Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electricity and Magnetism
Uploaded by
Darwin Lajato TipdasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electricity and Magnetism
Uploaded by
Darwin Lajato TipdasCopyright:
Available Formats
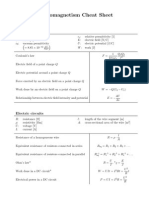
FORMULAS
in
ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM
CURRENT
where:
I = current, Amperes (A)
Q = electric charge, Coulombs (C)
t = time, seconds (s)
Note:
1 C = electrons
= protons
VOLTAGE
where:
V = voltage, Volts (V)
W = work, Joules (J)
Q = electric charge, Coulombs (C)
Note:
1 Volt (V) = 1 Joule (J) / Coulomb (C)
RESISTANCE
where:
R = resistance, Ohms ()
= resistivity or specific resistance, -m and -CM/ft units
L = length, meters (m) or feet (ft)
A = area of cross-section, and circular mil (CM) units
Note:
1 CM = /4 square mil
1 inch = 1000 mils
TEMPERATURE EFFECT ON RESISTANCES
where:
= initial temperature, C
= temperature at (positive for conductors, negative for insulators and approximately zero for some
alloys)
T = inferred absolute zero temperature
= -234.5 C for annealed copper
CONDUCTANCE
where:
G = conductance, Siemens (S) or mhos
R = resistance, Ohms ()
TRACTIVE FORCE OF A MAGNET
where:
F = force, Newtons (N)
A = total area of contact ()
B = flux density (Wb/ or T)
= absolute permeability or permeability of free space or vacuum
= H/m
FORCE BETWEEN TWO PARALLEL CONDUCTORS
where:
F = force, Newtons (N)
l = length of each conductors in meters
d = distance between conductors in meters
= current carried by conductor A
= current carried by conductor B
FORCE OF ATTRACTION OR REPULSION BETWEEN
MAGNETIC POLES
where and are the magnetic pole strengths in Weber (Wb)
d = distance between poles in m
k = proportionality constant
where:
= relative permeability
= absolute permeability or permeability of free space or vacuum
= H/m
MAGNETIC FLUX DENSITY
where:
B = magnetic flux density, Weber/meter (Wb/m) or Tesla (T)
= magnetic flux, Weber (Wb)
A = area, square meter
RELUCTANCE
where:
R = reluctance, (
L = length of magnetic path, m
A = area of cross-section,
= permeability of material, H/m
mmf = magnetomotive force
= magnetic flux, Weber (Wb)
You might also like
- CH 20-35 Physics NotesDocument7 pagesCH 20-35 Physics NotesMichael BlairNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 9 FormulasDocument13 pagesPhysics Class 9 FormulasJatin Gupta73% (63)
- Physics Formulas & SI UnitDocument14 pagesPhysics Formulas & SI Unitönemsiz biriNo ratings yet
- Magnetic FieldsDocument29 pagesMagnetic FieldsNatassja AshleyNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Electrical Cheat SheetDocument10 pagesElectrical Cheat SheetNarcisa RudnicNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument40 pagesDocumentHaseeb AhemdaniNo ratings yet
- B. Electricity - Basic PrinciplesDocument4 pagesB. Electricity - Basic PrinciplesXyxy LofrancoNo ratings yet
- D.C. Machin BaidaDocument53 pagesD.C. Machin BaidaLeonard ValdezNo ratings yet
- Maths Application SumsDocument36 pagesMaths Application SumsBalakamuNo ratings yet
- BasicDocument10 pagesBasicAkram ElhdeeNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PDFDocument170 pagesUnit 2 PDFSaurabh RajNo ratings yet
- Ep&c2 El2Document16 pagesEp&c2 El2Jeffrey Wong QYNo ratings yet
- Category: Physics FormulasDocument24 pagesCategory: Physics FormulasKalpana ShankarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Electric Current & ResistivityDocument5 pagesChapter 8 - Electric Current & ResistivityFritz NatividadNo ratings yet
- Current Resistivity and ResistanceDocument36 pagesCurrent Resistivity and Resistancecarmela chanNo ratings yet
- Electromag Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesElectromag Cheat SheetAlex Muresan0% (1)
- Pre TaskDocument5 pagesPre Taskkevin narvaez henriquezNo ratings yet
- Transmitters and CalculationsDocument26 pagesTransmitters and CalculationsByond TheuniversNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics ProjectShivam JindalNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas: G G (1-d) RDocument6 pagesPhysics Formulas: G G (1-d) Ronewing949No ratings yet
