Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Steam Sale Codes
Uploaded by
Shrawan SrivastavaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Steam Sale Codes
Uploaded by
Shrawan SrivastavaCopyright:
Available Formats
SECTION I - USE OF STEAM TABLES
LINEAR INTERPOLATION
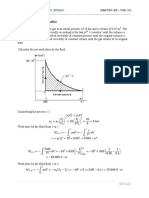
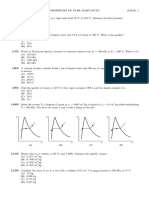
Consider a curve y = f(x)
Y
Y=f(x)
actual point
Y2
2
approximated point
Y1
X1 X X2
Let X1, X2 be the x-values of two adjacent points, 1, 2 on the curve and let Y1, Y2 be the
corresponding values of the dependent variable Y.
Need to find the Y-value corresponding to a point, lying between 1 and 2, having the X-value X.
Approximate portion of curve between 1 and 2 by a line (linear) segment as shown.
Using the concept of similar triangles,
Y Y1
(Y2 Y1
(X X1 ) (X 2 X1 )
Use of the steam tables
Example: 1 kg of steam at 7 bars and 12% quality is heated in a system at constant pressure to
210C. Find the change in the specific volume, internal energy and enthalpy of steam.
Process in equilibrium diagrams
T
T2 = 210C
T1 =164.97C
T2=210C
P = 7bar
= 0.7MPa
P1 = 0.7MPa
= P2
T1=164.97C
Section I Use of Steam Tables
Page 2
T2 > Tsat = 164.97C corresponding to P2 = 0.7 MPa (7 bars) steam is a superheated vapour
at state 1.
Property values at the initial state
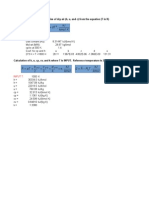
v1 x 1 v g1 (1 x 1 ) v f1 0.12(0.2729) 0.88(0.001108) 0.03372 m 3 / kg
u 1 u f1 x 1 u fg1 696.44 0.12(1876.1) 921.57 kJ / kg
h 1 h f1 x 1 h fg1 697.22 0.12( 2066.3) 945.18 kJ / kg
(see Table A5, p. 770 of Cengel & Boles for these values)
Property values at the final state
P2 = 0.7 MPa and T2 = 210C not available in the superheated steam tables (see Table A6, p.
772 of Cengel & Boles) double interpolation necessary.
P 0.6MPa , T 200C v1* 0.3529 m 3 / kg, u 1* 2638.9 kJ / kg, h 1* 2850.1 kJ / kg
P 0.6MPa , T 250C v *2 0.3938 m 3 / kg, u *2 2720.9 kJ / kg, h *2 2957.2 kJ / kg
P 0.6MPa , T 210C
v * 0.3520 (0.3938 0.3520)
v * 0.3604 m 3 / kg
( 210 200)
( 250 200)
u * 2638.9 ( 2720.9 2638.9)
u * 2655.3 kJ / kg
( 210 200)
( 250 200)
h * 2850.1 ( 2957.2 2850.1)
h * 2871.5 kJ / kg
( 210 200)
( 250 200)
P 0.8MPa , T 200C v1** 0.2608 m 3 / kg, u 1** 2630.6 kJ / kg, h 1** 2839.3 kJ / kg
P 0.8MPa , T 250C v *2* 0.2931 m 3 / kg, u *2* 2715.5 kJ / kg, h *2* 2950.0 kJ / kg
P 0.8MPa , T 210C
v ** 0.2608 (0.2931 0.2608)
v ** 0.2673 m 3 / kg
( 210 200)
(250 200)
u ** 2630.6 (2715.5 2630.6)
u ** 2647.6 kJ / kg
(210 200)
(250 200)
h ** 2839.3 ( 2950.0 2839.3)
h ** 2861.4 kJ / kg
(210 200)
( 250 200)
P2 0.7MPa , T2 210C
( v 2 0.3604) (0.2673 0.3604)
v 2 0.3139 m 3 / kg
(0.7 0.6)
(0.8 0.6)
u 2 2655.3 (2647.6 2655.3)
u 2 2651.4 kJ / kg
(0.7 0.6)
(0.8 0.6)
h 2 2871.5 (2861.4 2871.5)
h 2 2866.5 kJ / kg
(0.7 0.6)
( 0 .8 0 .6 )
Change in property values
v = v2 v1 = 0.3139 0.03372 = 0.2802 m3/kg
Section I Use of Steam Tables
u = u2 u1 = 2651.4 921.57 = 1729.8 kJ/kg
h = h2 h1 = 2866.5 945.18 = 1921.3 kJ/kg
Page 3
Using the appropriate tables for water and water vapour, fill in the blanks in the following
table:
Temperature, [C]
280
Pressure, [MPa]
Mass, [kg]
480
0.7
1.0
Specific Volume, [m3/kg]
2.0
1.3
8.0
0.35
3.5
3.0
0.3852
Volume, [m3]
