Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circle Parabola Hyperbola Ellipse Conic Sections
Uploaded by
Anonymous PSzbyyR6r0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageThis document summarizes key properties and equations for conic sections including circles, parabolas, hyperbolas, and ellipses. Circles are defined using a center-radius form equation. Parabolas are defined by quadratic equations where the shape opens to the right or left depending on the coefficient. Hyperbolas are aligned with the x or y-axis and have asymptotes defined by linear equations. Ellipses are oriented on the x-axis with eccentricity between 0 and 1. The general form quadratic equation is used to identify which conic section is represented. Rotation and translation transformations on the equations are also summarized.
Original Description:
conics formula
Original Title
Conics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes key properties and equations for conic sections including circles, parabolas, hyperbolas, and ellipses. Circles are defined using a center-radius form equation. Parabolas are defined by quadratic equations where the shape opens to the right or left depending on the coefficient. Hyperbolas are aligned with the x or y-axis and have asymptotes defined by linear equations. Ellipses are oriented on the x-axis with eccentricity between 0 and 1. The general form quadratic equation is used to identify which conic section is represented. Rotation and translation transformations on the equations are also summarized.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageCircle Parabola Hyperbola Ellipse Conic Sections
Uploaded by
Anonymous PSzbyyR6rThis document summarizes key properties and equations for conic sections including circles, parabolas, hyperbolas, and ellipses. Circles are defined using a center-radius form equation. Parabolas are defined by quadratic equations where the shape opens to the right or left depending on the coefficient. Hyperbolas are aligned with the x or y-axis and have asymptotes defined by linear equations. Ellipses are oriented on the x-axis with eccentricity between 0 and 1. The general form quadratic equation is used to identify which conic section is represented. Rotation and translation transformations on the equations are also summarized.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
CONICS
Circle: General form: x + y + Dx + Ey + F = 0
Center-radius form: ( x h )2 + (y k )2 = r 2
2
Family:
+ y 2 + D 1 x + E 1y + F 1 + k ( x 2 + y 2 + D 2 x + E 2 y + F 2 ) = 0
If k = 1, the result will be a straight line called the radical axis.
If the given circles intersect in two points, this line passes
through them. If the circles intersect at one point, the
radical axis is tangent at this point. If the circles have no
common point, the radical axis is between them,
perpendicular to a line joining their centers.
Parabola: Opening right if a > 0:
y2 = 4ax
F(a, 0)
(y - k)2 = 4a(x - h)
F(h + a, k)
V(0, 0)
V(h, k)
Opening up if a > 0:
x2 = 4ay
(x - h)2 = 4a(y - k)
V(0, 0)
V(h, k)
F(0, a)
F(h, k + a)
Hyperbola: Aligned with x-axis (reverse x and y terms,
or x-h and y-k, for y-axis alignment):
2
2
2
2
x
y
2
2
2
(x h )
(y k )
c =a +b
=
1
=1
2
2
2
2
Asymptotes:
h
a
k
b
=0
Eccentricity: e = c , e > 1
a
The eccentricity of a parabola = 1.
Identifying Conics: Ax 2 + Bxy + Cy 2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0
If B 2 4ac < 0 then: ellipse, point or no graph
If B 2 4ac > 0 then: hyperbola or 2 intersecting lines
If B 2 4ac = 0 then: parabola, 2 parallel lines, 1 line,
or no graph
Rotation and Translation of Conics:
If there is a B term, rotation is required.
If there is a D or E term, translation is required.
If A = C , = 45o
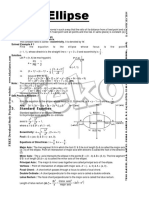
Elipse: X-axis orientation (reversed positions of a and b
indicate y-axis orientation): c 2 = a 2 b 2
p + q = 2a
2
2
2
2
2
2
x
y
(x h )
(y k )
a >b
+ 2 =1
+
=1
2
2
2
a
Eccentricity: e = c/a, 0 < e < 1
If A C , tan 2 =
cos 2 = 2 cos 1
x = x cos y sin
y = x sin y cos
B
A C
Find h, k values for an equation with an xy term by substituting
x' + h and y' + k for x and y. Perform multiplication. Factor out
x' and y' and find values of h and k to eliminate them.
