Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Iceng 03
Uploaded by
mmanharOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Iceng 03
Uploaded by
mmanharCopyright:
Available Formats
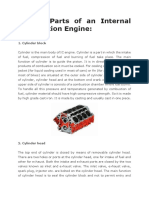
Ic eng03
Crankshaft:
This is connected to the piston through the connecting rod and converts the
linear motion of
the piston into the rotational motion of the flywheel. The journals of the
crankshaft are
supported on main bearings, housed in the crankcase. Counter-weights and the
flywheel
bolted to the crankshaft help in the smooth running of the engine.
Engine Bearings:
The crankshaft and camshaft are supported on anti-friction bearings. These
bearings must be
capable of with standing high speed, heavy load and high temperatures.
Normally, cadmium,
silver or copper lead is coated on a steel back to give the above characteristics.
For single
cylinder vertical/horizontal engines, the present trend is to use ball bearings in
place of main
bearings of the thin shell type.
Valves:
To allow the air to enter into the cylinder or the exhaust,
gases to escape from the cylinder,
valves are provided, known as inlet and exhaust valves
respectively. The valves are mounted
either on the cylinder head or on the cylinder block.
Camshaft:
The valves are operated by the action of the camshaft,
which has separate cams for the inlet,
and exhaust valves. The cam lifts the valve against the
pressure of the spring and as soon as it
changes position the spring closes the valve. The cam gets
drive through either the gear or
sprocket and chain system from the crankshaft. It rotates at
half the speed of the camshaft.
You might also like
- Steam TurbineDocument53 pagesSteam Turbineadehriya100% (1)
- Construction of Automotive EngineDocument83 pagesConstruction of Automotive EngineSaqlain Mushtaque FahimNo ratings yet
- Engine Design and Components: Crank ShaftDocument17 pagesEngine Design and Components: Crank Shaftanjali sharmaNo ratings yet
- Clyde Mark Rosales ReportDocument6 pagesClyde Mark Rosales ReportCarlton Jove AjosNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Internal Combustion EnginesDocument116 pagesUnit IV Internal Combustion Enginesjaycee68No ratings yet
- Principal Moving and Related Components: Learning ObjectivesDocument31 pagesPrincipal Moving and Related Components: Learning ObjectivesSujay NahaldeNo ratings yet
- Components of Ic Engine T613010Document9 pagesComponents of Ic Engine T613010Kolte RushikeshNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT AutotronicsDocument28 pagesChatGPT AutotronicsGokul Thalapthy Harish KumarNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Cylinder Block Cylinder Head, GasketsDocument49 pagesCH 1 Cylinder Block Cylinder Head, GasketsBogdan Constantin CristeaNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit IVDocument116 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit IVA.R. Pradeep Kumar100% (4)
- Engine Lower en D and Lubricati On System Theor yDocument26 pagesEngine Lower en D and Lubricati On System Theor yAriel PortugalNo ratings yet
- Report of Cam ShaftDocument85 pagesReport of Cam ShaftkotoyayNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Engines: Block 3 Day 14 Mr. MollahDocument74 pagesAircraft Engines: Block 3 Day 14 Mr. Mollahmohammad mollahNo ratings yet
- Pp2-Lec Note 1Document10 pagesPp2-Lec Note 1Marine EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Heads & ValvesDocument95 pagesCylinder Heads & ValvesFrank MosesNo ratings yet
- Engine Parts FunctionsDocument20 pagesEngine Parts FunctionsMikaelarae GermanNo ratings yet
- IC Engine Chapter-1-2Document41 pagesIC Engine Chapter-1-2desnetselomonNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Construction&OperationDocument27 pages1.1 Construction&OperationAniket 19SB18No ratings yet
- Lec 1 - Marine EngineeringDocument41 pagesLec 1 - Marine EngineeringArwa HusseinNo ratings yet
- MSD Unit 5Document32 pagesMSD Unit 5Vikas RathodNo ratings yet
- Construction of Automotive EngineDocument55 pagesConstruction of Automotive EngineArindom NagNo ratings yet
- IC Engines: - Dhruv ShahDocument21 pagesIC Engines: - Dhruv ShahAshitaNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Internal Combustion EnginesDocument116 pagesUnit IV Internal Combustion EnginesvelavansuNo ratings yet
- Dr.S.Sivalakshmi Associate Professor Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument55 pagesDr.S.Sivalakshmi Associate Professor Department of Mechanical EngineeringVishvesh T SNo ratings yet
