Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vibrating Sample Magnetometer: Safety First
Vibrating Sample Magnetometer: Safety First
Uploaded by
Areef BillahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vibrating Sample Magnetometer: Safety First
Vibrating Sample Magnetometer: Safety First
Uploaded by
Areef BillahCopyright:
Available Formats
Vibrating Sample Magnetometer Home Page
Vibrating Sample Magnetometer
SWT Physics Department
SAFETY FIRST
Turn on the equipment ONLY in the order specified.
Failure to cool the vibration exciter during operation will lead to a system meltdown!
VSM PRINCIPLES
A vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) operates on Faraday's Law of Induction, which tells
us that a changing magnetic field will produce an electric field. This electric field can be
measured and can tell us information about the changing magnetic field. A VSM is used to
measure the magnetic behavior of magnetic materials.
For more information on magnetic properties and hysteresis curves, go to the Kerr
Magnetometer page.
A VSM operates by first placing the sample to be studied in a constant magnetic field. If the
sample is magnetic, this constant magnetic field will magnetize the sample by aligning the
magnetic domains, or the individual magnetic spins, with the field. The stronger the constant
field, the larger the magnetization will be. The magnetic dipole moment of the sample will
create a magnetic field around the sample, sometimes called the magnetic stray field. As the
sample is moved up and down, this magnetic stray field is changing as a function of time and
can be sensed by a set of pick-up coils.
The alternating magnetic field will cause an electric field in the pick-up coils according to
Faraday's Law of Induction. This current will be proportional to the magnetization of the
sample. The greater the magnetization, the greater the induced current.
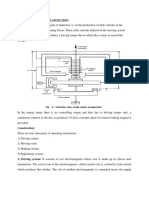
The induction current is amplified by a transimpedance amplifier and lock-in amplifier. The
various components are hooked up to a computer interface. Using controlling and monitoring
software, the system can tell you how much the sample is magnetized and how its
magnetization depends on the strength of the constant magnetic field. A typical measurement
of a sample is taken in the following manner:
the strength of the constant magnetic field is set.
file:///D|/manuals/vsm/vsm.htm (1 of 5)5/22/2006 5:48:24 AM
Vibrating Sample Magnetometer Home Page
the sample begins to vibrate
the signal received from the probe is translated into a value for the magnetic moment of
the sample
the strength of the constant magnetic field changes to a new value. no data is taken
during this transition
the strength of the constant magnetic field reaches its new value
the signal from the probe again gets translated into a value for the magnetization of the
sample
the constant magnetic field varies over a given range, and a plot of magnetization (M)
versus magnetic field strength (H) is generated.
PARTS OF THE VSM
The VSM consists of ten parts:
water cooled electromagnet and power supply
vibration exciter and sample holder (with angle indicator)
sensor coils
Hall probe
amplifier
control chassis
lock in amplifier
meter
computer interface
Water cooled electromagnet and power supply
The water cooled electromagnet, along with the power supply, generate the constant magnetic
field used to magnetize the sample.
Vibration exciter and sample holder (with angle indicator)
The sample holder rod is attached to the vibration exciter, and the end of it hangs down in
between the pole pieces. The exciter moves the sample up and down at a set frequency,
typically 85Hz. The sample rod can be rotated to achieve the desired orientation of the sample
to the constant magnetic field. There are also three knobs for controlling the x,y, and z
positions of the sample.
Sensor coils
The sample produces an alternating current in these coils at the same frequency as the
file:///D|/manuals/vsm/vsm.htm (2 of 5)5/22/2006 5:48:24 AM
Vibrating Sample Magnetometer Home Page
vibration of the sample. The signal generated contains the information about the
magnetization of the sample.
Amplifier
The amplifier does just that - amplifies the signal created by the sensor coils.
Control chassis
This controls the 85Hz oscillation of the exciter.
Lock in amplifier
This amplifier is tuned to pick up only signals at the vibrating frequency. This eliminates noise
from the environment, such as from the overhead lights or hovering spacecraft nearby (unless
the noise happens to be an 85Hz signal).
Meter
This is used to measure something important.