- 1.1 Review of Magnetic Circuits and Its PropertiesDocument65 pages1.1 Review of Magnetic Circuits and Its PropertiesChimi WangmoNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 9 FormulasDocument13 pagesPhysics Class 9 FormulasEKLABAY SONINo ratings yet
- MAGNETIC CIRCUITS and PRINCIPLES OF MACHINERY SummaryDocument8 pagesMAGNETIC CIRCUITS and PRINCIPLES OF MACHINERY SummaryGIAN CARLO DONIDANo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas: G G (1-d) RDocument6 pagesPhysics Formulas: G G (1-d) RAitazaz AhsanNo ratings yet
- Eddy Current Inspection FormulaDocument4 pagesEddy Current Inspection FormulaUdhayakumar VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- Formulas For The Skin EffectDocument13 pagesFormulas For The Skin EffectzerferuzNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFormula SheetMax MartinNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Parameters RevisedDocument72 pagesTransmission Line Parameters RevisedrajuwithualwaysNo ratings yet
- Dkk01-Electrical Circuit AnalysisDocument42 pagesDkk01-Electrical Circuit AnalysisadhiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12.1 - Current, Resisitivity, and ResistanceDocument13 pagesLesson 12.1 - Current, Resisitivity, and ResistanceLaihcaNo ratings yet
- Flohberger ReportDocument26 pagesFlohberger Reportdivya AshishNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of ElectricityDocument18 pagesBasic Principles of ElectricityJohn Jacob TandangNo ratings yet
- Mod. 1 Basic ElectricalDocument21 pagesMod. 1 Basic Electricalderping lemon100% (1)
- Introduction To The Propagating Wave On A Single Conductor: Background & HistoryDocument30 pagesIntroduction To The Propagating Wave On A Single Conductor: Background & HistoryMagnethosNo ratings yet
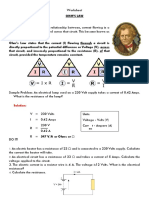
- Ohms Law Modular WorksheetDocument4 pagesOhms Law Modular WorksheetStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 IntroductionDocument33 pagesLesson 1 IntroductionEVITH BERNALDEZ. ALMONIANo ratings yet
- Main Lab Report1Document47 pagesMain Lab Report1sonalNo ratings yet
- Ch-3 - Current ElectricityDocument29 pagesCh-3 - Current Electricitygkgthe1No ratings yet
- Analogy of Thermal and Electrical ParametersDocument1 pageAnalogy of Thermal and Electrical ParametersVenkat BandapalleNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity (Theory)Document8 pagesCurrent Electricity (Theory)arshz100% (1)
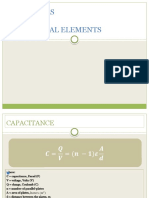
- Electrical ElementsDocument13 pagesElectrical ElementsDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument44 pagesElectricityKirancivilNo ratings yet
- Conductors, Dielectrics, and Capacitance PDFDocument115 pagesConductors, Dielectrics, and Capacitance PDFaelle00No ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument7 pagesCurrent Electricitylakhbhat2020No ratings yet
- Module1 TransmissionLinesDocument7 pagesModule1 TransmissionLinesFrancis LebadesusNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesFrom EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Physics Formula SheetDocument10 pagesPhysics Formula SheetAkash Akash PrakashNo ratings yet
- 17 Capacitors and Inductors in AC CircuitsDocument12 pages17 Capacitors and Inductors in AC CircuitsAbhijit PattnaikNo ratings yet
- EXP3Document13 pagesEXP3fairuz.binte.khaledNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Eletronic PrinciplesDocument206 pagesElectrical and Eletronic PrinciplesvelisbarNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A Spark Discharge As An Adjustable Acoustic Source For Scale Model MeasurementsDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of A Spark Discharge As An Adjustable Acoustic Source For Scale Model MeasurementsPanayiotis SeoolasNo ratings yet
- Assignment No11 NanoDocument5 pagesAssignment No11 Nanoarvind kumarNo ratings yet
- EEB326 Electrical Machines I - Lectures 1-3-2013Document110 pagesEEB326 Electrical Machines I - Lectures 1-3-2013Derrick Maatla MoadiNo ratings yet
