Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Interference On Idle Channel
Uploaded by
Naveed RazaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Interference On Idle Channel
Uploaded by
Naveed RazaCopyright:
Available Formats
Microsoft PowerPoint - 03810_19_A(idlech)
Page 1 of 8
Idle Channel Measurements
BTS measures the uplink interference on idle channels
9 001
D
10
A
/
F
N
E
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
Figure 19 - 1
GSM Radio Network Features
Main Purpose of the Feature
To provide information to the Channel Administration feature
Allocate the most suitable idle channel for a connection
Collection of statistics on UL interference
Quality
Frequency plan
9 001
10
D
A
/
F
N
E
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
Figure 19 - 2
http://dc124.4shared.com/doc/p6ROJDDx/preview.html
GSM Radio Network Features
1/25/2012
Microsoft PowerPoint - 03810_19_A(idlech)
Page 2 of 8
Interference
Unbalanced frequency plan
Some frequencies are always disturbed
Long term variations
External interferers
Short term variations
Channel allocation/release in co/adjacent channels
5
9 001
D
10
A
/
F
N
E
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
Figure 19 - 3
GSM Radio Network Features
ICM - the Measurement Function
Uplink measurements of interference on idle channels (TCHs
and SDCCHs)
Implemented in the BTS
The measurements on TCH and SDCCH are made in the
same way as on active channels
9 001
10
D
A
/
F
N
E
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
Figure 19 - 4
http://dc124.4shared.com/doc/p6ROJDDx/preview.html
GSM Radio Network Features
1/25/2012
Microsoft PowerPoint - 03810_19_A(idlech)
Page 3 of 8
The Measurement Function
Averaging in the BTS
One interference sample every SACCH period (~0.5s)
INTAVE
length of the running average filter
Reporting to BSC
When IB, the Interference Band, for a channel changes
=> BTS sends report to BSC in message RF Resource
Indication
9 001
D
10
A
/
F
N
E
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
GSM Radio Network Features
Figure 19 - 5
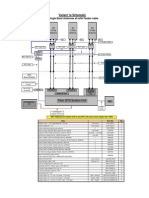
Idle Channel Measurements
IB: Interference Band
-110dBm
IB1
IB2
IB3
IB4
IB5
LOW
0
HIGH
2
LIMIT1: 2
(-108 dBm)
12
9 001
10
D
A
/
F
N
E
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
22
RXLEV
63
LIMIT3: 12
(-98 dBm)
LIMIT2: 6
(-104 dBm)
-47dBm
LIMIT4: 22
(-88 dBm)
Figure 19 - 6
http://dc124.4shared.com/doc/p6ROJDDx/preview.html
GSM Radio Network Features
1/25/2012
Microsoft PowerPoint - 03810_19_A(idlech)
Page 4 of 8
Frequency Hopping ?
Mean value of the the interference on the time slots in the
hopping sequence
FH => Interference averaging
=> decreased influence of ICM
=> not possible to identify high interfered frequencies
Interference on time slot basis will still be conquered
Non-hopping BCCH
5
9 001
D
10
A
/
F
N
E
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
Figure 19 - 7
GSM Radio Network Features
Channel Release
Normal release the channel is placed in the
same Interference Band as that it was taken from at
channel allocation.
Abnormal release for full rate channels (due to
dropped call) ? the channel is placed in the
Interference Band immediately above that it was
taken from at channel allocation.
? the
Abnormal release for half rate channels
channel is placed in the same Interference Band
(as in normal release) if its corresponding half rate
channel is idle
9 001
10
D
A
/
F
N
E
After a channel release, the BTS reports the UL i.f. for that
channel to the BSC within two SACCH periods.
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
Figure 19 - 8
http://dc124.4shared.com/doc/p6ROJDDx/preview.html
GSM Radio Network Features
1/25/2012
Microsoft PowerPoint - 03810_19_A(idlech)
Page 5 of 8
Dual Rate Channels
The BTS measures the interference on the channels individually.
When evaluating the interference level for a FR channel composed of two
HR channels, the BSC uses the average of the interference bands for the
HR channels.
