Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Osmosis
Uploaded by
api-296833859Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Osmosis
Uploaded by
api-296833859Copyright:
Available Formats
Osmosis
Osmosis: The net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential to a region
of lower water potential, through a partially permeable membrane, as a result of random motion.
solute + solvent = solution
Water potential: The tendency of water to move out of a solution.
Water always moves down a water potential gradient.
The water potential of pure water at atmospheric pressure is 0.
Water potential depends on two factors:
- How much water the solution contains in relation to solute
The contribution of the concentration of the solution to the water potential is called the
solute potential (the extent to which solute molecules decrease the water potential of the
solution).
The more solute molecules in a solution, the lower the tendency of water to leave the
solution (water potential).
- How much pressure is applied to the solution
The contribution of pressure to the water potential is called the pressure potential.
The higher the pressure, the higher the water potential.
Osmosis
in animals
- If the water potential of the surrounding solution is too low an animal cell will shrink.
- If the water potential of the solution is the same as inside the cell, the cell will remain normal.
- If the water potential of the surrounding solution is too high, water will enter the cell by
osmosis, causing the cell to swell and then burst.
Osmosis in plants
- If the water potential of the surrounding solution is high, water will enter the cell. But, the
strong and rigid cell wall will push back against the expanding protoplast (living part of the
cell) and the pressure will rise rapidly (pressure potential) until the water potential inside and
outside the cell are equal and equilibrium is reached.
- When the cell wall is fully inflated, it is said to be turgid.
- water potential = solute potential + pressure potential
- If the water potential is much lower in the surrounding solution, water will leave the cell by
osmosis, causing the protoplast to shrink until it does not exert any pressure on the cell wall at
all. At this point pressure potential is 0, so water potential = solute potential.
As the protoplast shrinks, it pulls away from the cell wall. This process is called plasmolysis.
The point at which plasmolysis is about to occur and pressure has just reached zero is called
incipient plasmolysis.
You might also like
- Fluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceFrom EverandFluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Water RelationDocument62 pagesWater RelationBlister CountNo ratings yet
- OsmosisDocument3 pagesOsmosisgrace.a.sun18No ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level Biology (5090) : Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument55 pagesCambridge O Level Biology (5090) : Movement Into and Out of CellsMoinuddin SummitNo ratings yet
- 1 Plant Water BalanceDocument36 pages1 Plant Water BalanceOratile SehemoNo ratings yet
- OsmosisDocument19 pagesOsmosisdamyangdcsNo ratings yet
- MOvement in and Out of Cells - Osmosis & Active TransportDocument4 pagesMOvement in and Out of Cells - Osmosis & Active TransportTshepo O MotsemmeNo ratings yet
- Bio 100 - 2Document19 pagesBio 100 - 2Duain Areed MostafaNo ratings yet
- 5-Mechanisms of Active and Pasive Transport Through TheDocument61 pages5-Mechanisms of Active and Pasive Transport Through Thec3rberussNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3diffusion in Living OrganismsDocument10 pagesChapter - 3diffusion in Living OrganismsBoney StephenNo ratings yet
- Unit2 - Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument54 pagesUnit2 - Membrane Structure and FunctionAlbert Chon100% (1)
- UNIT 2. Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument48 pagesUNIT 2. Transport Across The Cell Membranemunyanezaolivier422No ratings yet
- OsmosisDocument2 pagesOsmosisUmasalam OdawaNo ratings yet
- Water PotentialDocument2 pagesWater Potentialll2997271No ratings yet
