Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 Basic Laws of Electric Circuits 31
2 Basic Laws of Electric Circuits 31
Uploaded by
anothersomeguy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageThis document discusses basic electric circuit laws including:
- Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) which states that the sum of the voltages around any closed loop in a circuit must be zero.
- Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) which states that the algebraic sum of currents in a node of a circuit is zero.
- Voltage and current sources, including ideal and real sources.
- International units for measuring circuit quantities such as voltage, current, resistance, power and energy.
- Series and parallel resistive circuits including calculating total resistance, voltage, and current in series circuits using the voltage divider rule.
Original Description:
e reqr qer ergqer gqeq e
Original Title
[ok]pok]
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses basic electric circuit laws including:
- Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) which states that the sum of the voltages around any closed loop in a circuit must be zero.
- Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) which states that the algebraic sum of currents in a node of a circuit is zero.
- Voltage and current sources, including ideal and real sources.
- International units for measuring circuit quantities such as voltage, current, resistance, power and energy.
- Series and parallel resistive circuits including calculating total resistance, voltage, and current in series circuits using the voltage divider rule.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 page2 Basic Laws of Electric Circuits 31
2 Basic Laws of Electric Circuits 31
Uploaded by
anothersomeguyThis document discusses basic electric circuit laws including:
- Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) which states that the sum of the voltages around any closed loop in a circuit must be zero.
- Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) which states that the algebraic sum of currents in a node of a circuit is zero.
- Voltage and current sources, including ideal and real sources.
- International units for measuring circuit quantities such as voltage, current, resistance, power and energy.
- Series and parallel resistive circuits including calculating total resistance, voltage, and current in series circuits using the voltage divider rule.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
vi
Understandable electric circuits
Basic laws of electric circuits
Objectives
2.1 Power and Energy
2.1.1 Work
2.1.2 Energy
2.1.3 Power
2.1.4 The reference direction of power
2.2 Kirchhoffs voltage law (KVL)
2.2.1 Closed-loop circuit
2.2.2 Kirchhoffs voltage law (KVL)
2.2.3 KVL #2
2.2.4 Experimental circuit of KVL
2.2.5 KVL extension
2.2.6 The physical property of KVL
2.3 Kirchhoffs current law (KCL)
2.3.1 KCL #1
2.3.2 KCL #2
2.3.3 Physical property of KCL
2.3.4 Procedure to solve a complicated problem
2.3.5 Supernode
2.3.6 Several important circuit terminologies
2.4 Voltage source and current source
2.4.1 Voltage source
2.4.1.1 Ideal voltage source
2.4.1.2 Real voltage source
2.4.2 Current source
2.4.2.1 Ideal current source
2.4.2.2 Real current source
2.5 International units for circuit quantities
2.5.1 International system of units (SI)
2.5.2 Metric prefixes (SI prefixes)
Summary
Experiment 2: KVL and KCL
31
31
31
31
32
32
34
36
36
36
38
38
40
41
41
41
41
44
44
46
47
47
48
48
48
50
50
52
53
53
54
55
57
Seriesparallel resistive circuits
Objectives
3.1 Series resistive circuits and voltage-divider rule
3.1.1 Series resistive circuits
3.1.1.1 Total series voltage
3.1.1.2 Total series resistance (or equivalent resistance)
3.1.1.3 Series current
3.1.1.4 Series power
3.1.2 Voltage-divider rule (VDR)
3.1.3 Circuit ground
63
63
63
63
65
65
66
66
67
70
You might also like
- Thomas Fischer Weiss - Cellular Biophysics, Vol. 2 - Electrical Properties-A Bradford Book (1996)Document300 pagesThomas Fischer Weiss - Cellular Biophysics, Vol. 2 - Electrical Properties-A Bradford Book (1996)RhinometalI&CNo ratings yet
- Practical Electrical Engineering (PDFDrive)Document673 pagesPractical Electrical Engineering (PDFDrive)zeromeans100% (11)
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument520 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringAriv Azhagan97% (29)
- Hands On Electronics A Practical Introduction To Analog and Digital Circuits by Daniel M Kaplan and Christopher G WhiteDocument228 pagesHands On Electronics A Practical Introduction To Analog and Digital Circuits by Daniel M Kaplan and Christopher G WhiteInstalatiiGenerale100% (2)
- (C. Christopoulos, A. Wright (Auth.) ) Electrical PDFDocument619 pages(C. Christopoulos, A. Wright (Auth.) ) Electrical PDFNicolás Cáceres García100% (2)
- Principles and Application Lithium Secondary BatteriesDocument7 pagesPrinciples and Application Lithium Secondary BatteriesGonzalo Almeida0% (1)
- Electrochemical Supercapacitors For Energy Storage and DeliveryDocument8 pagesElectrochemical Supercapacitors For Energy Storage and DeliverykandasamyNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits A Primer by JC OlivierDocument263 pagesElectric Circuits A Primer by JC Olivierretrueke1170No ratings yet
- Electric Circuits A PrimerDocument263 pagesElectric Circuits A Primernohaymanera100% (2)
- Chapter 2 - DC Circuit and Network TheoremDocument48 pagesChapter 2 - DC Circuit and Network Theoremalifzakaria446No ratings yet
- Electrical Power System Protection PDFDocument18 pagesElectrical Power System Protection PDFAlberto José Bermúdez AriasNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Electrical Circuits Lecture-4&5Document19 pagesFundamental of Electrical Circuits Lecture-4&5Abdulalaziz AltabshNo ratings yet
- High-Temperature Superconducting Materials Science and Engineering: New Concepts and TechnologyFrom EverandHigh-Temperature Superconducting Materials Science and Engineering: New Concepts and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrodynamics: David J. Griffiths Reed CollegeDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Electrodynamics: David J. Griffiths Reed CollegeMustafa Alper SelverNo ratings yet
- Lab 04 - KVL, KCL, Nodal AnalysisDocument9 pagesLab 04 - KVL, KCL, Nodal Analysiskumarkk1987No ratings yet
- Introduction To Circuit Analysis Part 2Document41 pagesIntroduction To Circuit Analysis Part 2justinapriochanNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electrical EngineeringDocument14 pagesBasics of Electrical EngineeringvenkateswararaoNo ratings yet
- Eee 2213-CNT IiDocument116 pagesEee 2213-CNT IiLeila CheropNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electrical Engineering - A Text Book For First Year B Tech Students of Engineering (All Specializations)Document11 pagesBasics of Electrical Engineering - A Text Book For First Year B Tech Students of Engineering (All Specializations)dennyNo ratings yet
- Yang-Circuit Systems With MATLAB and PSpice-2007Document538 pagesYang-Circuit Systems With MATLAB and PSpice-2007nelsonNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electrical Engineering - A Text Book For First Year B Tech Students of Engineering (All Specializations)Document11 pagesBasics of Electrical Engineering - A Text Book For First Year B Tech Students of Engineering (All Specializations)ArfaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuit TheoryDocument2 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuit Theoryghftyftfhfhg50% (4)
- Chapter 2 - Basic Laws PDFDocument35 pagesChapter 2 - Basic Laws PDFNisha KamelNo ratings yet
- Ee6201 Circuit TheoryDocument150 pagesEe6201 Circuit TheorysachidanandamsureshNo ratings yet
- Bee Lab MannualDocument45 pagesBee Lab MannualanUGLYcatNo ratings yet
- Electronics For Technicians and Engineers PDFDocument618 pagesElectronics For Technicians and Engineers PDFJorge Roa50% (2)
- Thesis 2009 Haj HassanDocument251 pagesThesis 2009 Haj HassanAnfal DARNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Electrochemical Engineering Pablo D Giunta Full ChapterDocument67 pagesAn Introduction To Electrochemical Engineering Pablo D Giunta Full Chapterandrea.davis765100% (4)
- Front MatterDocument23 pagesFront Mattersqrt3No ratings yet
