Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I V R I E R: Experiment 1: Resistor Colour Code Objectives
I V R I E R: Experiment 1: Resistor Colour Code Objectives
Uploaded by
anothersomeguy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageConductance is the reciprocal of resistance. Ohm's law expresses the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance. It states that current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance. The conductance form of Ohm's law states that current is directly proportional to conductance and voltage. Reference directions and polarities must be defined for current and voltage. Electrical quantities like charge, EMF, resistance, and current have standard units like coulombs, volts, ohms, and amperes. Experiment 1 introduces using a breadboard and multimeter to measure resistor values based on color codes.
Original Description:
qererergrg vbcvb svbfwrth wrt
Original Title
Ls,
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentConductance is the reciprocal of resistance. Ohm's law expresses the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance. It states that current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance. The conductance form of Ohm's law states that current is directly proportional to conductance and voltage. Reference directions and polarities must be defined for current and voltage. Electrical quantities like charge, EMF, resistance, and current have standard units like coulombs, volts, ohms, and amperes. Experiment 1 introduces using a breadboard and multimeter to measure resistor values based on color codes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageI V R I E R: Experiment 1: Resistor Colour Code Objectives
I V R I E R: Experiment 1: Resistor Colour Code Objectives
Uploaded by
anothersomeguyConductance is the reciprocal of resistance. Ohm's law expresses the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance. It states that current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance. The conductance form of Ohm's law states that current is directly proportional to conductance and voltage. Reference directions and polarities must be defined for current and voltage. Electrical quantities like charge, EMF, resistance, and current have standard units like coulombs, volts, ohms, and amperes. Experiment 1 introduces using a breadboard and multimeter to measure resistor values based on color codes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
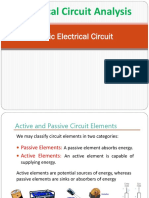
Basic concepts of electric circuits
Conductance (G): It is the reciprocal of resistance: G 1/R.
Ohms law: It expresses the relationship between current I, voltage V and
resistance R.
I
V
R
or
E
R
Conductance form of Ohms law: I GV.
Reference direction of current: Assuming an arbitrarily chosen current
direction as the reference direction of current:
If I 4 0 actual current direction is consistent with the reference current
direction.
If I 5 0 actual current direction is opposite to the reference current
direction.
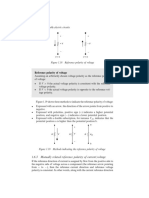
Reference polarity of voltage: Assuming an arbitrarily chosen voltage
polarity as the reference polarity of voltage:
If V 4 0 actual voltage polarity is consistent with the reference voltage
polarity.
If V 5 0 actual voltage polarity is opposite to the reference voltage
polarity.
Mutually related polarity of voltage and current: If the reference current
direction is assigned by an arrow pointing from to 7 voltage of the
component, then the reference current direction and reference voltage
polarity is consistent.
Symbols and units of electrical quantities:
Quantity
Quantity symbol
Unit
Unit symbol
Charge
EMF
Work (energy)
Resistance
Resistivity
Conductance
Current
Voltage
Q
E
W
R
r
G
I
V or E
Coulomb
Volt
Joule
Ohm
Ohm " metres
Siemens or mho
Ampere
Volt
C
V
J
O
O"m
S or
A
V
Experiment 1: Resistor colour code
Objectives
Become familiar with the breadboard
Interpret the colour code for resistors
Measure resistors with a multimeter (ohmmeter function)
25
You might also like
- Passive & ActiveDocument10 pagesPassive & ActiveSidhartha Sankar RoutNo ratings yet
- Malla Reddy CollegeDocument119 pagesMalla Reddy CollegeMehemudkhan pathanNo ratings yet
- Phy152 Lecture NoteDocument9 pagesPhy152 Lecture NoteAbubakar Olarewaju khaleedNo ratings yet
- Resistive Circuits: Resistive Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesResistive Circuits: Resistive Ohm's LawAmey KhawaleNo ratings yet
- Ohm LawDocument4 pagesOhm LawAnonymous jdC36sKP57No ratings yet
- Electricity NotesDocument10 pagesElectricity NotesCarlos KasambiraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 DC Circuit AnalysisDocument42 pagesUnit 1 DC Circuit AnalysislekoringoeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits UNIT-1 Introduction To Electrical CircuitsDocument17 pagesElectrical Circuits UNIT-1 Introduction To Electrical CircuitsJuniorNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument5 pagesOhms LawRaj Kumar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 1.6.3 Mutually Related Reference Polarity of Current/voltageDocument1 page1.6.3 Mutually Related Reference Polarity of Current/voltageanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits: ElectricityDocument9 pagesElectric Circuits: ElectricityFernanda VillacísNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Chapter 1-Introduction SemiconDocument25 pagesWeek 1 Chapter 1-Introduction Semiconn nudgeNo ratings yet
