Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NPSH Learning
NPSH Learning
Uploaded by
Hitendra PanchalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NPSH Learning
NPSH Learning
Uploaded by
Hitendra PanchalCopyright:
Available Formats
Art Montemayor
NPSH Calculations
Sep 19, 1997
1. DEFINITIONS
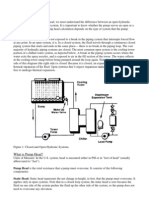
Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH)
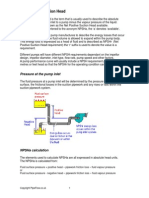
The pressure exerted on the liquid at the pump suction minus the
liquid vapor pressure. The NPSH is the result of the following
arithmetic:
The pressure above the source liquid level
plus the elevation of the liquid level above the
pumps suction inlet nozzle
minus the elevation of the pumps suction inlet
nozzle
minus the fluids friction loss in the suction line
minus the vapor pressure of the liquid fluid.
All the previous values should be consistent in absolute pressure
units.
Bubble Point Liquid
A liquid at its boiling point (B.P.).
Sub-cooled Liquid
A liquid at a temperature less than its boiling point.
Vapor Pressure (V.P.)
The pressure exerted by a liquids molecules at the surface. It is
a function of the liquids temperature. When the V.P. equals the
environmental pressure, the liquid is at its boiling point.
Specific Gravity
The specific gravity of a liquid is the ratio of its weight density
at a specified temperature to that of water at the standard
temperature of 60 oF (62.371 lb/ft3).
2. CONVERSIONS
Pressure, Feet of liquid
=
=
(psi) (144 sq. in./sq. ft.) (cu. Ft./62.371 lb) (1/Specific Gravity)
(psi) (2.308/ Specific Gravity)
Flowrate, US gpm
=
=
=
(lb/hr) (hr/60 min) (gal/8.3378 lb)(1/Specific Gravity)
(lb/hr) / (500.268 * Specific Gravity)
(lb/hr) / (500 * Specific Gravity)
3. CALCULATING THE NPSH
a) Do not take credit for liquid levels in tanks, vessels, etc. Pump must be able to work even when the
level in the source vessel approaches zero height;
b) Use specific gravities obtained at the pumping temperature. (The specific gravity is a function of
temperature);
c) Most pump suctions are 2 - 3 feet above grade if the pump base is at grade;
d) Suction lines are usually sized for 0.1 - 0.2 psi/100 ft. In calculating the NPSH, one can usually
assume 0.2 psi for a suction line pressure drop; and,
e) Very few pumps require more than 12 - 15 ft of available NPSH (NPSHa); rarely is more than 20
feet needed. (Exceptions are: multi-stage boiler feed water pumps pumping boiling water over a
pressure drop of 200 - 600 psi)
Page 1 of 4
Art Montemayor
NPSH Calculations
Sep 19, 1997
EXAMPLE 1:
A boiling liquid (or Bubble Point liquid) pumped out of an open tank:
Pressure existing @ the pump suction is
Pressure above liquid
Tank bottom elevation
Pump suction elevation
Suction friction loss
=
=
=
=
14.7 psia
0.2 psia
=
=
=
=
Atmospheric,
Open Tank
34 ft
+10 ft
- 3 ft
-0.5 ft
Press. @ pump suction
Fluid Vapor Pressure
Available NPSH
=
=
=
14.7 psia
=
=
=
40.5 ft
-34 ft
6.5 ft
900"
w ater @ 212 oF
10 ft
If the pump size or the liquid flow rate requires more
available NPSHa, the source tank should be raised until
the total NPSHa is in excess of the minimum required.
Friction = 0.2 psi
3 ft
EXAMPLE 2:
A non-boiling liquid (or subcooled liquid) pumped out
of an open tank:
Pressure existing @ the pump suction is
Pressure above liquid
Tank bottom elevation
Pump suction elevation
Suction friction loss
=
=
=
=
Press. @ pump suction
Fluid Vapor Pressure
Available NPSH
=
=
=
14.7 psia
0.2 psia
1.0 psia
=
=
=
=
34 ft
+10 ft
- 3 ft
-0.5 ft
=
=
=
40.5 ft
-2.3 ft
38.2 ft
Specify the NPSHa as 20 ft
Atmospheric,
Open Tank
water @ 100 oF
900"
Friction = 0.2 psi
NOTE: Very few pumps need more than 20 ft of NPSHa.
The source tank can be lowered, if desired.
A cooler can be installed on the pumps suction line to
lower the suction temperature and, subsequently, the
suction Vapor Pressure.
