Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.6.3 Mutually Related Reference Polarity of Current/voltage
Uploaded by
anothersomeguyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.6.3 Mutually Related Reference Polarity of Current/voltage
Uploaded by
anothersomeguyCopyright:
Available Formats
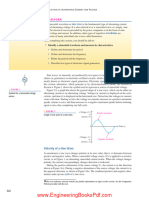
22 Understandable electric circuits
+ +
+V V
V>0 V<0
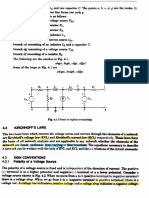
Figure 1.18 Reference polarity of voltage
Reference polarity of voltage
Assuming an arbitrarily chosen voltage polarity as the reference polarity
of voltage:
If V 4 0 the actual voltage polarity is consistent with the reference
voltage polarity.
If V 5 0 the actual voltage polarity is opposite to the reference vol-
tage polarity.
Figure 1.19 shows three methods to indicate the reference polarity of voltage:
Expressed with an arrow, the direction of the arrow points from positive to
negative.
Expressed with polarities, positive sign () indicates a higher potential
position, and negative sign (7) indicates a lower potential position.
Expressed with a double subscription, for instance Vab, indicates that the
potential position a is higher than the potential position b.
a
+
R V R V R Vab
Figure 1.19 Methods indicating the reference polarity of voltage
1.6.3 Mutually related reference polarity of current/voltage
If the reference direction of current is assigned by flow from the positive side to
the negative side of voltage across a component (the reference arrow pointing
from to 7), then the reference current direction and reference voltage
polarity is consistent. In other words, along with the current reference direction
You might also like
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- KVL and KCLDocument7 pagesKVL and KCLsamNo ratings yet
- Reference Direction of CurrentDocument1 pageReference Direction of CurrentanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- BEE Unit3Document50 pagesBEE Unit3Aman PailwanNo ratings yet
- Vector Group TrafoDocument46 pagesVector Group Trafoseptian dwirathaNo ratings yet
- ECEG-1551-FEC-Lec - 02 - DC AnalysisDocument100 pagesECEG-1551-FEC-Lec - 02 - DC AnalysisErmias MesfinNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: in This Chapter We Will Introduce The Following New ConceptsDocument13 pagesOhm's Law: in This Chapter We Will Introduce The Following New ConceptsharsimuNo ratings yet
- I V R I E R: Experiment 1: Resistor Colour Code ObjectivesDocument1 pageI V R I E R: Experiment 1: Resistor Colour Code ObjectivesanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Phys122A 21-Sp16Document20 pagesPhys122A 21-Sp16Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Electric PotentialDocument12 pagesChapter 23 Electric PotentialDinanti PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff' S Voltage LowDocument2 pagesKirchhoff' S Voltage LowpriteshNo ratings yet
- 2103-Abj - Note - Fluid Mechancis - Conventions For The Angles Beta and Alpha For Turbomachine Blades and Euler and Mechanical Power PDFDocument6 pages2103-Abj - Note - Fluid Mechancis - Conventions For The Angles Beta and Alpha For Turbomachine Blades and Euler and Mechanical Power PDFMǾhămed TăwfiķNo ratings yet
- I2Document4 pagesI2surajNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Impedance Measurement: V I I V +ZDocument12 pagesUnit-V Impedance Measurement: V I I V +ZJebas ManovaNo ratings yet
- EE204 Lecture Notes Lecture 04Document8 pagesEE204 Lecture Notes Lecture 04Haimanot DubaleNo ratings yet
- 11-Fault Locator With 2 Ended MeasurementDocument14 pages11-Fault Locator With 2 Ended MeasurementtajudeenNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff Voltage LawDocument2 pagesKirchhoff Voltage LawVũ Hải ĐăngNo ratings yet
- SPLM 1 - Power in Balanced Three Phase SystemDocument22 pagesSPLM 1 - Power in Balanced Three Phase SystemJhorwen SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics (Formula Sheet)Document6 pagesElectrostatics (Formula Sheet)Sukanya PaulNo ratings yet
- Prof M. Rashid KhanDocument15 pagesProf M. Rashid KhanMuhammad UbaidNo ratings yet
- BEE-Unit - IDocument44 pagesBEE-Unit - Ipavankumar tvvNo ratings yet
- Short Questions: (CHAPTER 13) Current ElectricityDocument14 pagesShort Questions: (CHAPTER 13) Current ElectricityEhtesham Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Eee NotesDocument40 pagesEee NotesSumiran SharmaNo ratings yet