Computer Interface
The software makes data collection easier by automating the control of the various
components during data collection. The data can be graphed and plotted on the printer.
VSM OPERATION PROCEDURES
Mounting the sample
Place a small amount of rubber cement on the back of the sample
Attach the sample to one of the rods, depending on how the measurement is to
be taken
Stand the rod upright in the metal can on the counter and allow the cement to dry
for about 10 minutes
Turning on the system
Turn on the DI (deionized) water supply.
It is located at the back of the room on
the floor. Turn the red handle and let the water run through the system and into
the sink. WAIT FOR THE WATER TO FLOW INTO THE SINK BEFORE DOING
ANYTHING ELSE.
Turn on the power supply to the electromagnets. It is the large blue box behind
the electromagnetic coils.
file:///D|/manuals/vsm/vsm.htm (3 of 5)5/22/2006 5:48:24 AM
Vibrating Sample Magnetometer Home Page
Turn on the SS250 amplifier. This is the one at the bottom of the rack on the
computer desk.
Turn on the control chassis ( in the middle of the rack)
Turn on the lock in amplifier
Turn on the Beckman Voltmeter.
Place it in the 20V DC range
Turn on the computer, then the plotter.
Running the computer software
Enter the password
Type "Win" at the prompt
At the "READY TO ROLL" window, click OK.
The measurement software should
load automatically.
Double click on the "Manual setup" icon at the left hand bottom corner of the
screen.
In the "Commands" section of the pop-up window, click on "Setup"
In the "9600 Environment Setup" window,
make the following changes:
Curve type = Hysteresis
MASS Sample Mass = 6.48E-02 g
DEN Sample Density = 5.00E0 g/cc
*HRG Field Range = 1.00E04 Oe
AVERAGE = Disabled
SYNTHESIZE = Disabled
TEST SPEED = Quick
*BRG Induction Range = 1.00E01 Oe
*VIB Vibration Toggle = Off
*TC Time Constant = 0.1s
Peak Field = 5000 Oe
Click OK
Calibration
Carefully attach the Ni rod to the VSM
Under "Setup", make the following changes:
Test Speed = Quick
Induction Range = 10 emu
Peak Field = 5,000 Oe
Field Range = 10,000 Oe
Time Constant = 0.1 sec
Under "Set", make the following changes:
Field = 5,000 Oe
Vibration = On
Optimization
Use the top most knob on the right side of the VSM to adjust the left-right
orientation of the sample with respect to the Hall probe. Find the maximum
attainable value for M.
file:///D|/manuals/vsm/vsm.htm (4 of 5)5/22/2006 5:48:24 AM
Vibrating Sample Magnetometer Home Page
Use the small knob on the front of the machine to adjust the front-back orientation
of the sample with respect to the Hall probe. Find the maximum attainable value
for M.
Use the large knob to adjst the vertical position of the sample with respect to the
Hall probe. Find the maximum value attainable for M.
Calibrating the Lock-In amplifier
After optimization, m should be 3.55-3.56 for the Ni sample. If not, then:
Use the small calibration screw driver to adjust the small calibration pot
(potentiometer) on the Lock-In amplifier.
Verify the calibration by rotating the Quadrant knob through each position:
Quadrant I: M=3.55
Quadrant II: M=0
Quadrant III: M= -3.55
Quadrant IV: M=0
If any of the values are different than listed, use the small Phase Knob to
set them to the prescribed values
Run a quick measurement to verify the calibration by clicking on "Sample" then
"Curve"
The system is now calibrated.
Taking a measurement
Replace the Ni calibration rod with the sample to be measured.
Use the large cylinder on the top of the VSM to rotate the sample such that the
magnetic field passes through the desired axis
If the sample touches either pole face, adjust the sample's right-left
orientation to provide clearance as it rotates.
Center the sample between the pole pieces
Optimize again with a field of 5,000 Oe (see Optimization)
Under "Setup", make the following change:
Induction Range = 0.1emu. Leave all other settings the same.
