Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Midsem Question Paper 2015
Uploaded by
shashankmay18Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Midsem Question Paper 2015
Uploaded by
shashankmay18Copyright:
Available Formats
BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, PILANI
ME/MF F 244: Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines
SECOND SEMESTER 2014-2015
Max Marks: 35
Mid Semester Examination (CLOSED BOOK)
Duration: 90 mins
Date: 9th March, 2015 (9 - 10:30 AM)
Q1a. What is the assumption in analysis of mechanisms which allows treatment of kinematics and
dynamics separately? Explain
[1]
Q1b. Which follower motion do you recommend for a high-speed cam and why?
[1]
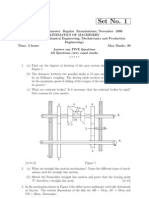
Q1c. Refer Fig Q1c, Determine the number of degrees of freedom associated with this machine.
Links 3 and 4, 5 and 6, 8 and 9 form piston-cylinder pair.
[3]
Fig Q1c
Fig Q2
All calculations and diagrams for question 2 and 3 are to be done in the drawing sheet provided.
Q2. In the mechanism shown in Fig Q2, the angular velocity of link 2 is 2 rad/s (CCW) and the
angular acceleration is 5 rad/s2 (CW). Various lengths of the links are AC = 5.2 length unit,
AB = 6 units, and CD = 10 units.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Draw position diagram and mention scale.
Draw velocity and acceleration diagrams and mention their scales.
Draw a table and tabulate the magnitudes of
the velocities and accelerations of slider B and point D.
the angular velocity and angular acceleration of link CD (i.e. 4 and 4).
[2]
[3+4]
[2+4]
[1+2]
Q3. Layout profile of a cam operating a flat-faced, translating, radial follower and with the
following data:
Base circle radius = 40 mm
Total rise = 40 mm
The rise occurs with SHM over 90o of cam rotation. The follower dwells for 100o of cam
rotation prior to the beginning of the rise and dwells 80o of cam rotation at the end of the rise.
Then the follower lowers down during the rest of the cam rotation with uniform motion.
If the cam rotates at uniform speed of 150 rpm in counter clock-wise direction, calculate the
maximum velocity and acceleration of the follower during the rise.
[12]
You might also like
- Shape Memory Alloy Actuators: Design, Fabrication, and Experimental EvaluationFrom EverandShape Memory Alloy Actuators: Design, Fabrication, and Experimental EvaluationNo ratings yet
- Cms College of Engineering, Namakkal: Unit 1 - Basics of MechanismsDocument17 pagesCms College of Engineering, Namakkal: Unit 1 - Basics of MechanismsRajueswarNo ratings yet
- Design Optimization of Fluid Machinery: Applying Computational Fluid Dynamics and Numerical OptimizationFrom EverandDesign Optimization of Fluid Machinery: Applying Computational Fluid Dynamics and Numerical OptimizationNo ratings yet
- EMG 2208 - Mechanics of Machines - Assignment - MMU Sept 2012Document4 pagesEMG 2208 - Mechanics of Machines - Assignment - MMU Sept 2012Charles OndiekiNo ratings yet
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesFrom EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesNo ratings yet
- 10ME/AU44: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartDocument2 pages10ME/AU44: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartsatheeshNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Large-Range Compliant Micropositioning SystemsFrom EverandDesign and Implementation of Large-Range Compliant Micropositioning SystemsNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDocument8 pagesMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery Question BankDocument7 pagesKinematics of Machinery Question BankpanneerthambiNo ratings yet
- Upto 2010 KomDocument36 pagesUpto 2010 KomRajueswarNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel and Stacks Field Repair ManualFrom EverandPressure Vessel and Stacks Field Repair ManualRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Me2220 Mkup Suppl 2017Document4 pagesMe2220 Mkup Suppl 2017Harish KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkNo ratings yet
- Unit Wise 16 Mark QuestionsDocument29 pagesUnit Wise 16 Mark QuestionsPreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- Helicopter Flight Dynamics: Including a Treatment of Tiltrotor AircraftFrom EverandHelicopter Flight Dynamics: Including a Treatment of Tiltrotor AircraftNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery May2006 Rr222105Document11 pagesKinematics of Machinery May2006 Rr222105Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.joe_134No ratings yet
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDocument8 pagesMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruNo ratings yet