- 10 ElectricityDocument4 pages10 ElectricitySunil SeerviNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Ohms Law and IV Graphs NotesDocument1 page5.2 Ohms Law and IV Graphs NotesMichaela NunnNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument11 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectObito UchihaNo ratings yet
- Study Material and Notes of CH 12 Electricity Class 10th. Topics in The ChapterDocument5 pagesStudy Material and Notes of CH 12 Electricity Class 10th. Topics in The ChapterSavita ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Quick Notes PDFDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 7 Quick Notes PDFEmmy NurulazwanaNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITY Imp NotesDocument2 pagesELECTRICITY Imp Notesq-tipNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Electricity: ChargeDocument6 pagesRevision Notes On Electricity: ChargeJahnavi MeharNo ratings yet
- Parallel CircuitDocument9 pagesParallel CircuitnisasoberiNo ratings yet
- PotentiometerDocument7 pagesPotentiometerCarmella Mae QuidiligNo ratings yet
- I V R I E R: 1.5.6 Memory Aid For Ohm's LawDocument1 pageI V R I E R: 1.5.6 Memory Aid For Ohm's LawanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Circuit Elements: Voltage & Current Sources Electrical Resistance (Ohm's Law) Kirchhoff's LawsDocument26 pagesCircuit Elements: Voltage & Current Sources Electrical Resistance (Ohm's Law) Kirchhoff's Lawsgulzar ahmadNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit AnalysisDocument21 pagesBasic Circuit AnalysisDei PehNo ratings yet
- Electricity FinalDocument10 pagesElectricity Finalwoodchris402No ratings yet
- EE1 FEE1-Course3Document19 pagesEE1 FEE1-Course3ALEXIS sNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law PDFDocument4 pagesOhms Law PDFE-Biz NetworkNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 06 Mar 2022Document5 pagesAdobe Scan 06 Mar 2022Jitender GuptaNo ratings yet
- Systems of Units (Si .)Document16 pagesSystems of Units (Si .)Nim Nim GhaziNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 1Document22 pagesLecture 4 1Rohan WorkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electric CircuitDocument81 pagesIntroduction To Electric Circuitkaushallyaa navindranNo ratings yet
- 26 - Direct-Current Circuits - R K Parida.Document11 pages26 - Direct-Current Circuits - R K Parida.MonicaNo ratings yet
- Task5 LabViewDocument3 pagesTask5 LabViewMuhammad AfzaalNo ratings yet
- Note-1 Ke17303Document77 pagesNote-1 Ke17303Firas RodzlanNo ratings yet
- PowerDocument1 pagePowerAmey KhawaleNo ratings yet
- Aim of ProjectDocument5 pagesAim of Projectaayush sinhaNo ratings yet
- Phy 061 Electrodynamics (Circuits - Series and Parallel)Document8 pagesPhy 061 Electrodynamics (Circuits - Series and Parallel)Angel Lou LiwagonNo ratings yet
- Power As A Function of ResistanceDocument1 pagePower As A Function of ResistancesenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- SourcesDocument8 pagesSourcesrupalimandal865No ratings yet
- Power Triangle, Power Factor and Power Factor Correction MethodDocument10 pagesPower Triangle, Power Factor and Power Factor Correction MethodVedant SheshkerNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Topic 2 Electricity Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesAQA Physics Topic 2 Electricity Knowledge OrganiserMary Ann MaherNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electric CircuitsDocument78 pagesPrinciples of Electric CircuitsEvbaruNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document7 pagesLesson 5Stephen Maina NjorogeNo ratings yet
- ECA Unit 1Document48 pagesECA Unit 1Komalaselvan VNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document5 pagesExperiment 4Jasmine KaurNo ratings yet
- Notes Electric CircuitDocument5 pagesNotes Electric CircuitSTACEYLEEN CYENTHIA LADIUN BK22110177No ratings yet
- Class 10th ScienceDocument16 pagesClass 10th ScienceparveezNo ratings yet
- (4.2) e - ResistanceDocument8 pages(4.2) e - ResistanceShaikh Usman AiNo ratings yet
- DC CircuitsDocument120 pagesDC CircuitsSukanta MallickNo ratings yet
- Electricity and DC Circuit 2.0Document29 pagesElectricity and DC Circuit 2.0tony masaruNo ratings yet
- Current & Voltage Sources ConversionsDocument15 pagesCurrent & Voltage Sources ConversionsMONEER THAMEERNo ratings yet
- PEKA 1 Ohms Law FM5Document5 pagesPEKA 1 Ohms Law FM5Nur Syafiqah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Up Polytechnic 2nd Semester Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument65 pagesUp Polytechnic 2nd Semester Basic Electrical EngineeringDeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- Resistor, Ohm's Law, Power and Energy: Prepared By: Alexander T. Montero, Ree, RmeDocument47 pagesResistor, Ohm's Law, Power and Energy: Prepared By: Alexander T. Montero, Ree, RmeMarc Jairro GajudoNo ratings yet
- Su4c9 by Adel KhamisDocument8 pagesSu4c9 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of DC CircuitsDocument8 pagesFundamentals of DC CircuitstettehsackeyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19Document18 pagesLecture 19ABISHAINo ratings yet