Quality, [%]
60
Moisture Content, [%]
Enthalpy, [kJ/kg]
Internal Energy, [kJ/kg]
20
2779.6
3005.4
You might also like
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- CH 09Document22 pagesCH 09hirenpatel_universalNo ratings yet
- Isobaric ProcessDocument24 pagesIsobaric ProcessWhindy Bagawisan CasugaNo ratings yet
- 8 16Document3 pages8 16ejans54No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Tut-2Document24 pagesChapter 8 - Tut-2Raghav ChhaparwalNo ratings yet
- ME 24-221 Thermodynamics I Solutions Entropy ChangeDocument4 pagesME 24-221 Thermodynamics I Solutions Entropy ChangeMarcelo AlegriaNo ratings yet
- CalculationsDocument2 pagesCalculationsLeoNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics Exam 2018 Wirh SolutionsDocument9 pagesApplied Thermodynamics Exam 2018 Wirh SolutionsFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- A PistonDocument3 pagesA PistonSamuel NapitupuluNo ratings yet
- Thermo ProblemsDocument8 pagesThermo ProblemsChrister John UyNo ratings yet
- HWSolutions PDFDocument42 pagesHWSolutions PDFJames AhnNo ratings yet
- Problems on Regenerative Cycle Steam TurbineDocument6 pagesProblems on Regenerative Cycle Steam TurbineMurvin VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document29 pagesTutorial 1pendrive80No ratings yet
- Section 2Document11 pagesSection 2عبدالرحمن التميميNo ratings yet
- Thermo HWDocument6 pagesThermo HWMuhammad Fawwad ObaidaNo ratings yet
- Thermo ExcerciseDocument28 pagesThermo ExcerciseAizel Jeong Aizel JeongNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Turbin Uap 2Document3 pagesPerhitungan Turbin Uap 2Khäirůl ŰmãmNo ratings yet
- 12th PhysucsvipDocument3 pages12th Physucsvipphysics a2No ratings yet
- Assumptions 1) This Is A Steady-Flow Process Since There Is No Change With Time. 2) The Kinetic andDocument5 pagesAssumptions 1) This Is A Steady-Flow Process Since There Is No Change With Time. 2) The Kinetic andKarumon UtsumiNo ratings yet
- Ciclo BraytonDocument17 pagesCiclo BraytonNubia Bergamini100% (2)
- Be Mechanical-Engineering Semester-3 2019 December Thermodynamics-CbcgsDocument14 pagesBe Mechanical-Engineering Semester-3 2019 December Thermodynamics-CbcgsHarsh KbddhsjNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2 Quiz #3 - T01: Name: ID #: Problem:: 1 Mark 1 MarkDocument2 pagesThermodynamics 2 Quiz #3 - T01: Name: ID #: Problem:: 1 Mark 1 MarkPratulya KolheNo ratings yet
- ME 24-221 Thermodynamics I Solutions To Extra Problems in Chapter 9: November 17, 2000 J. MurthyDocument6 pagesME 24-221 Thermodynamics I Solutions To Extra Problems in Chapter 9: November 17, 2000 J. MurthyKen Joshua ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Termo Isı 1011 Örnek4Document13 pagesTermo Isı 1011 Örnek4Şafak MeçoNo ratings yet
- HW 5 SolnDocument7 pagesHW 5 SolnNik Hafiy HafiziNo ratings yet
- Solution #9Document7 pagesSolution #9KinnonPangNo ratings yet
- Air PropDocument4 pagesAir PropWrya SaeedNo ratings yet
- Isentropic Efficiency IIDocument4 pagesIsentropic Efficiency IIrgopikrishna313No ratings yet
- Isentropic Efficiency II PDFDocument4 pagesIsentropic Efficiency II PDFrgopikrishna313No ratings yet