- Kom Assignment QuestionDocument8 pagesKom Assignment QuestionrajapratyNo ratings yet
- Upto 2010 KomDocument36 pagesUpto 2010 KompsnasabariNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery Question BankDocument92 pagesKinematics of Machinery Question BankNatesha Sundharan100% (2)
- Kinematics of Machinery November Am Rr222105Document12 pagesKinematics of Machinery November Am Rr222105Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNo ratings yet
- 9A14402 Theory of MachinesDocument8 pages9A14402 Theory of MachinessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- ME6401-Kinematics of MachineryDocument11 pagesME6401-Kinematics of Machineryappuanandh7811No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machinery GATE BitsDocument8 pagesDynamics of Machinery GATE BitsVenkateswar Reddy MallepallyNo ratings yet
- 16 Mark QuestionDocument6 pages16 Mark QuestionMECH HODNo ratings yet
- Chapter One and Chapter 2 WorksheetDocument9 pagesChapter One and Chapter 2 WorksheetSena MekoninNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms and Mechanical DesignDocument9 pagesMechanisms and Mechanical DesignNizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDocument9 pagesMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruNo ratings yet
- ME2203 M.J 2007Document0 pagesME2203 M.J 2007Venkatesh RajamaniNo ratings yet
- r05310304 Kinematics of MachineryDocument10 pagesr05310304 Kinematics of MachinerySRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- 9A03401 Kinematics of MachineryDocument8 pages9A03401 Kinematics of MachinerysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Acceleration AnalysisDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Acceleration Analysisameet_sata20000% (1)
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDocument9 pagesMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDocument8 pagesMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruNo ratings yet
- Question Bank KomDocument11 pagesQuestion Bank KomStar SathishNo ratings yet
- Me1252 Kinematics of MachineryDocument3 pagesMe1252 Kinematics of MachineryManikandan SelvamNo ratings yet
- TOM Question BankDocument10 pagesTOM Question BankMadhan Kumar GovindarajuNo ratings yet
- KDMDocument3 pagesKDMDeep RavalNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineryDocument20 pagesKinematics of Machineryvenkatkavin0% (1)
- V Semster 2018Document32 pagesV Semster 2018Sanjay CNo ratings yet
- B.Tech (PT) - Mechanical - II YEAR - III SEM - (R) 2012 PDFDocument12 pagesB.Tech (PT) - Mechanical - II YEAR - III SEM - (R) 2012 PDFmohamed irshadNo ratings yet
- 9A14402 Theory of MachinesDocument8 pages9A14402 Theory of MachinessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.kbhaskar66No ratings yet
- R05 Set No. 2Document12 pagesR05 Set No. 2Rajesh KannanNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityKrinal AdakiNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDocument9 pagesMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruNo ratings yet
- Mechanism WorksheetDocument8 pagesMechanism Worksheetnatnaelzelalem03No ratings yet
- 9A03401 Kinematics of MachineryDocument8 pages9A03401 Kinematics of MachinerysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignDocument8 pages9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- A.R Engineering College: Villupuram Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument14 pagesA.R Engineering College: Villupuram Department of Mechanical EngineeringVENKATESHNo ratings yet
- B Tech - 4 Sem (Grading) Course Code: ME 403 Subject Name: Theory of Machines Important Questions Unit - 1Document6 pagesB Tech - 4 Sem (Grading) Course Code: ME 403 Subject Name: Theory of Machines Important Questions Unit - 1suneel kumar rathoreNo ratings yet
- Me6401 Kinematics of Machinery UNIT-I (Basics of Mechanism)Document8 pagesMe6401 Kinematics of Machinery UNIT-I (Basics of Mechanism)Ãraviñdhañ RändýNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery Anna University Question Papers CompiledDocument77 pagesKinematics of Machinery Anna University Question Papers CompiledNatesha SundharanNo ratings yet
- rr310304 Kinematics of MachineryDocument11 pagesrr310304 Kinematics of MachinerySRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- 06me44 Dec 13 VTUDocument2 pages06me44 Dec 13 VTUArun DixitNo ratings yet
- MP2002-Tut 4-5Document7 pagesMP2002-Tut 4-5Ashwin Kumar ChandranNo ratings yet
- Manual TheoryDocument50 pagesManual Theoryيوسف ابو فروةNo ratings yet
- Microteaching Title SlideDocument13 pagesMicroteaching Title Slideshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Hydraulic IndustrialDocument56 pagesHydraulic IndustrialKuni Faizah100% (1)