- 3 - Movement in and Out of CellsDocument22 pages3 - Movement in and Out of CellsRashed Nada100% (1)
- Kaumaram Sushila International Residential School Grade:-9 IGCSE Sub: - Biology CHAPTER: - UNIT 3 NotesDocument10 pagesKaumaram Sushila International Residential School Grade:-9 IGCSE Sub: - Biology CHAPTER: - UNIT 3 NotesAkil BabujiNo ratings yet
- Osmosis: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesOsmosis: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaallanlopez_2009No ratings yet
- Water Movement Within A PlantDocument21 pagesWater Movement Within A PlantJoshGarciaNo ratings yet
- Ch-3 Movement Into & Out of CellDocument27 pagesCh-3 Movement Into & Out of CellHaziq KhanNo ratings yet
- Bio CH 3Document15 pagesBio CH 3SourabhiNo ratings yet
- Osmosis: Dr. Afshan Gul Department of PhysiologyDocument31 pagesOsmosis: Dr. Afshan Gul Department of Physiologyfatima zahraNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellDocument6 pagesMovement in and Out of CellMahamudul HassanNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell Water TransportDocument26 pagesPlant Cell Water TransportEdwin AlejoNo ratings yet
- Movement - S-Cool, The Revision WebsiteDocument8 pagesMovement - S-Cool, The Revision WebsiteThilini BadugeNo ratings yet
- HURDCO International School: Subject-Biology Chapter 3: Diffusion, Osmosis and Surface Area: Volume RatioDocument26 pagesHURDCO International School: Subject-Biology Chapter 3: Diffusion, Osmosis and Surface Area: Volume RatioMahin IslamNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument5 pagesCELLSJermaine CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Topic 1-Osmosity and Tonicity - EditedDocument6 pagesTopic 1-Osmosity and Tonicity - Editedsalve joy villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Semipermeable MembranesDocument4 pagesOsmosis and Semipermeable MembranesAarhan KhanNo ratings yet
- PlasmolysisDocument5 pagesPlasmolysisMalin Hamdan0% (1)
- Biology CourseworkDocument13 pagesBiology CourseworkMiss_M90100% (1)
- Transport System in PlantsDocument38 pagesTransport System in PlantsRochelleCasador180100% (1)
- Osmotic Pressure: Definition, Equation and ExamplesDocument8 pagesOsmotic Pressure: Definition, Equation and ExamplesSohail JihadiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport MechanismsDocument34 pagesCellular Transport MechanismsDhuhaa YusufNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering Project: OsmosisDocument18 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Project: OsmosisKeerthiNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Osmosis LabInfoDocument10 pagesDiffusion Osmosis LabInfoOliver GunthorpeNo ratings yet
- 3 Diffusion & OsmosisDocument27 pages3 Diffusion & OsmosisnasserkhanNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument31 pagesCell TransportjhabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Movement in and Out of CellDocument32 pagesChapter 3 Movement in and Out of Cellkiera angNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Cell Content 2Document34 pagesOsmosis and Cell Content 2Ñïà ǸìæNo ratings yet
- Devrim Öz Arslan Osmosis and tonicity (3)Document28 pagesDevrim Öz Arslan Osmosis and tonicity (3)ozerbilge24No ratings yet
- Diffusion & Osmosis LabDocument17 pagesDiffusion & Osmosis LabDee Mar0% (1)
- Water Potential ExplainedDocument4 pagesWater Potential ExplainedjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS: KEY CELLULAR PROCESSESDocument3 pagesDIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS: KEY CELLULAR PROCESSESshaniah100% (1)
- Transport in PlantsDocument12 pagesTransport in PlantsNisa ShaqiriNo ratings yet
- Diffusion 222Document3 pagesDiffusion 222jinky_julianNo ratings yet
- Biology (Form4)Document1 pageBiology (Form4)ralsy_95No ratings yet
- REVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDocument4 pagesREVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDavé TranNo ratings yet
- Water Potential NotesDocument2 pagesWater Potential NotesAditi SundharNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch11 Transport in PlantDocument6 pages11 Biology Notes ch11 Transport in PlantMuskan VarlaniNo ratings yet
- BIOL111 Cell Transport Lecture NotesDocument27 pagesBIOL111 Cell Transport Lecture NotesJasmine CatanaNo ratings yet
- L 3 Tonicity and OsmolarityDocument32 pagesL 3 Tonicity and OsmolaritysNo ratings yet
- How Osmosis Works to Transport Water Across Cell MembranesDocument21 pagesHow Osmosis Works to Transport Water Across Cell MembranesRazana Rastam0% (1)
- Cell Transport MechanismsDocument12 pagesCell Transport MechanismsAirinne GuardoNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisDocument6 pagesActivity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisThea Calyn WalicanNo ratings yet
- Water PotentialDocument2 pagesWater PotentialsmellybottomNo ratings yet
- Cellular Function and OsmosisDocument3 pagesCellular Function and OsmosisizzahNo ratings yet
- Tonicity Osmosis HyperHypoIsoDocument30 pagesTonicity Osmosis HyperHypoIsoBHADUIWAKNo ratings yet
- Mechanism: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement ofDocument4 pagesMechanism: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement ofm bilalNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument10 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsarhampracticeNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Presentation@Document20 pagesOsmosis Presentation@Dima ArafatNo ratings yet
- 6Document5 pages6api-296833859No ratings yet
- TranscriptoneDocument2 pagesTranscriptoneapi-296833859No ratings yet
- 3Document2 pages3api-296833859No ratings yet
- Negative Effects of Growing Herbicide Resistant Crops IncludeDocument3 pagesNegative Effects of Growing Herbicide Resistant Crops Includeapi-296833859No ratings yet
- 4Document2 pages4api-296833859No ratings yet
- 1Document3 pages1api-296833859No ratings yet
- Selective Advantage Natural Selection Selection Pressure: Speciation SpeciesDocument2 pagesSelective Advantage Natural Selection Selection Pressure: Speciation Speciesapi-296833859No ratings yet
- 9Document1 page9api-296833859No ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2api-296833859No ratings yet
- Selective AdvantagesDocument2 pagesSelective Advantagesapi-296833859No ratings yet
- The Founder Effect: Genetic DriftDocument1 pageThe Founder Effect: Genetic Driftapi-296833859No ratings yet
- 9Document1 page9api-296833859No ratings yet
- Limiting FactorDocument2 pagesLimiting Factorapi-296833859No ratings yet
- 8Document1 page8api-296833859No ratings yet
- Background Genes Progeny TestingDocument1 pageBackground Genes Progeny Testingapi-296833859No ratings yet
- The Founder Effect: Genetic DriftDocument1 pageThe Founder Effect: Genetic Driftapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Inbreeding Interbreeding Outbreeding Inbreeding DepressionDocument1 pageInbreeding Interbreeding Outbreeding Inbreeding Depressionapi-296833859No ratings yet
- 4Document1 page4api-296833859No ratings yet
- Absorbance Spectrum Action SpectrumDocument2 pagesAbsorbance Spectrum Action Spectrumapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Photorespiration: Bundle Sheath CellsDocument1 pagePhotorespiration: Bundle Sheath Cellsapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Selection PressuresDocument1 pageSelection Pressuresapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Energy DensityDocument1 pageEnergy Densityapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Coevolution Fitness Natural Selection: Discontinuous VariationDocument2 pagesCoevolution Fitness Natural Selection: Discontinuous Variationapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Cytoplasm: GlycolysisDocument4 pagesCytoplasm: Glycolysisapi-296833859No ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2api-296833859No ratings yet
- Photophosphorylation:: PhotoactivationDocument1 pagePhotophosphorylation:: Photoactivationapi-296833859No ratings yet
- GahhDocument1 pageGahhapi-296833859No ratings yet
- PhotolysisDocument1 pagePhotolysisapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Anaerobic Respiration (In The: CytoplasmDocument1 pageAnaerobic Respiration (In The: Cytoplasmapi-296833859No ratings yet
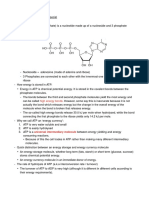
- High Energy Bonds: Universal Intermediary MoleculeDocument2 pagesHigh Energy Bonds: Universal Intermediary Moleculeapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Microbiology Laboratory EquipmentDocument3 pagesMicrobiology Laboratory EquipmentJeannette Richelle Dacillo67% (6)
- DPP - Biological ClassificationDocument8 pagesDPP - Biological ClassificationKisna guptaNo ratings yet
- MCAT2015 PreviewguideDocument153 pagesMCAT2015 PreviewguideMiao JingyaNo ratings yet
- 6 Chromosome Mutations Variation in Number and ArrangementDocument12 pages6 Chromosome Mutations Variation in Number and Arrangementrexartooz100% (2)
- IB Biology Topic 5 - Evolution & Biodiversity Revision SheetDocument1 pageIB Biology Topic 5 - Evolution & Biodiversity Revision SheetLexieNo ratings yet
- ASH SAP, Seventh Edition, 2019 PDFDocument798 pagesASH SAP, Seventh Edition, 2019 PDFDave Macedo100% (9)
- Fundamental of Plant Pathology PDFDocument219 pagesFundamental of Plant Pathology PDFrita4491% (11)
- Diseases of the Immune System ExplainedDocument55 pagesDiseases of the Immune System ExplainedMeera ANN AJINo ratings yet
- Nutrients, Food and Balanced Diet: Composition of Food 1. CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesNutrients, Food and Balanced Diet: Composition of Food 1. CarbohydratesRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes For CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 1 - Free PDF DownloadDocument8 pagesRevision Notes For CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 1 - Free PDF DownloadRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Lecture on amino acid metabolism and the urea cycleDocument41 pagesLecture on amino acid metabolism and the urea cycleQamar QamarNo ratings yet
- Dna Structure ReplicationDocument34 pagesDna Structure Replicationapi-277471896No ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument36 pagesLife Processes2erwr100% (1)
- Self Study Assignment On Marker Enzymes, Semiautonomous - PPTX 1740512Document20 pagesSelf Study Assignment On Marker Enzymes, Semiautonomous - PPTX 1740512aswinNo ratings yet
- Biomaterials, Implantable Medical Devices and Biomedical ScienceDocument50 pagesBiomaterials, Implantable Medical Devices and Biomedical ScienceDr. Mohammad Nazrul Islam100% (1)
- LO: To Understand The Use of Genetic Screening and The Issues RelatedDocument22 pagesLO: To Understand The Use of Genetic Screening and The Issues RelatedKevir ManNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Nursery Crop Propagation - Nursery ManagementDocument9 pagesBasic Principles of Nursery Crop Propagation - Nursery Managementlekh raj shivaNo ratings yet
- Bi 341 Chapter 7 Bacterial GeneticsDocument39 pagesBi 341 Chapter 7 Bacterial GeneticsMATHIXNo ratings yet
- RRL and RRS MalunggayDocument15 pagesRRL and RRS MalunggayKathleen Joy Costales MagtanongNo ratings yet
- Chapter06 LectureDocument40 pagesChapter06 Lecture7104No ratings yet
- Conferinta - USDC - 2019 Expression of Some Genes Implicated in Antioxidative Defense System in PDFDocument200 pagesConferinta - USDC - 2019 Expression of Some Genes Implicated in Antioxidative Defense System in PDFAna CalmîșNo ratings yet
- Darwin's Dilema ScriptDocument37 pagesDarwin's Dilema ScriptGex GeoNo ratings yet
- Regional Distribution of Human Trypsinogen 4Document11 pagesRegional Distribution of Human Trypsinogen 4László SzilágyiNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Anaerobic Rods and Major DiseasesDocument49 pagesGram Positive Anaerobic Rods and Major Diseasesjeevan ghimireNo ratings yet
- Practice Worksheet: Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument2 pagesPractice Worksheet: Fundamental Unit of LifeDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Noopept ReviewDocument14 pagesNoopept ReviewDonyitproNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S240589632201374X MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S240589632201374X MainApollonia VitelliNo ratings yet
- Cell Processes and MaintenanceDocument9 pagesCell Processes and MaintenanceJennifer ShabaNo ratings yet
- Bahagian B Dan C PPT SC 2019 t1Document15 pagesBahagian B Dan C PPT SC 2019 t1Anonymous RfKC0LciBKNo ratings yet
- Pex 03 03Document7 pagesPex 03 03Jila Hafizi100% (1)