Under "Set", make the following changes:
Field=5,000 Oe
Vibration=ON
To begin the measurement, click on "Sample", then "Curve".
file:///D|/manuals/vsm/vsm.htm (5 of 5)5/22/2006 5:48:24 AM
You might also like
- Simulation Activity 3 Zener Diode Voltage Regulation G1Document8 pagesSimulation Activity 3 Zener Diode Voltage Regulation G1Brix GarratonNo ratings yet
- Vibrating Sample MagnetometerDocument5 pagesVibrating Sample MagnetometerDhanapal Pal100% (2)
- Manual Takometro MegelliDocument21 pagesManual Takometro MegelliPablo Hernan Acuña25% (4)
- AC Measurements Using The Oscilloscope and Multimeter by Mr. David FritzDocument30 pagesAC Measurements Using The Oscilloscope and Multimeter by Mr. David FritzcsystemsNo ratings yet
- AC MeasurementsDocument30 pagesAC MeasurementsDiegoNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 CombinedDocument24 pagesUnit 6 Combinedbhuvanharish25No ratings yet
- Measurement and Calibration of DynamometerDocument7 pagesMeasurement and Calibration of DynamometerHimanshuKalbandheNo ratings yet
- 4 PDFDocument7 pages4 PDFHimanshuKalbandheNo ratings yet
- Weighing Instruments 1Document43 pagesWeighing Instruments 1Arijit MajumdarNo ratings yet
- 1a MWD Survey MeasurementsDocument22 pages1a MWD Survey MeasurementsAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lab 1: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) : ENGR 1000: Electrical and Computer Engineering ModuleDocument4 pagesLab 1: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) : ENGR 1000: Electrical and Computer Engineering ModuleEvan BurnsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document107 pagesLecture 8sampath bandaraNo ratings yet
- TVL - Ia: Quarter 3 - Module 3Document11 pagesTVL - Ia: Quarter 3 - Module 3Chiarnie LopezNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics Lab: Background InfoDocument11 pagesModern Physics Lab: Background Infojenny_zhou_9No ratings yet
- Microwave Oven: Service ManualDocument25 pagesMicrowave Oven: Service ManualJerry LeeNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material LabDocument44 pagesStrength of Material LabDeepak SahNo ratings yet
- Energy Meter Notes PDFDocument6 pagesEnergy Meter Notes PDFHarshitha BushipakaNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Control Systems LaboratoryDocument34 pagesInstrumentation and Control Systems LaboratoryMara DincoNo ratings yet
- Aqa A Level Physics - Required Practicals: JUNE 2017Document33 pagesAqa A Level Physics - Required Practicals: JUNE 2017LouisNo ratings yet
- Asim4k0r True Rms 4000 Count Digital Multimeter ManualDocument18 pagesAsim4k0r True Rms 4000 Count Digital Multimeter Manualbalcar amilcarNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Measurements: MECH 373Document18 pagesInstrumentation and Measurements: MECH 373RAJANo ratings yet
- Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM)Document33 pagesScanning Probe Microscopy (SPM)ArvindGovaNo ratings yet
- Shock Absorber Test RigDocument14 pagesShock Absorber Test RigShani KumarNo ratings yet
- Making Sense Out of Sensors: Jim Halderman Sinclair Community College Dayton, OhioDocument105 pagesMaking Sense Out of Sensors: Jim Halderman Sinclair Community College Dayton, OhioRandy00000100% (1)
- 1.Strength-of-Materials V+Document36 pages1.Strength-of-Materials V+sriramNo ratings yet
- PMMC DownloadDocument29 pagesPMMC DownloadSaumendra SarangiNo ratings yet
- EQCM TutorialDocument14 pagesEQCM TutorialWalter Ricardo BritoNo ratings yet
- CP 11 - Charging and Discharging CapacitorsDocument4 pagesCP 11 - Charging and Discharging CapacitorsΠIMΣR ҜHURRΔMNo ratings yet
