Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Some Handy Integrals: - Ax - Ax - Ax - Ax - Ax - Ax
Uploaded by
walaaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Some Handy Integrals: - Ax - Ax - Ax - Ax - Ax - Ax
Uploaded by
walaaCopyright:
Available Formats
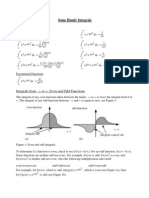
Some Handy Integrals
Gaussian Functions
1
0 eax2 dx = 2 a
1
0 x2 eax2 dx = 4a a
3
0 x4 eax2 dx = 8a2 a
135(2n1)
0 x2n eax2 dx =
a
2n+1an
1
dx = 2a
0 x eax
1
2a2
1
0 x5 eax2 dx = a3
n! 1
0 x2n+1 eax2 dx = 2 an+1
0 x3 eax
dx =
Exponential Functions
n!
0 xn eax dx = n+1
a
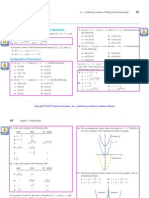
Integrals from - to : Even and Odd Functions
The integral of any even function taken between the limits - to is twice the integral from 0 to
. The integral of any odd function between - and is equal to zero, see Figure 1.
even
y
odd
0
x
integrals cancel
integrals add
2
(a). f(x) = eax
(b). [g(x) f(x)] = x eax
even
odd*even
Figure 1. Even and odd integrals.
To determine if a function is even, check to see if f(x) = f(-x). For an odd function, f(x) = f(-x).
Some functions are neither odd nor even. For example, f(x) = x is odd, f(x) = x2 is even, and
f(x) = x + x2 is neither odd nor even. The following multiplication rules hold:
even*even = even
odd*odd =even
odd*even = odd
Consider the integral of f(x) = eax , Figure 1a. The function is even so that - = 20 . Next
2
consider g(x) = x, which is odd, giving [g(x) f(x)] = x eax as overall odd (Figure 1b). The
integral is zero for the product function.
2
Colby College
You might also like
- Integration TechniquesDocument18 pagesIntegration Techniquesஏம்மனுஎல்லெ செலேச்டினோNo ratings yet
- Integral CalculusDocument25 pagesIntegral CalculusCarl Kristopher PeloniaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Magic of Definite IntegralDocument88 pagesMagic of Definite IntegralsagarNo ratings yet
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Solution Exercises 2011 PartIDocument27 pagesSolution Exercises 2011 PartIcecch001100% (1)
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Shape FunctDocument46 pagesShape FunctKashmir JamadarNo ratings yet
- 05 FiniteElementMethodDocument83 pages05 FiniteElementMethodmileNo ratings yet
- Formule Trigonometrice Derivarea Si Integrarea Functiilor CompuseDocument2 pagesFormule Trigonometrice Derivarea Si Integrarea Functiilor Compusekissu_diana281No ratings yet
- Some Handy Integrals: - Ax - Ax - Ax - Ax - Ax - AxDocument1 pageSome Handy Integrals: - Ax - Ax - Ax - Ax - Ax - Axlantea1No ratings yet
- Integrals ListDocument1 pageIntegrals ListSunil AnandNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.4Document21 pagesUnit 1.4Ayanda CebekhuluNo ratings yet
- Factorial of Negative One HalfDocument2 pagesFactorial of Negative One HalfBen HallNo ratings yet
- MANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction To Finite Elements: Shape Functions in 1DDocument29 pagesMANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction To Finite Elements: Shape Functions in 1DSanapala AmitNo ratings yet
- Chpt05-FEM For 2D SolidsnewDocument56 pagesChpt05-FEM For 2D SolidsnewKrishna MyakalaNo ratings yet
- Theory Definite Integrals PDFDocument35 pagesTheory Definite Integrals PDFvaranasilkoNo ratings yet
- Integration Formulas: 1. Common IntegralsDocument10 pagesIntegration Formulas: 1. Common IntegralsSharathBanakarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19 MMP-IIDocument6 pagesLecture 19 MMP-IISharmeen IqrazNo ratings yet
- Math 1Document86 pagesMath 1Naji ZaidNo ratings yet
- Instructor Dr. Karuna Kalita: Finite Element Methods in Engineering ME 523Document40 pagesInstructor Dr. Karuna Kalita: Finite Element Methods in Engineering ME 523Nitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Schrodinger Equation and Particle in A BoxDocument14 pagesSchrodinger Equation and Particle in A BoxDaniGlamNo ratings yet
- MAT 1 Week 2Document16 pagesMAT 1 Week 2AQUA JUICENo ratings yet
- CH 1 Functions 2Document15 pagesCH 1 Functions 2Mohammed GhallabNo ratings yet