- Electricity NotesDocument7 pagesElectricity NotesSURAJ RAIKARNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument6 pagesElectricityDarshita GolechhaNo ratings yet
- A A A A A: Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments CknowledgmentsDocument1 pageA A A A A: Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments Cknowledgments CknowledgmentsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- R R R R R: Eferences Eferences Eferences Eferences EferencesDocument1 pageR R R R R: Eferences Eferences Eferences Eferences EferencesanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- C C C C C: Ontents Ontents Ontents Ontents OntentsDocument1 pageC C C C C: Ontents Ontents Ontents Ontents OntentsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Processing: Fig. 16. Mature Luffa Gourd FruitsDocument1 pageProcessing: Fig. 16. Mature Luffa Gourd FruitsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- B B B B B: Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas RassicasDocument1 pageB B B B B: Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas Rassicas RassicasanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Y Y Y Y Y: Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong BeanDocument1 pageY Y Y Y Y: Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong Bean Ardlong BeananothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- F F F F F: Oreword Oreword Oreword Oreword OrewordDocument1 pageF F F F F: Oreword Oreword Oreword Oreword OrewordanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Sa'Lkfj'Alksjf'Alksjgf'JaDocument1 pageSa'Lkfj'Alksjf'Alksjgf'Jaanothersomeguy0% (1)
- B B B B B: Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet FamilyDocument1 pageB B B B B: Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet Family Eet FamilyanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- T T T T T: Omato Omato Omato Omato OmatoDocument1 pageT T T T T: Omato Omato Omato Omato OmatoanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- M M M M M: Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean UngbeanDocument1 pageM M M M M: Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean Ungbean UngbeananothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- B B B B B: Ean Ean Ean Ean EanDocument1 pageB B B B B: Ean Ean Ean Ean EananothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- D'fghae (Ruig (OeairDocument1 pageD'fghae (Ruig (OeairanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- JJJJJ: Ute Ute Ute Ute UteDocument1 pageJJJJJ: Ute Ute Ute Ute UteanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- L L L L L: Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce EttuceDocument1 pageL L L L L: Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce Ettuce EttuceanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- E E E E E: Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant GgplantDocument1 pageE E E E E: Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant Ggplant GgplantanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Humidity. S: Fig. 5. Seeds Stored in Air-Tight Containers To Prevent Them From Absorbing MoistureDocument1 pageHumidity. S: Fig. 5. Seeds Stored in Air-Tight Containers To Prevent Them From Absorbing MoistureanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable SeedsDocument1 pageVegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable Seeds Vegetable SeedsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Processing: Fig. 47. Extracting Seeds by HandDocument1 pageProcessing: Fig. 47. Extracting Seeds by HandanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Reference Direction of CurrentDocument1 pageReference Direction of CurrentanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Resistance: 1.5.3 OhmmeterDocument1 pageFactors Affecting Resistance: 1.5.3 OhmmeteranothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- A A A A A: Maranth Maranth Maranth Maranth MaranthDocument1 pageA A A A A: Maranth Maranth Maranth Maranth MaranthanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- 1.5.2 Factors Affecting ResistanceDocument1 page1.5.2 Factors Affecting ResistanceanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- O O O O O: Nion Nion Nion Nion NionDocument1 pageO O O O O: Nion Nion Nion Nion NionanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Compost & The Soil Food Web: ProtozoaDocument1 pageCompost & The Soil Food Web: ProtozoaanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Multimodal Networks and Intermodal ConnectorsDocument1 page1.4 Multimodal Networks and Intermodal ConnectorsanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Compost & The Soil Food Web: NematodesDocument1 pageCompost & The Soil Food Web: NematodesanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Equipment and Components: Breadboard GuideDocument1 pageEquipment and Components: Breadboard GuideanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- 1.6.3 Mutually Related Reference Polarity of Current/voltageDocument1 page1.6.3 Mutually Related Reference Polarity of Current/voltageanothersomeguyNo ratings yet
- Voltage V (Or Potential Difference)Document1 pageVoltage V (Or Potential Difference)anothersomeguyNo ratings yet