- Tangent GalvanometerDocument3 pagesTangent GalvanometerHawksmoor1888100% (1)
- Lecture2-Instrumentation and MeasurementsDocument34 pagesLecture2-Instrumentation and MeasurementsWali WQNo ratings yet
- Arjun PhysicsDocument22 pagesArjun Physicsarjunsinghbhadoriya7089No ratings yet
- Pec - Ics - Lab ManualDocument49 pagesPec - Ics - Lab ManualHussain ShaikNo ratings yet
- CH2 Measuring InstrumentDocument44 pagesCH2 Measuring Instrumentmuhammadzufayri40No ratings yet
- Study of Capacitive TransducerDocument5 pagesStudy of Capacitive TransducervinodNo ratings yet
- E Beam ManualDocument7 pagesE Beam ManualMarco SalvatoriNo ratings yet
- Fa19-Bee-180 Lab Rep 1 EtcsDocument13 pagesFa19-Bee-180 Lab Rep 1 EtcsRANA AHMADNo ratings yet
- Exp 4Document7 pagesExp 4Kewal Dharamshi100% (1)
- Contact/Non-Contact Tachometer Instruction ManualDocument7 pagesContact/Non-Contact Tachometer Instruction ManualNibin OdukkathilNo ratings yet
- MeasurementsDocument12 pagesMeasurementsRamesh TammineniNo ratings yet
- AC Measuring InstrumentsDocument79 pagesAC Measuring InstrumentsFebby PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Portable X-Ray Unit: 1. Manufacture Company InformationDocument17 pagesPortable X-Ray Unit: 1. Manufacture Company Informationcomphome100% (2)
- Diploma 3 Strength - of - MaterialsDocument26 pagesDiploma 3 Strength - of - MaterialsKumar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 SlidesDocument39 pagesLecture 4 SlidesLogeeshan VelmanickamNo ratings yet
- Experimental ObjectiveDocument17 pagesExperimental Objectivependrive80No ratings yet
- Synchronous MachineDocument34 pagesSynchronous Machinefakeacc04aNo ratings yet
- Sir J C Bose School of Engineering (Diploma: Adv Strength of Materials Lab ManualDocument47 pagesSir J C Bose School of Engineering (Diploma: Adv Strength of Materials Lab ManualdibyenindusNo ratings yet
- Microwave Engineering Labs ManualDocument23 pagesMicrowave Engineering Labs ManualAbrash Khan SikandriNo ratings yet
- 2013 - Multimeter 73794Document3 pages2013 - Multimeter 73794DongelxNo ratings yet
- Automotive Sensors and Actuators PDFDocument61 pagesAutomotive Sensors and Actuators PDFDeepak NaikNo ratings yet
- Atomic Force MicrosDocument29 pagesAtomic Force MicrosHitesh sharmaNo ratings yet
- PMMC MeasurementDocument97 pagesPMMC Measurementkiller raoNo ratings yet
- 4R6Lab1 GM Operation 2017Document3 pages4R6Lab1 GM Operation 2017tarek moahmoud khalifaNo ratings yet
- Buchepalli Venkayamma Subbareddy Engineering College: Microwave & Optical Communication Lab ManualDocument31 pagesBuchepalli Venkayamma Subbareddy Engineering College: Microwave & Optical Communication Lab ManualMalakonda Reddy0% (1)
- Chapter 5Document37 pagesChapter 5Yasser ElshaerNo ratings yet
- Hitachi S-4700 InstructionsDocument19 pagesHitachi S-4700 InstructionssuperheoNo ratings yet
- Kymograph Instruction Manual - HarvardDocument9 pagesKymograph Instruction Manual - HarvardDr. B. HariNo ratings yet
- Delco Radio Owner's Manual Model 633; Delcotron Generator InstallationFrom EverandDelco Radio Owner's Manual Model 633; Delcotron Generator InstallationNo ratings yet
- Boat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaFrom EverandBoat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaNo ratings yet
- 1946 - John Hersey, HiroshimaDocument3 pages1946 - John Hersey, Hiroshimaluke71747100% (1)
- Radio Wave Propagation For Communication and Probing The IonosphereDocument58 pagesRadio Wave Propagation For Communication and Probing The IonosphereRaúl Infante100% (1)
