0% found this document useful (0 votes)
274 views14 pagesPhysics Formulas & SI Unit
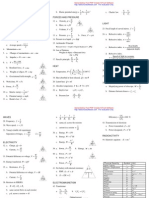
The document contains formulas from various scientific disciplines including thermodynamics, electricity, fluid mechanics, optics, and more. It provides the equations for calculating things like thermodynamic work and heat, electric field strength, fluid flow rates, lens magnification, and many other physical quantities. Over 50 different scientific formulas are presented in a concise list along with their variables and units.
Uploaded by
önemsiz biriCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
274 views14 pagesPhysics Formulas & SI Unit
The document contains formulas from various scientific disciplines including thermodynamics, electricity, fluid mechanics, optics, and more. It provides the equations for calculating things like thermodynamic work and heat, electric field strength, fluid flow rates, lens magnification, and many other physical quantities. Over 50 different scientific formulas are presented in a concise list along with their variables and units.
Uploaded by
önemsiz biriCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd