Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RMS Value: Statistics
Uploaded by
Anonymous 5tPxb6Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RMS Value: Statistics
Uploaded by
Anonymous 5tPxb6Copyright:
Available Formats
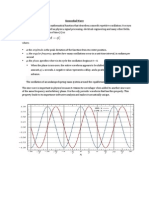
RMS Value
The root mean square (abbreviated RMS or rms), also known as the quadratic mean,
in statistics is a statistical measure defined as the square root of the mean of the squares of a
sample.[1]
RMS can also be calculated for a continuously varying function. In physics it is a characteristic of
a continuously varying quantity, such as a cyclically alternating electric current, obtained by taking
the mean of the squares of the instantaneous values during a cycle. It is equal to the value of the
direct current that would produce the same power dissipation in a resistive load.[1] This is a result
of Joule's first law, which states that the power in resistive load is proportional to the square of the
current (and, as a consequence of Ohm's law, also to the square of the voltage).
The name root mean square is simply a description: the square root of the arithmetic mean of
the squares of the samples. It is a particular case of the generalized mean, with exponent 2.
A Dictionary of Physics (6 ed.). Oxford University Press. 2009. ISBN 9780199233991.
You might also like
- Ohm S Law TutorialDocument17 pagesOhm S Law Tutorialchristopher pazmiño panchanaNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law ReportDocument8 pagesOhm's Law ReportFelicia Paya FrancisNo ratings yet
- Root Mean Square: VerificationDocument11 pagesRoot Mean Square: VerificationNick JohnNo ratings yet
- Root Mean SquareDocument9 pagesRoot Mean Squarebauro mikaereNo ratings yet
- Root Mean Square ValueDocument2 pagesRoot Mean Square ValueProximo DvNo ratings yet
- Average Electrical PowerDocument3 pagesAverage Electrical PowersenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- RMSDocument11 pagesRMSRsuneelNo ratings yet
- Sinusodial WaveDocument7 pagesSinusodial WaveDave PunzalanNo ratings yet
- His Article Is About The Law Related To ElectricityDocument22 pagesHis Article Is About The Law Related To ElectricitySandeep GuptaNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument28 pagesCurrent ElectricityTEK AYERNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument15 pagesOhm's Lawpaancute8982No ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: This Article Is About The Law Related To Electricity. For Other Uses, SeeDocument10 pagesOhm's Law: This Article Is About The Law Related To Electricity. For Other Uses, SeeAditya Singh BaisNo ratings yet
- Amplitude: Citations VerificationDocument5 pagesAmplitude: Citations VerificationAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics: (Subjects Duty English For Physics)Document6 pagesPhysics: (Subjects Duty English For Physics)naNo ratings yet
- Root Mean SquareDocument3 pagesRoot Mean SquaresenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- PHYS 331 - ElectronicsDocument87 pagesPHYS 331 - ElectronicsdennyNo ratings yet
- DC MotorsDocument8 pagesDC MotorsShamsuNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetismDocument24 pagesElectromagnetismTwinkle MoneraNo ratings yet
- M3 PPT 1 1 Phase Ac CircuitDocument67 pagesM3 PPT 1 1 Phase Ac CircuitUDhayNo ratings yet
- Resistors and Resistor CircuitsDocument4 pagesResistors and Resistor CircuitsBhanu K PrakashNo ratings yet
- Electrical EnergyDocument7 pagesElectrical EnergyCharlize Kristen MadriñanNo ratings yet
- U:uo (T L) : FunctionDocument1 pageU:uo (T L) : FunctionNurul Fahmi AriefNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge Electrons Conductor Wire Ions Electrolyte Plasma SI Ampere Coulomb AmmeterDocument2 pagesElectric Charge Electrons Conductor Wire Ions Electrolyte Plasma SI Ampere Coulomb AmmeterAzrul SyazwanNo ratings yet