- IPT PresentationDocument12 pagesIPT PresentationSandeep yekkaliNo ratings yet
- The Polynomials AssignmentDocument3 pagesThe Polynomials AssignmentMarc LambertNo ratings yet
- Curtain Wall With HZ & VL Louvers Structural Calculation For Building a-PART (6) at AXIS (34-42) - A'Document59 pagesCurtain Wall With HZ & VL Louvers Structural Calculation For Building a-PART (6) at AXIS (34-42) - A'نصر عبدالسلامNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ROBOTICS: ControlDocument15 pagesIntroduction To ROBOTICS: ControlMANOJ MNo ratings yet
- Steps in Fuzzy Logic EstimationDocument13 pagesSteps in Fuzzy Logic Estimationoloyede_wole3741No ratings yet
- ECSS Q ST 60 12C (31july2008)Document52 pagesECSS Q ST 60 12C (31july2008)jsadachiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Guide CompleteDocument255 pagesEngineering Guide CompleteMohammad RammalNo ratings yet
- Karamba 1 1 0 ManualDocument127 pagesKaramba 1 1 0 ManualLuca ValzanoNo ratings yet
- CulvertsDocument18 pagesCulvertsAmmar A. Ali100% (1)
- Maxwell's EquationsDocument19 pagesMaxwell's EquationsEr Ashish Baheti100% (1)
- Chapter 4: Axial Flow CompressorsDocument12 pagesChapter 4: Axial Flow CompressorsWin Min OoNo ratings yet
- Multivariate ApproximationDocument296 pagesMultivariate ApproximationAlexander GolikovNo ratings yet
- Ch06c EntropyDocument46 pagesCh06c EntropyJoshua ZikuNo ratings yet
- 02 Mineral ProcessingDocument37 pages02 Mineral ProcessingFrancisco Antonio Guerrero MonsalvesNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and Control Techniques For Maximum Energy Harvesting in Photovoltaic Systems.Document1 pagePower Electronics and Control Techniques For Maximum Energy Harvesting in Photovoltaic Systems.BLYNK STEELNo ratings yet
- Section 3A Vector Representation-Euclidean SpaceDocument11 pagesSection 3A Vector Representation-Euclidean SpaceHazwan HamidNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Magazine 2010 03Document78 pagesChemical Engineering Magazine 2010 03Ilia EframovichtNo ratings yet
- Momentum Equation Applied To The Problem of A Propeller in Oblique FlowDocument4 pagesMomentum Equation Applied To The Problem of A Propeller in Oblique FlowKrish FunkNo ratings yet
- Computers and Geotechnics: Dian-Qing Li, Xiao-Hui Qi, Zi-Jun Cao, Xiao-Song Tang, Kok-Kwang Phoon, Chuang-Bing ZhouDocument11 pagesComputers and Geotechnics: Dian-Qing Li, Xiao-Hui Qi, Zi-Jun Cao, Xiao-Song Tang, Kok-Kwang Phoon, Chuang-Bing ZhouDwi Aryanti NingrumNo ratings yet
- New-Problems-Chapter-21 Convective Mass TransferDocument2 pagesNew-Problems-Chapter-21 Convective Mass TransferKhanh NhiNo ratings yet
- Thermal Spray ProcessesDocument15 pagesThermal Spray Processesapi-3766939100% (2)
- Example 24.3-Flexural Strength of Prestressed Member Using Approximate Value For FDocument5 pagesExample 24.3-Flexural Strength of Prestressed Member Using Approximate Value For FUdaya KumarNo ratings yet
- Accelertion Head PDFDocument5 pagesAccelertion Head PDFEng AlfNo ratings yet
- "Derivation" of Canonical DistributionDocument2 pages"Derivation" of Canonical DistributionANDRÉS FELIPE SERRANO BARRIOSNo ratings yet
- Lake and Hirasaki (1981) (SPE-8436-PA)Document10 pagesLake and Hirasaki (1981) (SPE-8436-PA)Anonymous PO7VwbBnNo ratings yet
- J&F Chap3Document20 pagesJ&F Chap3nilamNo ratings yet
- Density, Relative Density (Specific Gravity), and Absorption of Coarse AggregateDocument6 pagesDensity, Relative Density (Specific Gravity), and Absorption of Coarse AggregatemickyfelixNo ratings yet
- Heriot-Watt University: Stage 2Document10 pagesHeriot-Watt University: Stage 2Noel BinoyNo ratings yet