- DX X F I or A: Numerical Analysis Ch.3: Numerical IntegrationDocument16 pagesDX X F I or A: Numerical Analysis Ch.3: Numerical Integrationابراهيم حسين عليNo ratings yet
- Math Analysis Lecture 3 2022Document16 pagesMath Analysis Lecture 3 2022ERRICK MCKOLENo ratings yet
- MANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction To Finite Elements: Shape Functions in 1DDocument29 pagesMANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction To Finite Elements: Shape Functions in 1DPrayag ParekhNo ratings yet
- Formulae,,key Points,, Algorithm (For Class 12 TH Maths)Document23 pagesFormulae,,key Points,, Algorithm (For Class 12 TH Maths)angusingh60No ratings yet
- Section 2 Basic Properties of FunctionDocument4 pagesSection 2 Basic Properties of FunctionIbrahim HasanovNo ratings yet
- Tcu11 01 05exDocument0 pagesTcu11 01 05exJagathisswary SatthiNo ratings yet
- MANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction To Finite Elements: Prof. Suvranu deDocument40 pagesMANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction To Finite Elements: Prof. Suvranu devenky364No ratings yet
- Module 3: Element Properties Lecture 8: Numerical Integration: One DimensionalDocument5 pagesModule 3: Element Properties Lecture 8: Numerical Integration: One DimensionalChethan .H.GNo ratings yet
- 2014 2 SARAWAK SMKStJoseph Kuching MATHS QADocument11 pages2014 2 SARAWAK SMKStJoseph Kuching MATHS QASK100% (3)
- Math Paper 3 Practice MSDocument47 pagesMath Paper 3 Practice MSRaahish KalariaNo ratings yet
- The Complex Inverse Trigonometric and Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument11 pagesThe Complex Inverse Trigonometric and Hyperbolic Functionscocomluis135790No ratings yet
- Appendix: Physical Constants and Mathematical RelationsDocument9 pagesAppendix: Physical Constants and Mathematical RelationsMarta HenriquesNo ratings yet
- Integration Formulas: 1. Common IntegralsDocument5 pagesIntegration Formulas: 1. Common IntegralssiegherrNo ratings yet
- Salcedo Part1Document5 pagesSalcedo Part1Carlos SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 Integration by PartsDocument4 pagesActivity No. 1 Integration by PartsrymacNo ratings yet
- Special Functions Supported by EasycalcDocument5 pagesSpecial Functions Supported by EasycalcMichael TaylorNo ratings yet
- Calculus of Variations ExamplesDocument7 pagesCalculus of Variations ExamplesBrianWeathersNo ratings yet
- Gammafunction 140928120556 Phpapp01Document45 pagesGammafunction 140928120556 Phpapp01G Nathan JdNo ratings yet
- Ial Maths fp3 Ex4fDocument37 pagesIal Maths fp3 Ex4fRafael Perez GuardiolaNo ratings yet
- Answers: E.G. Uv + VuDocument2 pagesAnswers: E.G. Uv + VuTubocurareNo ratings yet
- MANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction To Finite ElementsDocument42 pagesMANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction To Finite ElementsvishnugopalSNo ratings yet
- Ordinary, Singular Points, Power SeriesDocument19 pagesOrdinary, Singular Points, Power SeriesDhruv PathakNo ratings yet
- Discretization-Finite Difference, Finite Element Methods: D Dy Ax BX DX DX Dy DX Dy Ax A DXDocument6 pagesDiscretization-Finite Difference, Finite Element Methods: D Dy Ax BX DX DX Dy DX Dy Ax A DXratchagar aNo ratings yet
- 4 Node QuadDocument7 pages4 Node QuadSachin KudteNo ratings yet
- Inequalities تاحجارتملا: InequalityDocument31 pagesInequalities تاحجارتملا: Inequalityمهند محسن مخيلفNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Double and Triple Integrals Solutions Math 13, Spring 2010Document8 pagesExercises: Double and Triple Integrals Solutions Math 13, Spring 2010Colls MuntadaNo ratings yet
- Matrix Review SlidesDocument20 pagesMatrix Review SlidesFernando Sosa LopezNo ratings yet
- 27 2 Mult Ints Non RCTNGLR RgnsDocument21 pages27 2 Mult Ints Non RCTNGLR RgnsDaniel SolhNo ratings yet
- 5.periodic FunctionDocument7 pages5.periodic FunctionAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Solutions CHAPTER 1, Levine, Quantum Chemistry, 5Document1 pageProblem Set Solutions CHAPTER 1, Levine, Quantum Chemistry, 5Marcos ViníciusNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet