Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notez 1
Notez 1
Uploaded by
asluznetOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notez 1
Notez 1
Uploaded by
asluznetCopyright:
Available Formats
Computation of deflection of structures is necessary for the following reasons:
i.
If the deflection of a structure is more than the permissible, the structure will not look aesthetic and
will cause psychological upsetting of the occupants.
ii.
Excessive deflection may cause cracking in the materials attached to the structure. For example, if
the deflection of a floor beam is excessive, the floor finishes and partition walls supported on the
beam may get cracked and unserviceable.
11. Distinguish between pin jointed and rigidly jointed structure.
Pin jointed structure (Truss)
The joints permit change of angle between
connected members.
Rigidly jointed structure (Beam/Frame)
The members connected at a rigid joint will
maintain the angle between them even under
deformation due to loads.
The joints are incapable of transferring any
Members can transmit both forces and moments
moment to the connected members and vicebetween themselves through the joint.
versa.
The pins transmit forces between connected
members by developing shear.
Provision of rigid joints normally increases the
redundancy of the structures.
12. Which of the two arches, viz. circular and parabolic is preferable to carry a uniformly distributed
load? Why?
Parabolic arches are preferably to carry distributed loads. Because, both, the shape of the arch and the
shape of the bending moment diagram are parabolic. Hence the intercept between the theoretical arch and
actual arch is zero everywhere. Hence, the bending moment at every section of the arch will be zero. The
arch will be under pure compression which will be economical.
13. Explain with a sketch, the normal thrust and radial shear in an arch.
Let us take a section D of an arch. Let be the inclination
of the tangent at D. If H is the horizontal thrust and V
the vertical shear at D, from the free body of the arch,
it is clear that V and H will have normal and
radial components given by,
N = H cos + V sin
R = V cos - H sin
Here the direction of the normal thrust and the radial shear
is constantly changing from one end of the arch to the other, due to the curved shape of the arch, unlike
shear force and axial thrust in straight beam.
You might also like
- Thin Wall BeamsDocument32 pagesThin Wall BeamsAllan Marbaniang100% (1)
- Design of Columns and Struts in Structural SteelDocument20 pagesDesign of Columns and Struts in Structural SteelMaqsood83% (18)
- Arch ActionDocument14 pagesArch ActionvempadareddyNo ratings yet
- Watch and Clock Escapements A Complete Study in Theory and Practice of the Lever, Cylinder and Chronometer Escapements, Together with a Brief Account of the Origin and Evolution of the Escapement in HorologyFrom EverandWatch and Clock Escapements A Complete Study in Theory and Practice of the Lever, Cylinder and Chronometer Escapements, Together with a Brief Account of the Origin and Evolution of the Escapement in HorologyNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Box Girder BridgesDocument14 pagesBehaviour of Box Girder BridgesSachin MoreNo ratings yet
- Rigid Frames - Compression & Buckling: NotationDocument12 pagesRigid Frames - Compression & Buckling: Notationdarebusi1No ratings yet
- Axially Loaded MembersDocument59 pagesAxially Loaded MembersAshok Dargar67% (3)
- Bending ExperimentDocument17 pagesBending ExperimentaminNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandStress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (4)
- Introduction To Elastic StabilityDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Elastic Stabilitygirma kebede0% (1)
- Introduction To ShellsDocument14 pagesIntroduction To ShellskatsiboxNo ratings yet
- Topic: Unit - 1: Medha Neetu Prathyush A Keerthi Maseeh Varun GouravDocument35 pagesTopic: Unit - 1: Medha Neetu Prathyush A Keerthi Maseeh Varun GouravtejaswiniNo ratings yet
- Inclined ColumnDocument6 pagesInclined ColumnRabindraUpretiNo ratings yet
- Shear LagDocument17 pagesShear LagSukhwinder Singh GillNo ratings yet
- Barrel ShellsDocument6 pagesBarrel ShellsGoitom Teklay GebrekidanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Shear Forces and Bending MomentsDocument27 pagesChapter 1 - Shear Forces and Bending Momentslinus 24kNo ratings yet
- TorsionDocument18 pagesTorsionBhupesh GoyalNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Design of ShellsDocument7 pagesPreliminary Design of ShellsSarish KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lecture NoteDocument19 pagesChapter 2 Lecture NoteeyobNo ratings yet
- Module 3 ASTRENGM Cross Sectional PropertiesDocument19 pagesModule 3 ASTRENGM Cross Sectional PropertiesAllyssa RosaldoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 For STMDocument14 pagesChapter 2 For STMhaymanotNo ratings yet
- BeamDocument13 pagesBeamT/ROXNo ratings yet
- Eccentric Load PDFDocument6 pagesEccentric Load PDFvipulNo ratings yet
- Eccentric LoadDocument6 pagesEccentric LoadAtish Kumar100% (3)
- Self EvaluationDocument19 pagesSelf EvaluationRheanna SalutanNo ratings yet
- Paper Coupling BeamsDocument14 pagesPaper Coupling BeamsMatías Pino YáñezNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledEdward NaanmaNo ratings yet
- Deflections of BeamDocument27 pagesDeflections of BeamIrene Margaretha Lumban RajaNo ratings yet
- Ce6501 Sructural Analysis I Question Bank Kesavan Edition 2015Document19 pagesCe6501 Sructural Analysis I Question Bank Kesavan Edition 2015Vijay_Damam100% (1)
- Tds 2 Chap 5 EditedDocument12 pagesTds 2 Chap 5 EditedezakbelachewNo ratings yet
- 02 Stability NotionsDocument7 pages02 Stability NotionsHema PenmatsaNo ratings yet
- Bending StressDocument16 pagesBending Stresspalash1401No ratings yet
- Memik Palev Simelinisemik MofezifeviDocument2 pagesMemik Palev Simelinisemik Mofezifevihanna alemhuNo ratings yet
- Design of DomesDocument40 pagesDesign of DomesnittaNo ratings yet
- Som Unit - VDocument14 pagesSom Unit - Viliyasiliyas6721No ratings yet
- 5-Prestress Diagram - Equivalent LoadsDocument15 pages5-Prestress Diagram - Equivalent Loadssamuel tejedaNo ratings yet
- Group 7Document31 pagesGroup 7Baby John lystier NadayaoNo ratings yet
- LectureDocument8 pagesLectureRohit PareekNo ratings yet
- Beam (Structure) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesBeam (Structure) - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadonodoni0008No ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document6 pagesExperiment 5Mehboob MeharNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Columns DesignDocument33 pagesLecture 4 Columns DesignOlesea NesterencoNo ratings yet
- SM II 1Document128 pagesSM II 1lokesh.ecb2658No ratings yet
- ColumnsDocument5 pagesColumnsayalwNo ratings yet
- COLUMNDocument24 pagesCOLUMNBaysa CamadNo ratings yet
- Buckling A Mechanical Failure ModeDocument238 pagesBuckling A Mechanical Failure Modeindra100% (1)
- BSC103C Pre-recordedLecture Topic9 v3.2Document60 pagesBSC103C Pre-recordedLecture Topic9 v3.2fxl62920No ratings yet
- Deflection of BeamsDocument2 pagesDeflection of BeamsDrSn PadhiNo ratings yet
- DICE501 - Steel Structures Design-Notes Unit-1Document17 pagesDICE501 - Steel Structures Design-Notes Unit-1Soumyadeep ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Arch DesignDocument16 pagesArch DesignATHULNo ratings yet
- Advance Structural Systems: UNIT-1Document26 pagesAdvance Structural Systems: UNIT-1shipwreckwaveNo ratings yet
- CE6501 Structural Analysis I 2 Marks Unit 3 PDFDocument14 pagesCE6501 Structural Analysis I 2 Marks Unit 3 PDFJuan WagnerNo ratings yet
- RC II - chapter-4-LNDocument67 pagesRC II - chapter-4-LNFenta NebiyouNo ratings yet
- ILD Short AnswersDocument6 pagesILD Short AnswersPrakash PatelNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument30 pagesStrength of MaterialsYusf ari jerjisNo ratings yet
- CE8395 Solid MechanicsDocument4 pagesCE8395 Solid Mechanics26 MaheshkannanNo ratings yet
- Beam 1Document5 pagesBeam 1saheed tijaniNo ratings yet
- Flexural Stresses in Beams - IDocument3 pagesFlexural Stresses in Beams - IZewdieNo ratings yet
- An Analytical Solution For In-Plane Free Vibration and Stability of Loaded Elliptic ArchesDocument17 pagesAn Analytical Solution For In-Plane Free Vibration and Stability of Loaded Elliptic ArchesJinho JungNo ratings yet