- MT22MVD018 Nano 11Document5 pagesMT22MVD018 Nano 11arvind kumarNo ratings yet
- Electric Current and Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesElectric Current and Ohm's LawSheldon MillerNo ratings yet
- Unit-III Fundamentals of Electromagnatism & Transformers: Magnetic CircuitDocument10 pagesUnit-III Fundamentals of Electromagnatism & Transformers: Magnetic CircuitPathan NagulMeeraNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper Applied Electromagnetic TheoryDocument2 pagesModel Question Paper Applied Electromagnetic TheoryakhilarajNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Advanced Router ConfigurationDocument3 pagesLab 2 - Advanced Router ConfigurationDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Continuation Report KBP Radio CodeDocument36 pagesContinuation Report KBP Radio CodeDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Part I From Article 18 To Article 33Document63 pagesPart I From Article 18 To Article 33Darwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Design Rules For MORBN20 Process PDFDocument5 pagesDesign Rules For MORBN20 Process PDFDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Piano Chord ChartDocument2 pagesPiano Chord Chartjosephdahiroc838467% (6)
- Tipdas Lab1Document4 pagesTipdas Lab1Darwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Course Number Description Grade Teacher Year Semester Units Finalgp Gpweight FinunitsDocument7 pagesCourse Number Description Grade Teacher Year Semester Units Finalgp Gpweight FinunitsDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- 2007 Broadcast Code Revised June 15 2011Document35 pages2007 Broadcast Code Revised June 15 2011Rayan NaluaNo ratings yet
- 8 10Document8 pages8 10Darwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- 1 7Document4 pages1 7Darwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- AUP Arduino Lab1 TipdasDocument4 pagesAUP Arduino Lab1 TipdasDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Ave Maria-F RamirezDocument3 pagesAve Maria-F RamirezDencio LardizabalNo ratings yet
- 11Document1 page11Darwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- RoboticsDocument20 pagesRoboticsDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Flow ChartDocument1 pageFlow ChartDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- 1 2Document8 pages1 2Darwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Advanced ElectronicsDocument2 pagesAdvanced ElectronicsDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Matlab Music SynthesisDocument11 pagesMatlab Music SynthesisDarwin Lajato Tipdas0% (1)
- Piano Chord ChartDocument2 pagesPiano Chord Chartjosephdahiroc838467% (6)
- Wireless Communication Final ProjectDocument34 pagesWireless Communication Final ProjectDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document4 pagesPart 1Darwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Electronic Door SecurityDocument2 pagesElectronic Door SecurityDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Design Proposal For Establishing A Company NetworkDocument1 pageDesign Proposal For Establishing A Company NetworkDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Adoptation Model Using Led Lamps at Buklod BahayanDocument41 pagesAdoptation Model Using Led Lamps at Buklod BahayanDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Part Ii. Awareness Level On The Use of Led Lamps Yes NoDocument2 pagesPart Ii. Awareness Level On The Use of Led Lamps Yes NoDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- MK8Document1 pageMK8Darwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- LED LampsDocument63 pagesLED LampsDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Advanced ElectronicsDocument2 pagesAdvanced ElectronicsDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Pass DoorDocument7 pagesPass DoorDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet
- Configure CiscoDocument1 pageConfigure CiscoDarwin Lajato TipdasNo ratings yet