- Components of An IC Engines PDFDocument6 pagesComponents of An IC Engines PDFHusnain ShenwariNo ratings yet
- Basic Components of Internal Combustion EnginesDocument62 pagesBasic Components of Internal Combustion EnginesEnergy KojoNo ratings yet
- Piston Engine ConstructionDocument150 pagesPiston Engine ConstructionHastian SuryaNo ratings yet
- Give Examples of Internal Combustion Engine That Is Commonly Used in Engineering FieldDocument11 pagesGive Examples of Internal Combustion Engine That Is Commonly Used in Engineering Fieldaruna MoonNo ratings yet
- Piston SlapDocument57 pagesPiston SlapRAJU T NNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Internal Combustion Engines: For Support Notes, Please Visit: WWW - Arpradeep.tk 1Document116 pagesUnit IV Internal Combustion Engines: For Support Notes, Please Visit: WWW - Arpradeep.tk 1Srinivas EedaraNo ratings yet
- Components or Parts of IC Engine With Its Function PDFDocument9 pagesComponents or Parts of IC Engine With Its Function PDFMilbert Vaz AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Marine Diesel EngineDocument5 pagesMarine Diesel Enginemy generalNo ratings yet
- Chapter-II Internal Combustion Engine: A. CylinderDocument16 pagesChapter-II Internal Combustion Engine: A. CylinderSajeet KarkeeNo ratings yet
- Midterm Topic No. 1 Cylinder AssemblyDocument13 pagesMidterm Topic No. 1 Cylinder AssemblyEarl Michaelo R. KalacasNo ratings yet
- Atb 203-Automotive Petrol Engines: M.Hema Kumar, M.Tech., Assistant Professor, Dept of Automobile EngineeringDocument65 pagesAtb 203-Automotive Petrol Engines: M.Hema Kumar, M.Tech., Assistant Professor, Dept of Automobile EngineeringMathankumar RNo ratings yet
- Connecting RodDocument10 pagesConnecting Rodsai venkata phanindra charyNo ratings yet
- Main Parts of An Internal Combustion EngineDocument9 pagesMain Parts of An Internal Combustion EngineVenkatNo ratings yet
- Wheel Set AssemblyDocument7 pagesWheel Set AssemblysumantlNo ratings yet
- Car Engine Components PPT SS and QuizDocument30 pagesCar Engine Components PPT SS and Quizgjoel0240No ratings yet
- ATEN 202 Lecture 2Document20 pagesATEN 202 Lecture 2EngrKaisanMuhammadUsmanNo ratings yet
- Engine ComponentsDocument31 pagesEngine ComponentsKyle Caducio100% (1)
- Part OneDocument9 pagesPart OneJesson Jade PahitNo ratings yet
- Engine ConstructionDocument66 pagesEngine Constructionace ebradoNo ratings yet
- Engine Component 1Document6 pagesEngine Component 1anuradhaNo ratings yet
- Steam Engine: Presented By: P - Deepak KumarDocument46 pagesSteam Engine: Presented By: P - Deepak KumarAccount PhoneNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Head and Guide ValvesDocument11 pagesCylinder Head and Guide ValvesSamiran BuragohainNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document51 pagesLesson 1Yashien Kate PachesNo ratings yet
- Types of Internal Combustion EnginesDocument18 pagesTypes of Internal Combustion EnginesMoayadNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 2 by b3Document16 pagesASSIGNMENT 2 by b3devmarineacademyNo ratings yet
- IC EnginesDocument72 pagesIC EnginesSRINIVAS TNo ratings yet
- Both Internal Combustion Engines and External Combustion Engines Are Known As Heat EnginesDocument70 pagesBoth Internal Combustion Engines and External Combustion Engines Are Known As Heat EnginesBalaji GaneshNo ratings yet
- Valve Gear and Valve TimingDocument41 pagesValve Gear and Valve TimingbroNo ratings yet
- Parts of An Internal Combustion Engine: by Manjunath ChincholiDocument13 pagesParts of An Internal Combustion Engine: by Manjunath ChincholimanjunathNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Head and Guide ValvesDocument12 pagesCylinder Head and Guide ValvesSamiran BuragohainNo ratings yet
- CrankshaftDocument5 pagesCrankshaftnguyen xuan minhNo ratings yet
- Turbine SystemDocument52 pagesTurbine SystemHamid Ariz100% (1)
- Pages From Ganz - Turbina-6Document1 pagePages From Ganz - Turbina-6palanaruvaNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- Construction and Manufacture of AutomobilesFrom EverandConstruction and Manufacture of AutomobilesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Design Phylosophy of Tractor CabinDocument1 pageDesign Phylosophy of Tractor CabinmmanharNo ratings yet
- Stor 1 FDocument1 pageStor 1 FmmanharNo ratings yet
- Stor 1 DDocument1 pageStor 1 DmmanharNo ratings yet
- Stor 1 eDocument1 pageStor 1 emmanharNo ratings yet
- Stor 1 BDocument1 pageStor 1 BmmanharNo ratings yet
- Stor 1 CDocument1 pageStor 1 CmmanharNo ratings yet
- Stor 1 ADocument1 pageStor 1 AmmanharNo ratings yet