- Instructions on Modern American Bridge BuildingFrom EverandInstructions on Modern American Bridge BuildingNo ratings yet
- NotedDocument1 pageNotedasluznetNo ratings yet
- AlumiDocument1 pageAlumiasluznetNo ratings yet
- Design of Heel Element Load (KN) Distance From Heel (M) B.M at Heel (KNM)Document1 pageDesign of Heel Element Load (KN) Distance From Heel (M) B.M at Heel (KNM)asluznetNo ratings yet
- CourseDocument1 pageCourseasluznetNo ratings yet
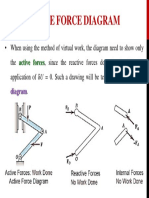
- Principle of Virtual Work: The External Virtual Work Must Be Equal To The Internal Virtual WorkDocument1 pagePrinciple of Virtual Work: The External Virtual Work Must Be Equal To The Internal Virtual WorkasluznetNo ratings yet
- SssssDocument1 pageSssssasluznetNo ratings yet
- Mu Mu/bd P Min P: Design of Toe Element Load (KN) Distance From Heel (M)Document1 pageMu Mu/bd P Min P: Design of Toe Element Load (KN) Distance From Heel (M)asluznetNo ratings yet
- Castigliano'S Theorem: 3/15/2017 Dept. of Civil Engineering, UEC, Vallivattom 4Document1 pageCastigliano'S Theorem: 3/15/2017 Dept. of Civil Engineering, UEC, Vallivattom 4asluznetNo ratings yet
- 2 Dynamics of A Seismically Isolated StructureDocument1 page2 Dynamics of A Seismically Isolated StructureasluznetNo ratings yet
- Curtailment of Bars: ST st1 st2 1 2 2 2Document1 pageCurtailment of Bars: ST st1 st2 1 2 2 2asluznetNo ratings yet
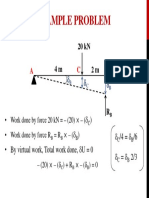
- Example Problem: ) ) - by Virtual Work, Total Work Done, U 0 /4 /6 2/3Document1 pageExample Problem: ) ) - by Virtual Work, Total Work Done, U 0 /4 /6 2/3asluznetNo ratings yet
- Proportioning of Wall: 0.6 To 0.75 For SurchargedDocument2 pagesProportioning of Wall: 0.6 To 0.75 For SurchargedasluznetNo ratings yet
- Check For Soil Pressure at BaseDocument1 pageCheck For Soil Pressure at BaseasluznetNo ratings yet
- Stability Analysis: 0.5 X K X PDocument2 pagesStability Analysis: 0.5 X K X PasluznetNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Beams AreDocument1 pageDifferent Types of Beams AreasluznetNo ratings yet
- Response of Sdof System Subjected Impulse Loading: Matlab CodingDocument3 pagesResponse of Sdof System Subjected Impulse Loading: Matlab CodingasluznetNo ratings yet
- Design of StemDocument1 pageDesign of StemasluznetNo ratings yet
- Calculate Deflection at C, Using Unit Load MethodDocument1 pageCalculate Deflection at C, Using Unit Load MethodasluznetNo ratings yet
- MechDocument1 pageMechasluznetNo ratings yet
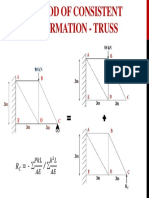
- Method of Consistent Deformation - TrussDocument1 pageMethod of Consistent Deformation - TrussasluznetNo ratings yet
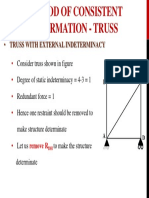
- Method of Consistent Deformation - Truss: - Truss With External IndeterminacyDocument1 pageMethod of Consistent Deformation - Truss: - Truss With External IndeterminacyasluznetNo ratings yet
- Stiffness MethodDocument1 pageStiffness MethodasluznetNo ratings yet
- Mechanics 4Document2 pagesMechanics 4asluznetNo ratings yet
- Influence Line Diagram: DeformationDocument2 pagesInfluence Line Diagram: DeformationasluznetNo ratings yet
- E I A LDocument6 pagesE I A LasluznetNo ratings yet
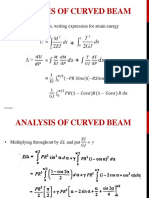
- Analysis of Curved Beam: - To Calculate Deflection, Writing Expression For Strain EnergyDocument3 pagesAnalysis of Curved Beam: - To Calculate Deflection, Writing Expression For Strain EnergyasluznetNo ratings yet
- Integration Using Calculator: - IllustrationDocument1 pageIntegration Using Calculator: - IllustrationasluznetNo ratings yet
- Node Node: No. of Elements Total Length MM Dia 1 MM Dia 2 Farctor Area 1 MM Area 2 MMDocument3 pagesNode Node: No. of Elements Total Length MM Dia 1 MM Dia 2 Farctor Area 1 MM Area 2 MMasluznetNo ratings yet
- T T S /G A: A (RC Frame) A (Brick Infill) A HDocument2 pagesT T S /G A: A (RC Frame) A (Brick Infill) A HasluznetNo ratings yet
- Node Node: No. of Elements Total Length MM Dia 1 MM Dia 2 Farctor Area 1 MM Area 2 MMDocument3 pagesNode Node: No. of Elements Total Length MM Dia 1 MM Dia 2 Farctor Area 1 MM Area 2 MMasluznetNo ratings yet