9 001
D
10
A
/
F
N
E
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
Figure 19 - 9
GSM Radio Network Features
Channel Administration by Means of ICM
Which channel in the selected Resource Type
In the normal channel selection case, in all traffic cases except Intra-cell
handover, the following process is applied:
1. If half rate is requested, select the group of idle channels that have been
partly allocated for half rate (in order to save the completely idle TCHs for
FR).
2. If no partly allocated channels for half rate were found, select the group of
idle channels from the least adaptable TCH capabilities group.
3. Among these channels, select a group of channels according to the status
of the TCH on the BCCH allocation preference parameter, CHALLOC. The
value of this parameter is used to determine if an idle non-hopping TCH on
the BCCH frequency should be allocated first, last or if there is no
preference.
4. Among these channels, the group of TCHs or SDCCHs with the lowest
interference band is selected if the Idle Channel Measurement feature is
active.
5. Among these channels, the group of TCHs or SDCCHs hopping over as
5
9 001
10
D
A
/
F
N
E
many frequencies as possible is selected.
6. Among these remaining channels, a TCH or SDCCH is allocated in
accordance with the first in first out principle.
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
Figure 19 - 10
http://dc124.4shared.com/doc/p6ROJDDx/preview.html
GSM Radio Network Features
1/25/2012
Microsoft PowerPoint - 03810_19_A(idlech)
Page 6 of 8
GPRS Selection of Packet Data Channels
GPRS Channel Administration can use the ranking of channels into
interference bands as helpful information when selecting dedicated and
on-demand PDCHs from the circuit switch domain.
When a PDCH is reconfigured to a TCH the channel is placed in the
interference band it was in before it was allocated as PDCH.
Idle Channel Measurements are not performed on PDCHs.
9 001
D
10
A
/
F
N
E
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
Figure 19 - 11
GSM Radio Network Features
Evaluation
Channel Event Recording (CER)
Mean number of idle channels per IB per Resource Type
Information of individual logical channels
IB statistics per logical channel
9 001
10
D
A
/
F
N
E
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
Figure 19 - 12
http://dc124.4shared.com/doc/p6ROJDDx/preview.html
GSM Radio Network Features
1/25/2012
Microsoft PowerPoint - 03810_19_A(idlech)
Page 7 of 8
Evaluation
9 001
D
10
A
/
F
N
E
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
Figure 19 - 13
GSM Radio Network Features
Figure 19 - 14
GSM Radio Network Features
Evaluation
9 001
10
D
A
/
F
N
E
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
http://dc124.4shared.com/doc/p6ROJDDx/preview.html
1/25/2012
Microsoft PowerPoint - 03810_19_A(idlech)
Page 8 of 8
Main Controlling Parameters
LIMIT1..LIMIT4
Threshold limits for defining the different interference bands
INTAVE
Running average filter length for the interference measurements
9 001
D
10
A
/
F
N
E
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
GSM Radio Network Features
Figure 19 - 15
Parameter Setting
Default parameter setting:
Recommended values
LIMIT1: 2
SSDES + 92
LIMIT2: 6
SSDES + 100
LIMIT3: 12
SSDES + 108
LIMIT4: 22
SSDES + 129
25
INTAVE = 6
9 001
10
D
A
/
F
N
E
038 13 - EN/LZU 108 3704 Rev A
Figure 19 - 16
http://dc124.4shared.com/doc/p6ROJDDx/preview.html
GSM Radio Network Features
1/25/2012
You might also like
- Blues CheatDocument77 pagesBlues CheatRobbie ChambersNo ratings yet