- Cdlab Manual 2023-2024Document71 pagesCdlab Manual 2023-2024sivabavatharniiNo ratings yet
- Sample 7600Document11 pagesSample 7600Retyuin100% (1)
- EE8251 Circuit Theory NotesDocument147 pagesEE8251 Circuit Theory Notessaravanakmar vNo ratings yet
- Digby D. Macdonald (Auth.) - Transient Techniques in Electrochemistry-Springer US (1977)Document335 pagesDigby D. Macdonald (Auth.) - Transient Techniques in Electrochemistry-Springer US (1977)richard.salvador.ramirezNo ratings yet
- Tutorial LetterDocument14 pagesTutorial LetterGerryRushNo ratings yet
- Section Index: (LHD) Electrical Wiring DiagramDocument5 pagesSection Index: (LHD) Electrical Wiring DiagramdienusiNo ratings yet
- FlursDocument12 pagesFlurssimonNo ratings yet
- Flexible Power Transmission: The HVDC OptionsFrom EverandFlexible Power Transmission: The HVDC OptionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electrochemistry of SolidsDocument250 pagesElectrochemistry of Solidsmarcelo.rodriguesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basic LawsDocument15 pagesChapter 2 Basic LawsChristian Muli0% (1)
- (Lecture #1) Transients in Power SystemDocument11 pages(Lecture #1) Transients in Power SystemMaroof Raza33% (3)
- Basic Laws (A)Document51 pagesBasic Laws (A)James Mosi CalandraNo ratings yet
- Fund - Circuit Chap TwoDocument29 pagesFund - Circuit Chap TwoERMIAS AmanuelNo ratings yet
- The Electrical Properties of Disordered Metals PDFDocument254 pagesThe Electrical Properties of Disordered Metals PDFRafael olivaresNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument5 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringSayyid JifriNo ratings yet
- School of Ece and EeDocument211 pagesSchool of Ece and EeRaviKumarNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument129 pagesThesisHabes NoraNo ratings yet
- Linear and Nonlinear Waves Textbook)Document334 pagesLinear and Nonlinear Waves Textbook)E Vachan RaoNo ratings yet
- WorkShop Practice Lab MannualDocument128 pagesWorkShop Practice Lab MannualAliHaiderNo ratings yet
- 52 (High Voltage DC Transmission Line) ReportDocument35 pages52 (High Voltage DC Transmission Line) ReportNehul PatilNo ratings yet
- ME442 Chapter2Document41 pagesME442 Chapter2AlanNo ratings yet
- Sorular 2Document1 pageSorular 2İlknur KeskinNo ratings yet
- Coupled Inductors - ZhangDocument243 pagesCoupled Inductors - ZhangNATHAN PINHEIRO ROCHANo ratings yet
- Circuit II PDFDocument729 pagesCircuit II PDFbehrooz100% (3)
- Electrical Technology Nov 2019 (Electronics) EngDocument23 pagesElectrical Technology Nov 2019 (Electronics) EngKhathutshelo KharivheNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Devices and Circuits Second Edition PDFDocument383 pagesPower Electronics Devices and Circuits Second Edition PDFRuben Ignacio Salazar Baez100% (7)
- 01 Elektronika Dasar Circuit AbstractionDocument33 pages01 Elektronika Dasar Circuit AbstractionfranksteinarNo ratings yet
- Automatic Frequency Control of An Induction FurnaceDocument85 pagesAutomatic Frequency Control of An Induction FurnaceNarendra BholeNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Electromagnetism - David DugdaleDocument378 pagesEssentials of Electromagnetism - David DugdaleLuis AugustoNo ratings yet
- A A A A A: Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments CknowledgmentsDocument1 pageA A A A A: Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments CknowledgmentsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Sa'Lkfj'Alksjf'Alksjgf'JaDocument1 pageSa'Lkfj'Alksjf'Alksjgf'Jaanothersomeguy0% (1)