- Ch11 - AC Power AnalysisDocument4 pagesCh11 - AC Power Analysisnovendri11No ratings yet
- Ohm S Law TutorialDocument17 pagesOhm S Law Tutorialchristopher pazmiño panchanaNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Ac CircuitsDocument17 pagesUnit Ii Ac CircuitsBalu ChanderNo ratings yet
- Power (Physics)Document6 pagesPower (Physics)girishpampari1No ratings yet
- Introduction To AC CircuitsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To AC CircuitsKeerthi Keerthana100% (1)
- Principles and Definition of Ohms LawDocument36 pagesPrinciples and Definition of Ohms LawIrfanNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureFrom EverandMathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureNo ratings yet
- Jose RizalDocument11 pagesJose RizalBaet RayanNo ratings yet
- How Voltage, Current, and Resistance RelateDocument6 pagesHow Voltage, Current, and Resistance RelateebasaytunoNo ratings yet
- 07 TT 02 ElectromagneticDocument4 pages07 TT 02 ElectromagneticAzad RahmanNo ratings yet
- Form FactorDocument4 pagesForm FactortusharNo ratings yet
- Current, Voltage and ResistanceDocument18 pagesCurrent, Voltage and ResistanceJustine FariscalNo ratings yet
- AC Fundamentals & Circuit Theory: Prepared By: Monmoy JahanDocument30 pagesAC Fundamentals & Circuit Theory: Prepared By: Monmoy JahanRehnuma NoorNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current Investigatory Project 12th Isc 2017Document39 pagesAlternating Current Investigatory Project 12th Isc 2017mayank kashyap77% (22)
- The Electromagnetic ForceDocument7 pagesThe Electromagnetic Forcepsychic_jason0071319No ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument11 pagesAttachmentThian Fang MingNo ratings yet
- AC Circuit Notes LolDocument19 pagesAC Circuit Notes LolcatdrinkslemonadeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics of Electric PowerDocument2 pagesMathematics of Electric PowerVidulaNo ratings yet
- Circuits LoveDocument10 pagesCircuits LoveMabethNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Basics of EnergyDocument23 pagesLesson 1 - Basics of EnergyaarivalaganNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 3Document13 pagesFundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 3richie cuizonNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Electriicy Notes HighlitedDocument9 pagesClass 10 Electriicy Notes HighlitedSTUDY MANTRANo ratings yet
- Cardiac Pacemaker DesignDocument30 pagesCardiac Pacemaker DesignVishwanath ShervegarNo ratings yet
- Circuit LabDocument46 pagesCircuit LabMiran SolankiNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Fbise FSC 2 CHAPTER - 13 CURRENT ELECTRICITYDocument5 pagesPhysics Notes Fbise FSC 2 CHAPTER - 13 CURRENT ELECTRICITYflyfalcon80% (5)
- Cou LombDocument8 pagesCou Lombbasit khanNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document124 pagesModule 2PrathamNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesLecture On Ohm's LawJanxi Carlisle ChuaNo ratings yet
- What Does An AC Voltmeter Measure?: Why Use RMS?Document35 pagesWhat Does An AC Voltmeter Measure?: Why Use RMS?Kelly BerryNo ratings yet
- Hysteresis and The E To H Transition in Radiofrequency Inductive DischargesDocument12 pagesHysteresis and The E To H Transition in Radiofrequency Inductive DischargesJitchanok WangkhanaiNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law Formula WheelDocument2 pagesOhms Law Formula WheelTesda SfistNo ratings yet
- BEE AC Circuit-1Document25 pagesBEE AC Circuit-1Niby J LouisNo ratings yet
- Eee Definations Unit 1Document6 pagesEee Definations Unit 1Rohit SinghNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument1 pageOhm's LawAdrielNo ratings yet
- Maximum Maximum: 222 Dynamical Theory (JnneDocument7 pagesMaximum Maximum: 222 Dynamical Theory (JnneMohammed NourNo ratings yet
- Power Factor - WikipediaDocument81 pagesPower Factor - WikipediaTUTU OPHILIANo ratings yet