Find h, k values for an equation with squares by factoring the
equation. The h, k values will appear reverse sign.
To translate an equation to a given origin, ADD the h, k values
to the x, y values in the equation.
Distance of a Directrix of an elipse or hyperbola to its
associated Focus: (used in Calculus III)
2
c (1 e )
a c
or
d =
d =
+ (a c )
2
e
Tom Penick
tomzap@eden.com
www.teicontrols.com/notes
03/10/99
You might also like
- Analytic Geometry: Engr. RenDocument48 pagesAnalytic Geometry: Engr. RenTristan100% (1)
- Maths Revision Formulas ResultsDocument5 pagesMaths Revision Formulas ResultsDarrenPurtillWrightNo ratings yet
- 10 04 Angle Between Two Curves PDFDocument15 pages10 04 Angle Between Two Curves PDFSri DNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Review Differential CalculusbDocument32 pagesIntroduction and Review Differential CalculusbRalph Piolo BuanNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Eq 2 DegDocument5 pagesCh5 Eq 2 DegVamsi YsNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument40 pagesConic SectionsMariel Milan100% (1)
- Ellipse Theory eDocument18 pagesEllipse Theory ethinkiit100% (1)
- Precalculus: Senior High School Grade 11Document28 pagesPrecalculus: Senior High School Grade 11Gerlie Jay-ann RamosNo ratings yet
- Second Degree EquationDocument5 pagesSecond Degree Equationaerogem618100% (1)
- Analytic Geometry HandoutsDocument15 pagesAnalytic Geometry HandoutsPauSomerhalderNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry - Lecture FineDocument110 pagesAnalytic Geometry - Lecture FineJosephbraken Balderama LabacanacruzNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry HandoutsDocument15 pagesAnalytic Geometry Handoutsdeguzmancarmenfe100% (1)
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Conic SectionDocument22 pagesConic SectionMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Applications of DerivativesDocument33 pagesApplications of DerivativesRiddhima MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Conic L19 20Document4 pagesConic L19 20fatimabinteziaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Coordinate Geometry and Conic SectionsDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Coordinate Geometry and Conic SectionsAik0% (1)
- Introduction To Calculus: H X F H X F X FDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Calculus: H X F H X F X FJonathan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry EssentialsDocument9 pagesAnalytic Geometry Essentials3 stacksNo ratings yet
- Lines and CirclesDocument2 pagesLines and CirclesJohnny MurrayNo ratings yet
- Day 2 1analytic GeometryDocument6 pagesDay 2 1analytic GeometryJhun Michael Locus100% (1)
- Conic SectionDocument28 pagesConic Sectionrajatbansal427100% (1)
- Sheet - 01 - CircleDocument20 pagesSheet - 01 - CircleMankirat SinghNo ratings yet
- ParabolaDocument10 pagesParabolaIshika SinghNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola ProblemsDocument16 pagesHyperbola Problemskishangopi123No ratings yet
- Equations of Conics - InfoDocument6 pagesEquations of Conics - Infoty trackNo ratings yet
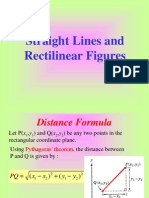
- Straight Lines and Rectilinear FiguresDocument40 pagesStraight Lines and Rectilinear FiguresChona Escoton AlcaydeNo ratings yet
- Two Dimensional Co-ordinate GeometryDocument29 pagesTwo Dimensional Co-ordinate Geometryshantam777No ratings yet