Page 3 of 4
10 ft
3 ft
Art Montemayor
NPSH Calculations
Sep 19, 1997
EXAMPLE 3:
A non-boiling liquid (or subcooled liquid) pumped out of a vented tank:
The vapor pressure of gasoline @ 100 oF = 7.0 psia
The Specific Gravity of gasoline @ 100 oF = 0.7
Pressure existing @ the pump suction is
Pressure above liquid
Tank bottom elevation
Pump suction elevation
Suction friction loss
=
=
=
=
Press. @ pump suction
Fluid Vapor Pressure
Available NPSH
=
=
=
14.7 psia
0.2 psia
7.0 psia
=
=
=
=
49 ft
+3 ft
- 3 ft
-0.7 ft
=
=
=
48.3 ft
-23.0 ft
25.3 ft
Gasoline @
100 oF
3 ft
Specify the NPSHa as 20 ft and state Flooded Suction.
EXAMPLE 4:
Sub-cooled liquid in a pit or a sump Pressure existing @ the pump suction is
Pressure above liquid
Tank bottom elevation
Pump suction elevation
Suction friction loss
=
=
=
=
Press. @ pump suction
Fluid Vapor Pressure
Available NPSH
=
=
=
14.7 psia
0.2 psia
1.0 psia
=
=
=
=
34 ft
+0 ft
- 0 ft
-0.5 ft
=
=
=
33.5 ft
-2.3 ft
31.2 ft
Specify the NPSHa as 20 ft and state Flooded Suction.
Design for one of the following conditions:
1. NPSHA > NPSHR + 5 feet of head
2. NPSHA > (NPSHR) (1.35)
. whichever of the two yields the larger answer.
Page 4 of 4
Cooling Water Tower
You might also like
- Pump Equations and Formulas CalculatorDocument11 pagesPump Equations and Formulas CalculatorOmar Elhady100% (2)
- 1 4 Calculation of Acoustic BHP 2014Document60 pages1 4 Calculation of Acoustic BHP 2014Luis Enrique Muñoz SeguraNo ratings yet
- Pump System CurveDocument133 pagesPump System Curvemohamed abd eldayem0% (1)
- NPSHDocument24 pagesNPSHneerajtrip123100% (1)
- Pump Head CalculationsDocument4 pagesPump Head CalculationsPrabhjot Singh SahiNo ratings yet
- How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesFrom EverandHow to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pump Suction CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesPump Suction Characteristicsvermaakash22No ratings yet
- Pump NPSHDocument3 pagesPump NPSHDurjoy ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- How Does Pump Suction Limit The FlowDocument6 pagesHow Does Pump Suction Limit The FlowNilesh GohelNo ratings yet
- Logics PumpsDocument155 pagesLogics PumpsKashif ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump Sizing, Selection and Design Practices (Hay)Document77 pagesCentrifugal Pump Sizing, Selection and Design Practices (Hay)Scribd_del75% (8)
- Reciprocating Pump CatalogDocument109 pagesReciprocating Pump Catalogmetasoniko2014100% (2)
- Arts NPSH TutorialDocument3 pagesArts NPSH TutorialDidier SanonNo ratings yet
- NPSH - Net Positive Suction HeadDocument9 pagesNPSH - Net Positive Suction Headlokeshjaddu6No ratings yet
- Mostafa-Understanding Expansion Tanks PDFDocument22 pagesMostafa-Understanding Expansion Tanks PDFmostafaabdelrazikNo ratings yet
- NPSH For Metering PumpsDocument7 pagesNPSH For Metering PumpsRahul S. ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- Net Positive Suction Head or NPSHDocument4 pagesNet Positive Suction Head or NPSHSathish LingamNo ratings yet
- NPSH and CavitationDocument29 pagesNPSH and CavitationEarl Josh ManansalaNo ratings yet
- Npsha Calculations: Liquids Line Sizing CriteriaDocument4 pagesNpsha Calculations: Liquids Line Sizing CriteriaDejan KovačNo ratings yet
- NPSH CalculationDocument19 pagesNPSH CalculationPatilea Daniela100% (1)
- Pumps & NPSH-Avoid ProblemsDocument4 pagesPumps & NPSH-Avoid ProblemsChem.EnggNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Lecture On Cavitation and Net Positive Suction HeadDocument16 pagesPowerpoint Lecture On Cavitation and Net Positive Suction HeadADMIN JAGONo ratings yet
- Cavitation 20002Document4 pagesCavitation 20002jochiee2324No ratings yet
- NPSHDocument5 pagesNPSHmbakhshi2No ratings yet
- NPSH Is An: Acronym Hydraulic Vapor PressureDocument5 pagesNPSH Is An: Acronym Hydraulic Vapor PressureSantosh Yellappa SulebhavikarNo ratings yet