- Space Policy SWAT Future Space Strategies 13 UnclassifiedDocument189 pagesSpace Policy SWAT Future Space Strategies 13 UnclassifiedSpaceStrategosNo ratings yet
- Procedure To Destroy Occultic or Cursed ObjectsDocument5 pagesProcedure To Destroy Occultic or Cursed ObjectsJuan Jaylou Ante100% (1)
- ZTE BSS Operation Quick Guide - Rev4Document81 pagesZTE BSS Operation Quick Guide - Rev4suharto MoestahalNo ratings yet
- Jewelry 7000 Years An International History and Illustrated Survey From The Collections of The - Hugh Tait - May 1991 - Abradale Books - 9780810981034 - Anna's ArchiveDocument264 pagesJewelry 7000 Years An International History and Illustrated Survey From The Collections of The - Hugh Tait - May 1991 - Abradale Books - 9780810981034 - Anna's Archiveeve100% (2)
- UMTS RNS I 05 20090530-NodeB (B8200 RRU) Installation Guide-69Document69 pagesUMTS RNS I 05 20090530-NodeB (B8200 RRU) Installation Guide-69oucht79100% (1)
- Sir Syed Ahmed Khan and Two Nation TheoryDocument11 pagesSir Syed Ahmed Khan and Two Nation TheoryZeeshan Saeed100% (5)
- PESTEL Analysis of MoroccoDocument2 pagesPESTEL Analysis of Moroccoethernalx67% (15)
- Teaching Listening and Speaking in Second and Foreign Language Contexts (Kathleen M. Bailey)Document226 pagesTeaching Listening and Speaking in Second and Foreign Language Contexts (Kathleen M. Bailey)iamhsuv100% (1)
- VIVO GSM UMTS Solution in 2011 - Huawei Internal V2 (20110120)Document104 pagesVIVO GSM UMTS Solution in 2011 - Huawei Internal V2 (20110120)Carlos AlbertoNo ratings yet
- TDQ 709018de 65FDocument1 pageTDQ 709018de 65FАлександрNo ratings yet
- HUAWEI BSC6000 Hardware Structure and System Description For V900R003-20071106-A-3.0Document87 pagesHUAWEI BSC6000 Hardware Structure and System Description For V900R003-20071106-A-3.0inf018No ratings yet
- Backhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsFrom EverandBackhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsKazi Mohammed Saidul HuqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 Introducing GSMDocument12 pagesChapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 Introducing GSMTafadzwa MashyNo ratings yet
- Understanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandUnderstanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeMaciej NawrockiNo ratings yet
- Instruction For Selecting GSM BTS Antenna Models-20021024-A-2.0Document41 pagesInstruction For Selecting GSM BTS Antenna Models-20021024-A-2.0Bagoes MardanieNo ratings yet
- BSNL Umts RF Design Document by HuaweiDocument13 pagesBSNL Umts RF Design Document by HuaweiBala ChandranNo ratings yet
- RAN Sharing Fallback East Java Area's: HUAWEI Technologies Co., LTDDocument13 pagesRAN Sharing Fallback East Java Area's: HUAWEI Technologies Co., LTDNoura Sayed AbdraboNo ratings yet
- RRU3801E Description V1.3Document11 pagesRRU3801E Description V1.3Gindo FerialNo ratings yet
- BBU3900 Hardware Description (V100 - 03)Document81 pagesBBU3900 Hardware Description (V100 - 03)ikkemagic100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Cellular Network Planning and Optimisation: 2G/2.5G/3G... Evolution to 4GFrom EverandFundamentals of Cellular Network Planning and Optimisation: 2G/2.5G/3G... Evolution to 4GNo ratings yet
- PTV Vissim - First Steps ENG PDFDocument34 pagesPTV Vissim - First Steps ENG PDFBeby RizcovaNo ratings yet
- Making Telecoms Work: From Technical Innovation to Commercial SuccessFrom EverandMaking Telecoms Work: From Technical Innovation to Commercial SuccessNo ratings yet
- RRUDocument9 pagesRRUsamNo ratings yet