- Hydraulics ParkerDocument71 pagesHydraulics Parkershashankmay18No ratings yet
- Leave PolicyDocument10 pagesLeave Policyshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Consent Form For Photos & VideosDocument1 pageConsent Form For Photos & Videosshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Cooling Towers3Document5 pagesCooling Towers3shashankmay18No ratings yet
- Dry Cooling Tower 1Document5 pagesDry Cooling Tower 1shashankmay18No ratings yet
- Cooling Towers2Document5 pagesCooling Towers2shashankmay18No ratings yet
- Just A Random UploadDocument1 pageJust A Random Uploadshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Just A Random UploadDocument12 pagesJust A Random Uploadshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Cooling Towers4Document5 pagesCooling Towers4shashankmay18No ratings yet
- Cooling Towers3Document5 pagesCooling Towers3shashankmay18No ratings yet
- Just A Random UploadDocument1 pageJust A Random Uploadshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Cooling TowersDocument5 pagesCooling Towersshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Wet Cooling Towers1Document5 pagesWet Cooling Towers1shashankmay18No ratings yet
- AgeDocument1 pageAgeshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Dry Cooling Tower 1Document5 pagesDry Cooling Tower 1shashankmay18No ratings yet
- CompositesDocument25 pagesCompositesshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Wet Cooling Towers 2Document5 pagesWet Cooling Towers 2shashankmay18No ratings yet
- Fluidized Bed Combustion of Solid FuelsDocument10 pagesFluidized Bed Combustion of Solid Fuelsshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Combustion Mechanism, Combustion Equipment and Firing MethodsDocument5 pagesCombustion Mechanism, Combustion Equipment and Firing Methodsshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Cyclone FurnaceDocument6 pagesCyclone Furnaceshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Philosophical Perspectives: Prof. Kumar Neeraj Sachdev Department of Humanities and Social Sciences 6168-FDocument13 pagesPhilosophical Perspectives: Prof. Kumar Neeraj Sachdev Department of Humanities and Social Sciences 6168-Fshashankmay18No ratings yet
- IDocument1 pageIshashankmay18No ratings yet
- IDocument1 pageIshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Organizational DevelopmentDocument20 pagesOrganizational Developmentshashankmay18100% (1)
- Rajesh P Mishra 2152A: Classical Optimization TheoryDocument22 pagesRajesh P Mishra 2152A: Classical Optimization Theoryshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Lect 7Document15 pagesLect 7shashankmay18No ratings yet
- Lect 121Document13 pagesLect 121shashankmay18No ratings yet
- Game Theory: Strategies Selected by The AdversariesDocument54 pagesGame Theory: Strategies Selected by The AdversariesPotnuru VinayNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesFrom EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- FreeCAD | Step by Step: Learn how to easily create 3D objects, assemblies, and technical drawingsFrom EverandFreeCAD | Step by Step: Learn how to easily create 3D objects, assemblies, and technical drawingsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchFrom EverandCATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemFrom EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsFrom EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNo ratings yet
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationFrom EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SketchUp Success for Woodworkers: Four Simple Rules to Create 3D Drawings Quickly and AccuratelyFrom EverandSketchUp Success for Woodworkers: Four Simple Rules to Create 3D Drawings Quickly and AccuratelyRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeFrom EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersFrom EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsFrom EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesFrom EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyFrom EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Beginning AutoCAD® 2020 Exercise WorkbookFrom EverandBeginning AutoCAD® 2020 Exercise WorkbookRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Autodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)From EverandAutodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesFrom EverandHandbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Autodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersFrom EverandAutodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersNo ratings yet