- Natalie Portmans Shaved Head Glossary of Firefighting Equipment#n Talk PageDocument34 pagesNatalie Portmans Shaved Head Glossary of Firefighting Equipment#n Talk PageMikelaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6Document2 pagesAssignment 6Amir Javed official100% (1)
- NPSHDocument4 pagesNPSHengineeringsynergy21No ratings yet
- NPSHA For PumpDocument11 pagesNPSHA For PumpHariharan KandasamyNo ratings yet
- Fluid Machine Problems - cavitation&NPSHDocument3 pagesFluid Machine Problems - cavitation&NPSHOstwald GarciaNo ratings yet
- NPSHDocument1 pageNPSHmass34449079No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Water at Rest and in Motion: Six Principles of Fluid PressureDocument63 pagesChapter 1: Water at Rest and in Motion: Six Principles of Fluid PressureOsama EL-AbdNo ratings yet
- Suction Head: The Energy EquationDocument6 pagesSuction Head: The Energy EquationthrillerxNo ratings yet
- Gas Lift - Unloading (Leslie Thompson)Document59 pagesGas Lift - Unloading (Leslie Thompson)Reza RamadhanNo ratings yet
- By James N. Mccoy, P: Resident, Echometer Co., Wichita Falls, TexDocument4 pagesBy James N. Mccoy, P: Resident, Echometer Co., Wichita Falls, TexoomhndyNo ratings yet
- For Turbine: For Pump & Compressor:: Design Parameter - NPH - NQH Specific Speed of TurbineDocument7 pagesFor Turbine: For Pump & Compressor:: Design Parameter - NPH - NQH Specific Speed of TurbineVirender SawaliyaNo ratings yet
- Dearator BFP RelationDocument6 pagesDearator BFP RelationpurnaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Suction Cavitation & Avoiding Ugly Pump Rental Repair BillsDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Suction Cavitation & Avoiding Ugly Pump Rental Repair Billsashumishra007No ratings yet
- 4 Pumps 1 (NPSH)Document26 pages4 Pumps 1 (NPSH)michelangelo lemonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 - FeedwaterDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 7 - FeedwaterFatih KayalarNo ratings yet
- Pump NPSH (Net Positive Suction Head)Document8 pagesPump NPSH (Net Positive Suction Head)farhan_katpar1838No ratings yet
- Valve Sizing ReviewDocument6 pagesValve Sizing ReviewedcielNo ratings yet
- Libro de BombasDocument260 pagesLibro de BombasBoris SalazarNo ratings yet
- Condensate Pumping: High Temperatures and Danger of Impeller Cavitation Is The Major Challenge of Condensate PumpingDocument2 pagesCondensate Pumping: High Temperatures and Danger of Impeller Cavitation Is The Major Challenge of Condensate PumpingcordobaluisfNo ratings yet
- GPM RevDocument138 pagesGPM RevJuan Cortes TorizNo ratings yet
- 2 Pump-Pipeline SysDocument39 pages2 Pump-Pipeline SysAdelChNo ratings yet
- Liquid Recirculation System-2Document7 pagesLiquid Recirculation System-2Behnam AshouriNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump: Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH)Document4 pagesCentrifugal Pump: Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH)Sohibul Burhan Ar-RosyidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 04 StaticHead - New2Document36 pagesLesson 04 StaticHead - New2Kandregula Mohan BabuNo ratings yet
- Example Problem On Determination of Point of Gas InjectionDocument2 pagesExample Problem On Determination of Point of Gas InjectionrehmanNo ratings yet
- Me151 MidtermsDocument18 pagesMe151 MidtermsJohnNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mahiney 5Document15 pagesFluid Mahiney 5Jacob BenningsNo ratings yet
- Friction Losses: Previous PageDocument12 pagesFriction Losses: Previous PageJoshua CoxNo ratings yet
- Design of ESP: - "Unlike Positive-Displacement Pumps, ESP Does Not Displace ADocument14 pagesDesign of ESP: - "Unlike Positive-Displacement Pumps, ESP Does Not Displace AMostafa Korttam100% (1)
- Centrifugal Pumps CavitationDocument34 pagesCentrifugal Pumps CavitationAhlem BrahimNo ratings yet