Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IGSCE CIE Formulae
Uploaded by
AKSHARA BALU [PPSB-BD010]Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IGSCE CIE Formulae
Uploaded by
AKSHARA BALU [PPSB-BD010]Copyright:
Available Formats
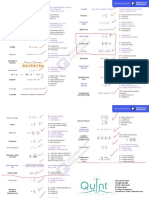
Physics IGCSE Formula
ρ(rho) = density (kg/m3
or g/cm3)
Density m = mass (kg or g) s-t graph Area under s-t graph = distance Area of trapezium =1/2× (a+b)×h
V = volume (m3 or cm3) a and b are parallel sides
Constant Speed S = speed (m/s) P = pressure (Pa=Pascal or N/m2)
Pressure
(only) D = distance (m) F = force (N)
t = time (s) A = area (m2)
Pressure in ρ = density (kg/m3)
Average speed = (u + v)/2 liquid g = gravity = 10 m/s2
Average speed
u = initial speed (m/s) h = height or depth (m)
v = final speed (m/s)
P = pressure(Pa)
Boyle’s law
a = acceleration (m/s2) V = volume(m3)
Acceleration u = initial velocity (m/s)
v = final velocity (m/s)
V = volume(m3)
Charles’ law
T = temperature(K=Kelvin)
Newton’s 2nd F = force (N)
law m = mass(kg)
a = acceleration (m/s2) P = pressure(Pa)
Pressure law
T = temperature(K)
W = weight (N)
Weight
g = gravity (m/s2) = 10 m/s2 P = pressure(Pa)
m = mass (kg) T = temperature(K)
Gas law
V = volume(m3)
F = Force (N)
Moment
d = perpendicular distance from W = work done (J=joule)
pivot (m or cm) F = force(N)
Work done
d = distance moved in direction of
principle of force (m)
moment
Q = heat energy(J)
Specific Heat
p = momentum (kgm/s) m = mass(kg)
capacity
m = mass (kg) c = specific heat capacity(J/kg C°)
Momentum ΔT = change in temperature (C°)
v = velocity (m/s)
I = Impulse (Ns or kgm/s) Q = heat energy (J)
m = mass (kg) Specific Latent
m = mass(kg)
Impulse u = initial velocity (m/s) heat
L = specific latent heat (J/kg)
v = final velocity (m/s)
F = Force (N) Thermal Q = heat energy(J)
t = time (s) Capacity C = Thermal capacity(J/C°)
ΔT = change in temperature (C°)
D-t graph Gradient of D-t graph = speed
GPE = gravitational potential
Gravitational energy (J)
s-t graph Gradient of s-t graph = acceleration potential energy g = gravity (10 m/s2)
h = height (m)
Physics IGCSE CIE Formula
KE = kinetic energy(J)
P = Power (W or J/s)
Kinetic energy m = mass(kg)
V = Voltage (V)
v = velocity(m/s)
Electrical Power I = Current (A)
R = Resistance (Ω)
P=power (W=Watt or J/s)
Power t = time (s)
E = energy or Work done(J)
t = time(s) Combine
resistance in
Eout = useful energy output (J) series circuit
Efficiency Ein = energy input(J)
Pout = power output(W) Don’t forget to flip it back.