- Processing: Fig. 16. Mature Luffa Gourd FruitsDocument1 pageProcessing: Fig. 16. Mature Luffa Gourd FruitsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- R R R R R: Eferences Eferences Eferences Eferences EferencesDocument1 pageR R R R R: Eferences Eferences Eferences Eferences EferencesanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- T T T T T: Omato Omato Omato Omato OmatoDocument1 pageT T T T T: Omato Omato Omato Omato OmatoanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Y Y Y Y Y: Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong BeanDocument1 pageY Y Y Y Y: Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong BeananothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- A A A A A: Maranth Maranth Maranth Maranth MaranthDocument1 pageA A A A A: Maranth Maranth Maranth Maranth MaranthanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- M M M M M: Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean UngbeanDocument1 pageM M M M M: Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean UngbeananothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- F F F F F: Oreword Oreword Oreword Oreword OrewordDocument1 pageF F F F F: Oreword Oreword Oreword Oreword OrewordanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- B B B B B: Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet FamilyDocument1 pageB B B B B: Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet FamilyanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- B B B B B: Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas RassicasDocument1 pageB B B B B: Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas RassicasanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- B B B B B: Ean Ean Ean Ean EanDocument1 pageB B B B B: Ean Ean Ean Ean EananothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- C C C C C: Ontents Ontents Ontents Ontents OntentsDocument1 pageC C C C C: Ontents Ontents Ontents Ontents OntentsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- L L L L L: Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce EttuceDocument1 pageL L L L L: Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce EttuceanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- D'fghae (Ruig (OeairDocument1 pageD'fghae (Ruig (OeairanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Processing: Fig. 47. Extracting Seeds by HandDocument1 pageProcessing: Fig. 47. Extracting Seeds by HandanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Humidity. S: Fig. 5. Seeds Stored in Air-Tight Containers To Prevent Them From Absorbing MoistureDocument1 pageHumidity. S: Fig. 5. Seeds Stored in Air-Tight Containers To Prevent Them From Absorbing MoistureanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- E E E E E: Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant GgplantDocument1 pageE E E E E: Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant GgplantanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- JJJJJ: Ute Ute Ute Ute UteDocument1 pageJJJJJ: Ute Ute Ute Ute UteanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
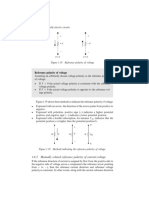
- 1.6.3 Mutually Related Reference Polarity of Current/voltageDocument1 page1.6.3 Mutually Related Reference Polarity of Current/voltageanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable SeedsDocument1 pageVegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable SeedsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- O O O O O: Nion Nion Nion Nion NionDocument1 pageO O O O O: Nion Nion Nion Nion NionanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Equipment and Components: Breadboard GuideDocument1 pageEquipment and Components: Breadboard GuideanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Compost & The Soil Food Web: ProtozoaDocument1 pageCompost & The Soil Food Web: ProtozoaanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- 1.5.2 Factors Affecting ResistanceDocument1 page1.5.2 Factors Affecting ResistanceanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Compost & The Soil Food Web: NematodesDocument1 pageCompost & The Soil Food Web: NematodesanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Resistance: 1.5.3 OhmmeterDocument1 pageFactors Affecting Resistance: 1.5.3 OhmmeteranothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Multimodal Networks and Intermodal ConnectorsDocument1 page1.4 Multimodal Networks and Intermodal ConnectorsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Voltage V (Or Potential Difference)Document1 pageVoltage V (Or Potential Difference)anothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Reference Direction of CurrentDocument1 pageReference Direction of CurrentanothersomeguyNo ratings yet