- 2nd Law Analysis For A Control VolumeDocument13 pages2nd Law Analysis For A Control VolumeSergey ShkapovNo ratings yet
- Gibbs Free Energy and Thermodynamic Functions ExplainedDocument40 pagesGibbs Free Energy and Thermodynamic Functions ExplainedDaniel Alvarez Vega67% (6)
- Assigned Thermo Problem 5Document3 pagesAssigned Thermo Problem 5Cubillan, Kenneth M.No ratings yet
- Borgnakke's Fundamentals of Thermodynamics: Global EditionDocument67 pagesBorgnakke's Fundamentals of Thermodynamics: Global Edition정윤서No ratings yet
- Properties of Pure Substances GuideDocument9 pagesProperties of Pure Substances GuideMahmoud AbdelghfarNo ratings yet
- Isobaric ProcessDocument24 pagesIsobaric ProcessBrando_Balagon75% (4)
- Chapter 09 SMDocument20 pagesChapter 09 SMalagurmNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10xx 2Document66 pagesLecture 10xx 2King Cyruz PabloNo ratings yet
- Air PropDocument4 pagesAir Propanup_nairNo ratings yet
- BSGS Sample Problems 2 - BB CollabDocument21 pagesBSGS Sample Problems 2 - BB CollabNeo GarceraNo ratings yet
- 1 - Energy and Energy BalancesDocument135 pages1 - Energy and Energy BalancesHabib Al-Aziz100% (2)
- Chapter 9 Examples&SolutionDocument42 pagesChapter 9 Examples&SolutionSami ullahNo ratings yet
- Reversible adiabatic processesDocument17 pagesReversible adiabatic processesmehmet hassanNo ratings yet
- THERMODYNAMICS SOLUTIONSDocument62 pagesTHERMODYNAMICS SOLUTIONSanthonytichaona100% (1)
- PPE PROBLEM SET Thermodynamics 2Document8 pagesPPE PROBLEM SET Thermodynamics 2Maria PerezNo ratings yet
- 51 ThermoDynamics ThermoDynamics PDFDocument5 pages51 ThermoDynamics ThermoDynamics PDFmozam haqNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Processes Murphy Chapter06 SolutionsDocument94 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Processes Murphy Chapter06 SolutionsEric Barnett29% (7)
- Ame Homework Solutions 1 Fall 2011Document33 pagesAme Homework Solutions 1 Fall 2011Ťhåŕüñ Kūmæř GøwđNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document5 pagesChapter 04stephen jamesNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument4 pagesSolutionradheNo ratings yet
- Entropy Notes and QuestionsDocument25 pagesEntropy Notes and Questionshirenpatel_universal100% (1)
- ThermodynamicsDocument33 pagesThermodynamicsJanneNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 - Jagonos, Ariel PDFDocument10 pagesAssignment 4 - Jagonos, Ariel PDFleno voiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Question 8Document2 pagesTutorial 3 - Question 8DiablofireZANo ratings yet
- Thermo 4 Quiz 1Document2 pagesThermo 4 Quiz 1Ndude MckenzeNo ratings yet
- Solution Week 9Document6 pagesSolution Week 9Ariadne ChuaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Law NotesDocument21 pages2nd Law NotesShrawan SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 1 Number: 1.1 Vocabulary and Notation For Different Sets of Numbers:natural NumbersDocument8 pages1 Number: 1.1 Vocabulary and Notation For Different Sets of Numbers:natural NumbersShrawan SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- I Helped YouDocument1 pageI Helped YouShrawan SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- FJGJGDocument75 pagesFJGJGShrawan SrivastavaNo ratings yet