingNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood Type Incompatibilty (Super Final)Document58 pagesABO Blood Type Incompatibilty (Super Final)Marc Michael Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- High Risk HPVDocument6 pagesHigh Risk HPVjawaralopangNo ratings yet
- Dog Bites As A Zoonotic Risk in Ecuador Need For The Implementation of A One Health Approach 2023Document6 pagesDog Bites As A Zoonotic Risk in Ecuador Need For The Implementation of A One Health Approach 2023Ayu Anggreny Layang DongaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Hypertension: Annals of Internal MedicinetDocument16 pagesPulmonary Hypertension: Annals of Internal MedicinetAlicia TGNo ratings yet
- Doctor and Clinical AssistantsDocument2 pagesDoctor and Clinical AssistantsIvan DwiputraNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Topic: Anatomy and Physiology of The Kidneys and The Urinary Tract/ Acute and Chronic Renal FailureDocument4 pagesWeek 1 Topic: Anatomy and Physiology of The Kidneys and The Urinary Tract/ Acute and Chronic Renal FailureMaikka IlaganNo ratings yet
- Killer Covid-19 - PARODIA E RAP-SODIA DI UN DELIRANTE COMPLOTTISTA PDF - EPUb by Kolbe Fabrizio Gregori - Probukdw243 PDFDocument59 pagesKiller Covid-19 - PARODIA E RAP-SODIA DI UN DELIRANTE COMPLOTTISTA PDF - EPUb by Kolbe Fabrizio Gregori - Probukdw243 PDFJack Daniel BristowNo ratings yet
- Neonatal SepsisDocument20 pagesNeonatal SepsisJustine Nyangaresi100% (1)
- BP Chart Boys Color WideDocument1 pageBP Chart Boys Color WidealbertNo ratings yet
- 2+ Years: PECARN Pediatric Minor Head Injury CT Guidelines For Children AgeDocument2 pages2+ Years: PECARN Pediatric Minor Head Injury CT Guidelines For Children AgeIna AguilarNo ratings yet
- Rekap List Produk E Cataloge PT AAM 2024Document15 pagesRekap List Produk E Cataloge PT AAM 2024harianto saidNo ratings yet
- Styrene Toxicological Overview: Key PointsDocument10 pagesStyrene Toxicological Overview: Key PointsanirudhNo ratings yet
- Chole Lithia Sis Path oDocument6 pagesChole Lithia Sis Path ogeloNo ratings yet