Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Electronics Components and Circuits
Uploaded by
Jove Tumimbang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesThis document provides an overview of several basic electronic components:
- Resistors reduce current flow and lower voltage levels within circuits. Capacitors store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. Diodes allow current to flow only in one direction and are made of semiconductor materials.
- Transistors amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power using semiconductor material with at least three terminals. Relays are electrically operated switches that use electromagnets or solid state components to control circuits.
- LEDs are semiconductor light sources that emit light when activated, with the color determined by the energy band gap of the material. They have two leads and work on the principle of electroluminescence.
Original Description:
buod
Original Title
Jovelyn N
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of several basic electronic components:
- Resistors reduce current flow and lower voltage levels within circuits. Capacitors store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. Diodes allow current to flow only in one direction and are made of semiconductor materials.
- Transistors amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power using semiconductor material with at least three terminals. Relays are electrically operated switches that use electromagnets or solid state components to control circuits.
- LEDs are semiconductor light sources that emit light when activated, with the color determined by the energy band gap of the material. They have two leads and work on the principle of electroluminescence.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesBasic Electronics Components and Circuits
Uploaded by
Jove TumimbangThis document provides an overview of several basic electronic components:
- Resistors reduce current flow and lower voltage levels within circuits. Capacitors store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. Diodes allow current to flow only in one direction and are made of semiconductor materials.
- Transistors amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power using semiconductor material with at least three terminals. Relays are electrically operated switches that use electromagnets or solid state components to control circuits.
- LEDs are semiconductor light sources that emit light when activated, with the color determined by the energy band gap of the material. They have two leads and work on the principle of electroluminescence.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Jovelyn N.
Tumimbang
BSINT-1
M.W.F. 2:00-3:00pm
Feb. 11, 2016
BASIC ELECTRONICS
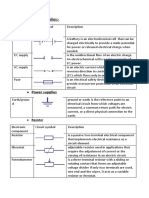
Resistors- is a passive two-terminal electrical component that
implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. Resistors
act to reduce current flow, and, at the same time, act to lower
voltage levels within circuits.
2 sample circuits
Capacitor- (originally known as a condenser) is a passive twoterminal electrical component used to store electrical energy
temporarily in an electric field.
2 Sample Circuits
Diode- is a specialized electronic component with two
electrodes called the anode and the cathode. Most diodes are
made with semiconductor materials such as silicon, germanium,
or selenium.
Types
of Blashy
Transistor- is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch
electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of
semiconductor material with at least three terminals for
connection to an external circuit.
2
Sample Circuit
Relay- is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an
electromagnet to mechanically operate a switch, but other
operating principles are also used, such as solid-state relays.
Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a
low-power signal (with complete electrical isolation between
control and controlled circuits), or where several circuits must
be controlled by one signal. The first relays were used in long
distance telegraph circuits as amplifiers: they repeated the
signal coming in from one circuit and re-transmitted it on
another circuit. Relays were used extensively in telephone
exchanges and early computers to perform logical operations .
LED(light-emitting diode)- is a two-lead semiconductor light
source. It is a pn junction diode, which emits light when
activated.[4] When a suitable voltage is applied to the leads,
electrons are able to recombine with electron holes within the
device, releasing energy in the form of photons. This effect is
called electroluminescence, and the color of the light
(corresponding to the energy of the photon) is determined by
the energy band gap of the semiconductor.
You might also like
- Essential Electronics Components GuideDocument48 pagesEssential Electronics Components GuidejojoNo ratings yet
- Electrical ParametersDocument16 pagesElectrical Parametersapi-295377694No ratings yet
- Resistor Capacitor Inductor Transistor DiodeDocument2 pagesResistor Capacitor Inductor Transistor Diodelekz re100% (2)
- Active and Passive Components: Kunal WakodeDocument3 pagesActive and Passive Components: Kunal WakodeKunal WakodeNo ratings yet
- Automatic Street Light Control with LDRDocument22 pagesAutomatic Street Light Control with LDRDevesh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Road Reflector SystemDocument68 pagesAutomatic Road Reflector SystemSujesh ChittarikkalNo ratings yet
- Eec 115 Experiment I & IiDocument12 pagesEec 115 Experiment I & IiOreoluwa OmiyaleNo ratings yet