- 03 04 Length of The PerpendicularDocument18 pages03 04 Length of The Perpendicularjitender8No ratings yet
- CIRCLEA Theory Solved Example IitjeeDocument11 pagesCIRCLEA Theory Solved Example IitjeeShashank ShekharNo ratings yet
- AnGeom Bridging 3Document9 pagesAnGeom Bridging 3blackmasqueNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal Module1Document12 pagesPre Cal Module1Azhy AquinoNo ratings yet
- 1705808131Document134 pages1705808131Study EasyNo ratings yet
- Equations of CirclesDocument19 pagesEquations of Circlesrohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Ellipse Formulae SheetDocument6 pagesEllipse Formulae SheetShehbaz ThakurNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal Lesson NotesDocument23 pagesPre Cal Lesson Notesnunezreneboy1No ratings yet
- Parabola (TN)Document27 pagesParabola (TN)Raju Singh100% (1)
- Jovic G. Rullepa: SST - Iii, Shs StemDocument36 pagesJovic G. Rullepa: SST - Iii, Shs StemMykhaela Louize GumbanNo ratings yet
- 4-Quadratic Surfaces PDFDocument9 pages4-Quadratic Surfaces PDFslowjamsNo ratings yet
- My LecturesDocument53 pagesMy Lecturesbanhus20No ratings yet
- Ellipses Drawing AlgoDocument22 pagesEllipses Drawing AlgoPuneet JindalNo ratings yet
- Ellipse 2012Document10 pagesEllipse 2012SantoshNo ratings yet
- Co OrdinateDocument37 pagesCo OrdinateVincent VetterNo ratings yet
- Definition and Properties of HyperbolaDocument16 pagesDefinition and Properties of HyperbolaSwapnil TripathiNo ratings yet
- WorkDocument38 pagesWorkJEE AspirantNo ratings yet
- Conics arjuna.docx (1)Document6 pagesConics arjuna.docx (1)ajgangster3No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry Key ConceptsDocument45 pagesAnalytic Geometry Key Conceptslynser chuaNo ratings yet
- O Be Obtained in A Situation Where A Give Line Cuts The Axes As Shown in The Figure BelowDocument11 pagesO Be Obtained in A Situation Where A Give Line Cuts The Axes As Shown in The Figure BelowEmmanuel isrealNo ratings yet
- Maths Hyperbola Notes TheoryDocument27 pagesMaths Hyperbola Notes TheoryKapil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document9 pagesChapter 2Sruthi NukalaNo ratings yet
- MATHS REVISION OF KEY FORMULAEDocument5 pagesMATHS REVISION OF KEY FORMULAEabhiNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument7 pagesMathematicsJay LiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Conics NotesDocument8 pagesModule 2 Conics NotesFons Roxas-ChuaNo ratings yet
- Rotation of AxesDocument9 pagesRotation of Axesapi-213604106No ratings yet
- MathDocument7 pagesMathner sevillaNo ratings yet
- Soalan 4-Circle and ElipseDocument6 pagesSoalan 4-Circle and ElipseHaooonNo ratings yet
- Ib VimpDocument2 pagesIb VimpSreenivasulu GNo ratings yet
- Chapter Practice Problems: Straight LinesDocument5 pagesChapter Practice Problems: Straight LinesvishwaiitkNo ratings yet
- Material On EllipsesDocument13 pagesMaterial On EllipsesThilakNo ratings yet
- Cadcamfordentalsistem 120423193443 Phpapp01Document12 pagesCadcamfordentalsistem 120423193443 Phpapp01Anonymous PSzbyyR6rNo ratings yet
- Torque 2015 en ScreenDocument28 pagesTorque 2015 en ScreenAnonymous PSzbyyR6rNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorsDocument4 pagesSemiconductorsGiezel RevisNo ratings yet
- The World Standard: High Performance Brushless MicromotorDocument2 pagesThe World Standard: High Performance Brushless MicromotorAnonymous PSzbyyR6rNo ratings yet