- Configuring RF UnitsDocument1 pageConfiguring RF Unitsnaeem05No ratings yet
- Site Installation Overview V1.0 20131021 - LabelDocument1 pageSite Installation Overview V1.0 20131021 - LabelOussama VernalNo ratings yet
- BTSM Local Operation GuideDocument17 pagesBTSM Local Operation GuideMalek HbNo ratings yet
- CountersDocument8 pagesCountersKHAZANENo ratings yet
- Huawei GSM DBS3900Document74 pagesHuawei GSM DBS3900إدريس طاهيريNo ratings yet
- RRU ECM Report - E202203291840-01-1Document31 pagesRRU ECM Report - E202203291840-01-1Délsio CabáNo ratings yet
- Huawei Co MPT Bts3900Document2 pagesHuawei Co MPT Bts3900Himanshu ButalaNo ratings yet
- 02 GU OC2021 E02 1 ZXSDR BTS Configuration For GU Co-Site 134Document135 pages02 GU OC2021 E02 1 ZXSDR BTS Configuration For GU Co-Site 134redou123No ratings yet
- 1) Install Antenna A. Connect Coax GPS Cable To LMPT/UMPT BoardDocument4 pages1) Install Antenna A. Connect Coax GPS Cable To LMPT/UMPT BoardBayu AzizNo ratings yet
- FXEFDocument5 pagesFXEFReza BordbarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Automatic NodeB and Cell Allocation in The BSC6910 Feature V1.0Document21 pagesIntroduction To The Automatic NodeB and Cell Allocation in The BSC6910 Feature V1.0Ariel MendozaNo ratings yet
- E14F05P16 Twin DiplexerDocument4 pagesE14F05P16 Twin DiplexerRomina Vargas ZuritaNo ratings yet
- License UsageDocument8 pagesLicense UsageKandeeban DeebanNo ratings yet
- 1) HUAWEI BTS3900 Hardware Structure (Modified)Document57 pages1) HUAWEI BTS3900 Hardware Structure (Modified)Mostafa A.SalamNo ratings yet
- l2100 - Frgu l21 RFDocument6 pagesl2100 - Frgu l21 RFcspkerNo ratings yet
- Nokia Metro BtsDocument8 pagesNokia Metro BtsVikas MishraNo ratings yet
- IcmDocument11 pagesIcmSarah ElbagoryNo ratings yet
- Huawei GSM Grfu: Wireless Case and TrainingDocument35 pagesHuawei GSM Grfu: Wireless Case and TrainingChristopher AiyapiNo ratings yet
- Huawei BTS, Configuration Coupling System: Ubaid FawadDocument78 pagesHuawei BTS, Configuration Coupling System: Ubaid FawadAakif HussainNo ratings yet
- L1800 GL1800 Evolution Solution 20130306 - V1.1Document15 pagesL1800 GL1800 Evolution Solution 20130306 - V1.1Ramses De LeeuwNo ratings yet
- r48 3500e3 Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesr48 3500e3 Datasheet PDFRoger Alfaro GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Mobilink 2G3G Swap Guide V1.8 20150406Document53 pagesMobilink 2G3G Swap Guide V1.8 20150406Imran Malik100% (2)
- Antenna Port-AMB4519R2V06 2T6S AntennaDocument1 pageAntenna Port-AMB4519R2V06 2T6S AntennaBorju AjeNo ratings yet
- 3900 Series Base Station Technical Description (13) (PDF) - enDocument678 pages3900 Series Base Station Technical Description (13) (PDF) - enAndar SihombingNo ratings yet
- Huawei RNC Site Maintenance Guide...Document13 pagesHuawei RNC Site Maintenance Guide...Zaheer Ahmed TanoliNo ratings yet
- Huawei GSM Dbs3900 Hardware Structure-20080807-Issue4.0Document50 pagesHuawei GSM Dbs3900 Hardware Structure-20080807-Issue4.0Mohammed Amine HalbabaNo ratings yet
- GSM Handover OptimizationDocument9 pagesGSM Handover OptimizationRoger ParsonsNo ratings yet
- Base Station Antenna: 1.5M 8-Port 2L2H Antenna With Integrated RCUDocument2 pagesBase Station Antenna: 1.5M 8-Port 2L2H Antenna With Integrated RCUСветланаNo ratings yet
- WNG012 L2100 NC DN CJ Slogohimo 56a0ecj 113623590Document46 pagesWNG012 L2100 NC DN CJ Slogohimo 56a0ecj 113623590Roni AndikaNo ratings yet
- CS-IMF 880.1-960 RJ 869-879 40dB DC: 27/03/2015 Sala E15V87P55Document3 pagesCS-IMF 880.1-960 RJ 869-879 40dB DC: 27/03/2015 Sala E15V87P55Muh IkramNo ratings yet