- SynopsisDocument12 pagesSynopsisGhazalpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- A Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT) Switch Is A Switch That Has 2 Inputs and 4 Outputs Each Input Has 2 Corresponding Outputs That It Can Connect ToDocument2 pagesA Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT) Switch Is A Switch That Has 2 Inputs and 4 Outputs Each Input Has 2 Corresponding Outputs That It Can Connect ToPaulo Taganas MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Basics of ElectronicsDocument15 pagesBasics of ElectronicsAbdul RazzakNo ratings yet
- Electronics Components GuideDocument5 pagesElectronics Components GuideChristine Jade MonteraNo ratings yet
- Electrical Components Performance in T.L.EDocument4 pagesElectrical Components Performance in T.L.EErika BalmoresNo ratings yet
- What are Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocument5 pagesWhat are Electronic Circuit SymbolsRolando Carlos FloresNo ratings yet
- U6 Prs 001Document6 pagesU6 Prs 001Juan Luis Moya RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Project in TLe 3Document5 pagesProject in TLe 3RG PrinceRed Ripalda BorlagdanNo ratings yet
- Electrical JINIsshDocument6 pagesElectrical JINIsshGROOT GamingYTNo ratings yet
- Basics of ElectronicsDocument15 pagesBasics of ElectronicsAtul KumarNo ratings yet
- Export DocumentDocument37 pagesExport DocumentEunjeru EspedidoNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument10 pagesBasic ElectronicsFrancess Mae AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentDocument1 pageElectronic ComponentJedediah D. MagannonNo ratings yet
- COMM2Document3 pagesCOMM2Ëbřâhîm MaĝëdNo ratings yet
- Experiment No:-02: Electrical SymbolsDocument6 pagesExperiment No:-02: Electrical SymbolsAdesh Bhortakke100% (2)
- Power SupplyDocument11 pagesPower SupplyShameerNo ratings yet
- Automatic Street Light ControllerDocument23 pagesAutomatic Street Light ControllerAnjali Sharma100% (2)
- Basic Circuit ComponentsDocument3 pagesBasic Circuit ComponentsJhoker SudzNo ratings yet
- Essential Electrical Components and How They Work Together To Create Incredible Modern Electrical SystemsDocument13 pagesEssential Electrical Components and How They Work Together To Create Incredible Modern Electrical SystemsSolomon GodwinNo ratings yet
- Workshop Lab Manual - 25.5.2022Document30 pagesWorkshop Lab Manual - 25.5.2022shreyarajput92542No ratings yet
- Capacitor: Some Publications Still Use The Old Resistor SymbolDocument6 pagesCapacitor: Some Publications Still Use The Old Resistor SymbolSarah Jane EgeraNo ratings yet
- FEEEDocument56 pagesFEEEnetra msajjan100% (1)
- Types of Diagram and SymbolsDocument7 pagesTypes of Diagram and SymbolsPrince John Rabano100% (1)
- CHMA Unit - IIIDocument6 pagesCHMA Unit - IIISayyan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Ces - Grade 7 - Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument8 pagesWeek 4 - Ces - Grade 7 - Basic Electronic ComponentsCarl Michael BermudezNo ratings yet
- Familiarization of Electrical DevicesDocument14 pagesFamiliarization of Electrical DevicesJerome BricenioNo ratings yet
- Remote Control LED: Final ProjectDocument18 pagesRemote Control LED: Final ProjectNoman MustafaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 1 Date: / / 20Document20 pagesExperiment No: 1 Date: / / 20programmerNo ratings yet
- Electronic Components - Functions& SymbolsDocument3 pagesElectronic Components - Functions& SymbolsGil Nacario91% (58)
- EE-301 Lab Manual FamiliarizationDocument5 pagesEE-301 Lab Manual FamiliarizationSaad khan100% (1)
- Electronics Is The Branch of Science That Deals With The Study of Flow and Control of Electrons (Electricity) and The StudyDocument2 pagesElectronics Is The Branch of Science That Deals With The Study of Flow and Control of Electrons (Electricity) and The StudyJeshiela UbaldoNo ratings yet
- Complect PresntionDocument13 pagesComplect PresntionKubra ĖdrisNo ratings yet
- Components 1. Diode: Semiconductor DiodesDocument8 pagesComponents 1. Diode: Semiconductor DiodesVaranasi RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- DocumentationDocument3 pagesDocumentationRyan RosarioNo ratings yet
- Design a Clap Activated SwitchDocument37 pagesDesign a Clap Activated SwitchSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorsDocument8 pagesSemiconductorsKathleen cheyenne EbajanNo ratings yet
- Resistor: V Iri VRDocument2 pagesResistor: V Iri VRDany AlfiyandiNo ratings yet
- Experiments EPLDocument24 pagesExperiments EPLMonicaSekarNo ratings yet
- Meralco Safety Tips for Home AppliancesDocument8 pagesMeralco Safety Tips for Home AppliancesKim SantosNo ratings yet
- Attachment - 1434787422739 - Familarization With Discrete ComponentsDocument14 pagesAttachment - 1434787422739 - Familarization With Discrete ComponentsRajan SharmaNo ratings yet
- الكترونيات القدرة تجربة 1Document8 pagesالكترونيات القدرة تجربة 1hosenalmalke.comNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit IndicatorDocument4 pagesShort Circuit IndicatorDasari Navya sriNo ratings yet
- Light Dependent Resistor-Physics Investigatory Project.Document16 pagesLight Dependent Resistor-Physics Investigatory Project.Saicharan NaiduNo ratings yet
- Circuits, EC, Symbols, SchematicDocument7 pagesCircuits, EC, Symbols, SchematicKyle Angelo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics: SymbolsDocument60 pagesElectrical and Electronics: SymbolsKristel LababitNo ratings yet
- ConnectorsDocument9 pagesConnectorsROHININo ratings yet
- 1 Basic Electronics P1 NotesDocument18 pages1 Basic Electronics P1 NotesEphraem RobinNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Components GlossaryDocument9 pagesElectronic Devices and Components Glossary6C-57 Mancilla Morales, Andy EliudNo ratings yet
- Basic of ElectronicsDocument14 pagesBasic of ElectronicsRahul DubeyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Domestic Electrical Equipment Maintenance Section 2Document11 pagesAssignment 1: Domestic Electrical Equipment Maintenance Section 2Ganabpaty ThiagarajanNo ratings yet