- ECG Patterns of ST Elevation or Q-WavesDocument2 pagesECG Patterns of ST Elevation or Q-Wavesangelabeatrice.arevalo.medNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 - EE238 Electrical Engineering FundamentalDocument30 pagesLec 1 - EE238 Electrical Engineering FundamentalMohamed GamalNo ratings yet
- E01 EFieldEquiPotentialDocument9 pagesE01 EFieldEquiPotentialVea CalpoturaNo ratings yet
- 02 Three Phase SystemDocument8 pages02 Three Phase SystemCCC ChowNo ratings yet
- 14 - 15 - H2 - Current of Electricity - Tutsoln PDFDocument5 pages14 - 15 - H2 - Current of Electricity - Tutsoln PDFeltytanNo ratings yet
- L2 Electrostatics Update1 SIDocument34 pagesL2 Electrostatics Update1 SIjihadNo ratings yet
- Capítulo 1 Basic Concepts - em - InglêsDocument49 pagesCapítulo 1 Basic Concepts - em - InglêsPaulinha BezerraNo ratings yet
- 1C V-I Characteristics of DiodeDocument44 pages1C V-I Characteristics of Diodeloharneha2004No ratings yet
- Electrodynamics: Name Class No. Absent SkorDocument6 pagesElectrodynamics: Name Class No. Absent SkorAhmad Fuad RosyidiNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase ProblemsDocument39 pages3 Phase ProblemsYamato KobayoshiNo ratings yet
- PHY167 4 Electric CircuitsDocument12 pagesPHY167 4 Electric CircuitsVoice of People جمہور کی آوازNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine & Control Systems: Lecture #3Document34 pagesElectrical Machine & Control Systems: Lecture #3Hatem DheerNo ratings yet
- Bridges: Electronic Instrumentation 15EC35Document41 pagesBridges: Electronic Instrumentation 15EC35Darshan rajNo ratings yet
- E01 Electric Field PDFDocument11 pagesE01 Electric Field PDFJoseph Lawrence CelesteNo ratings yet
- Physics PracticalDocument14 pagesPhysics PracticalAarushi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document32 pagesChapter 2Andrew NguyenNo ratings yet
- Experiment Data of Mos and PNDocument17 pagesExperiment Data of Mos and PNrrahuldalal10No ratings yet
- ECE 213 L1 - Fundamentals of Power SystemDocument31 pagesECE 213 L1 - Fundamentals of Power Systemvictorkaranjamwangi7015No ratings yet
- Parallel CircuitDocument9 pagesParallel CircuitnisasoberiNo ratings yet
- General Amp ConceptsDocument8 pagesGeneral Amp ConceptsSivakumar PothirajNo ratings yet
- 02 - Projection of LineDocument31 pages02 - Projection of LineVinay SinghNo ratings yet
- 3 PhaseDocument76 pages3 PhaseastridyoungtheoNo ratings yet
- Circuit LawsDocument44 pagesCircuit LawsBrian Mactavish MohammedNo ratings yet
- Short Questions: (Chapter 13) Current ElectricityDocument15 pagesShort Questions: (Chapter 13) Current ElectricityM n NoorNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Revision Notes Chapter 4Document15 pages12 Physics Revision Notes Chapter 4johana benjaminNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document125 pagesClass 1bhuvana71No ratings yet
- Electronics Fundamentals Circuits Devices and Applications 8th Edition by David M Buchla and Thomas L Floyd-347-352Document6 pagesElectronics Fundamentals Circuits Devices and Applications 8th Edition by David M Buchla and Thomas L Floyd-347-352haniptsaqip15No ratings yet
- Ip SolutionDocument23 pagesIp Solutionhariharanphysics02No ratings yet
- MagntismDocument23 pagesMagntismUsman qadriNo ratings yet
- 15EE46 Notes Module-1Document7 pages15EE46 Notes Module-1jagavannammaNo ratings yet
- OST De-44Document84 pagesOST De-44princekumar13785No ratings yet
- OST Ana214Document96 pagesOST Ana214princekumar13785No ratings yet
- PN Junction DiodeDocument4 pagesPN Junction DiodeRajesh PylaNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits 9TH 102Document6 pagesElectric Circuits 9TH 102Richard DapitoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Potential EnergyDocument2 pagesElectrical Potential EnergyabbsaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to the Physics and Electrochemistry of Semiconductors: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Physics and Electrochemistry of Semiconductors: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Processing: Fig. 16. Mature Luffa Gourd FruitsDocument1 pageProcessing: Fig. 16. Mature Luffa Gourd FruitsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Y Y Y Y Y: Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong BeanDocument1 pageY Y Y Y Y: Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong BeananothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- A A A A A: Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments CknowledgmentsDocument1 pageA A A A A: Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments CknowledgmentsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- R R R R R: Eferences Eferences Eferences Eferences EferencesDocument1 pageR R R R R: Eferences Eferences Eferences Eferences EferencesanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- B B B B B: Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas RassicasDocument1 pageB B B B B: Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas RassicasanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Sa'Lkfj'Alksjf'Alksjgf'JaDocument1 pageSa'Lkfj'Alksjf'Alksjgf'Jaanothersomeguy0% (1)
- M M M M M: Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean UngbeanDocument1 pageM M M M M: Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean UngbeananothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- D'fghae (Ruig (OeairDocument1 pageD'fghae (Ruig (OeairanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- F F F F F: Oreword Oreword Oreword Oreword OrewordDocument1 pageF F F F F: Oreword Oreword Oreword Oreword OrewordanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- B B B B B: Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet FamilyDocument1 pageB B B B B: Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet FamilyanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- B B B B B: Ean Ean Ean Ean EanDocument1 pageB B B B B: Ean Ean Ean Ean EananothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- T T T T T: Omato Omato Omato Omato OmatoDocument1 pageT T T T T: Omato Omato Omato Omato OmatoanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- C C C C C: Ontents Ontents Ontents Ontents OntentsDocument1 pageC C C C C: Ontents Ontents Ontents Ontents OntentsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable SeedsDocument1 pageVegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable SeedsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- JJJJJ: Ute Ute Ute Ute UteDocument1 pageJJJJJ: Ute Ute Ute Ute UteanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- E E E E E: Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant GgplantDocument1 pageE E E E E: Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant GgplantanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- L L L L L: Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce EttuceDocument1 pageL L L L L: Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce EttuceanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Humidity. S: Fig. 5. Seeds Stored in Air-Tight Containers To Prevent Them From Absorbing MoistureDocument1 pageHumidity. S: Fig. 5. Seeds Stored in Air-Tight Containers To Prevent Them From Absorbing MoistureanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- A A A A A: Maranth Maranth Maranth Maranth MaranthDocument1 pageA A A A A: Maranth Maranth Maranth Maranth MaranthanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- O O O O O: Nion Nion Nion Nion NionDocument1 pageO O O O O: Nion Nion Nion Nion NionanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- 1.5.2 Factors Affecting ResistanceDocument1 page1.5.2 Factors Affecting ResistanceanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Processing: Fig. 47. Extracting Seeds by HandDocument1 pageProcessing: Fig. 47. Extracting Seeds by HandanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Multimodal Networks and Intermodal ConnectorsDocument1 page1.4 Multimodal Networks and Intermodal ConnectorsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Equipment and Components: Breadboard GuideDocument1 pageEquipment and Components: Breadboard GuideanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Voltage V (Or Potential Difference)Document1 pageVoltage V (Or Potential Difference)anothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Resistance: 1.5.3 OhmmeterDocument1 pageFactors Affecting Resistance: 1.5.3 OhmmeteranothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Compost & The Soil Food Web: NematodesDocument1 pageCompost & The Soil Food Web: NematodesanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Compost & The Soil Food Web: ProtozoaDocument1 pageCompost & The Soil Food Web: ProtozoaanothersomeguyNo ratings yet