- 8 HUAWEI BTS3900 Hardware StructureDocument94 pages8 HUAWEI BTS3900 Hardware StructureSherinPmNo ratings yet
- Antenna Schemes 290607Document10 pagesAntenna Schemes 290607DmitriiSpiridonovNo ratings yet
- MRFUd Power ConfigurationDocument20 pagesMRFUd Power ConfigurationsamNo ratings yet
- CW Model TuningDocument6 pagesCW Model TuningUsman SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Huawei UMTS NodeB Configuration Principle-V5 (1) .0 (E) - 20070715Document38 pagesHuawei UMTS NodeB Configuration Principle-V5 (1) .0 (E) - 20070715mhd alomariNo ratings yet
- GSM Abis Dimensioning (2010324)Document10 pagesGSM Abis Dimensioning (2010324)Peyman AllahverdianNo ratings yet
- Cross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionFrom EverandCross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionNo ratings yet
- HW - Module 1 & 2 Exercise Questions To Be SolvedDocument7 pagesHW - Module 1 & 2 Exercise Questions To Be Solvedjaryal.sarthak.jaryalNo ratings yet
- TDS - 0121 - CapaCare Classic - 201912Document5 pagesTDS - 0121 - CapaCare Classic - 201912ayviwurbayviwurbNo ratings yet
- James Rachels - What Is MoralityDocument26 pagesJames Rachels - What Is MoralityKiara Lagrisola100% (1)
- The Top Level Diagram Is A Use Case Diagram That Shows The Actors andDocument5 pagesThe Top Level Diagram Is A Use Case Diagram That Shows The Actors andsin2pNo ratings yet
- Cosep v. People PDFDocument8 pagesCosep v. People PDFAlyssa Fatima Guinto SaliNo ratings yet
- Group1 App 005 Mini PTDocument8 pagesGroup1 App 005 Mini PTAngelito Montajes AroyNo ratings yet
- Sow English Year 2 2023Document12 pagesSow English Year 2 2023Noramaliza GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5 SelectionDocument7 pagesUnit - 5 SelectionEhtesam khanNo ratings yet
- Have To, Has To, Had To - Exercise 1 - Worksheet English GrammarDocument1 pageHave To, Has To, Had To - Exercise 1 - Worksheet English Grammarjonni jonsonNo ratings yet
- Clamp Selection Guide - Rev.12 - 3.24.2016 PDFDocument32 pagesClamp Selection Guide - Rev.12 - 3.24.2016 PDFgoran muhamdNo ratings yet
- English Civic (Malaysia Unique)Document6 pagesEnglish Civic (Malaysia Unique)WAN MOHD HAFIZ BIN WAN ALI -No ratings yet
- Structure Fires Caused by Hot Work: Marty AhrensDocument14 pagesStructure Fires Caused by Hot Work: Marty AhrensBurgosg ValeryNo ratings yet
- Grammar - File12 C ROMERO VIDALDocument3 pagesGrammar - File12 C ROMERO VIDALYuy Oré Pianto50% (2)
- 02 - Thank You Maam Square Task CardsDocument8 pages02 - Thank You Maam Square Task CardsMaria Evelyn Won100% (1)
- QP English Viii 201920Document14 pagesQP English Viii 201920Srijan ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 24 - Mubangizi-WHOPQP GMP Inspections UpdatesDocument17 pages24 - Mubangizi-WHOPQP GMP Inspections UpdatessamxuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Instructional PlanningDocument30 pagesChapter 3 - Instructional PlanningMadelyne BenitezNo ratings yet
- Edavaka VillageDocument160 pagesEdavaka VillageGokul KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Tpa6404 q1Document12 pagesTpa6404 q1siogNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3: Course Title: ECO101Document4 pagesAssignment 3: Course Title: ECO101Rashik AhmedNo ratings yet
- EBOOK6131f1fd1229c Unit 3 Ledger Posting and Trial Balance PDFDocument44 pagesEBOOK6131f1fd1229c Unit 3 Ledger Posting and Trial Balance PDFYaw Antwi-AddaeNo ratings yet
- RK20 Power Flow SparseDocument33 pagesRK20 Power Flow Sparsejohn smithNo ratings yet