Pin = power input(W) Combine
For 2 resistors
resistance in
f = frequency(Hz=hertz) parallel circuit
Frequency
T = time period(s)
n1 = no. of turns in primary
v = velocity of wave (m/s) n2 = no. of turns in secondary
Wave equation f = frequency (Hz) Transformer
V1 = voltage input
λ(lambda) = wavelength (m) V2 = voltage output
n1 = refractive index in medium 1
Refractive index n2 = refractive index in medium 2 I1 = current input(A)
(no unit) θ i= angle of incidence Transformer I2 = current output(A)
θr = angle of refraction (Efficiency V1 = voltage input(V)
refractive index in air = 1 100%) V2 = voltage output(V)
Refractive index speed of light in vacuum = 3×108
(n) m/s ≈ in air
θc = critical angle
Critical angle
n = refractive index
I = current (A or C/s)
Current (I) Q = charge (C=coulomb)
t = time (s)
V = voltage or Potential Difference
Voltage or (V or J/V)
Potential E = energy (J)
Difference (V) Q = charge (C)
V = voltage(V)
Ohm’s law
I = current(A)
R = resistance (Ω = Ohm)
You might also like
- Constant Speed (Only) Pressure: Density S-T GraphDocument2 pagesConstant Speed (Only) Pressure: Density S-T GraphmncbdlaNo ratings yet
- Constant Speed (Only) Pressure: Density S-T GraphDocument2 pagesConstant Speed (Only) Pressure: Density S-T GraphTxiped DxippNo ratings yet
- IGSCE-CIE-formula 2023Document2 pagesIGSCE-CIE-formula 2023Nour MuneerNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics FormulaeDocument2 pagesIGCSE Physics FormulaeelizabethNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics FormulaeDocument1 pageIGCSE Physics FormulaewidzoNo ratings yet
- Master Formula SheetDocument4 pagesMaster Formula SheetAmal Irshad100% (1)
- Matter and Energy II FormDocument17 pagesMatter and Energy II FormPaulNo ratings yet
- Equation SheetDocument7 pagesEquation SheetHe WhcsNo ratings yet
- Equations in PhysicsDocument2 pagesEquations in PhysicsDhruti MysoreNo ratings yet
- Igcse Physics FormulasDocument5 pagesIgcse Physics Formulasmohammad affan merchantNo ratings yet
- Igcse Physics All FormulasDocument4 pagesIgcse Physics All FormulasABDULLAHNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-01-23 at 9.26.22 AMDocument5 pagesScreenshot 2023-01-23 at 9.26.22 AMUmma HalimaNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionDocument4 pagesiGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionCamille67% (3)
- Physics Igcse All Imp FormulasDocument4 pagesPhysics Igcse All Imp FormulasDhruvil Desai100% (1)
- Igcse Physics All FormulasDocument4 pagesIgcse Physics All FormulasRichie Harvy77% (13)
- IGCSE Formula Booklet - PhysicsDocument1 pageIGCSE Formula Booklet - PhysicsgauthamNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Reference SheetDocument1 pagePhysical Science Reference Sheetmisterbrowner100% (1)
- OAT Bootcamp Physics Equation Sheet PDFDocument11 pagesOAT Bootcamp Physics Equation Sheet PDFjon100% (2)
- Bee6a674 Edexcel Igcse Physics Formula Sheet - WMDocument5 pagesBee6a674 Edexcel Igcse Physics Formula Sheet - WMcreepy carlieNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument7 pagesFormula SheetCarlos GómezNo ratings yet
- 0654 IGCSE Formulae (Equations)Document3 pages0654 IGCSE Formulae (Equations)BigBoiNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionDocument4 pagesiGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionYusuf100% (2)
- 0a. Equations Used in High School PhysicsDocument7 pages0a. Equations Used in High School PhysicsJo DiscordNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Formula Sheet 2Document2 pagesO Level Physics Formula Sheet 2Taha Maroof100% (1)
- Physics Formulas For JAMB Preparation: WhereDocument3 pagesPhysics Formulas For JAMB Preparation: WhereAhmad0% (1)
- Lengths To Be Measured Instruments AccuracyDocument2 pagesLengths To Be Measured Instruments AccuracyHomework SucksNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics Formulas PDFDocument2 pagesCSEC Physics Formulas PDFChloe Richardson100% (1)
- Physics Important ConceptsDocument2 pagesPhysics Important Conceptsazhar aliNo ratings yet
- Physics Important ConceptsDocument2 pagesPhysics Important Conceptsazhar aliNo ratings yet
- Physics Important ConceptsDocument2 pagesPhysics Important Conceptsazhar aliNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument2 pagesFormulasmandz27No ratings yet
- Important - Equations - in - Physics - For - IGCSE - Course-1 Too Imp 2Document5 pagesImportant - Equations - in - Physics - For - IGCSE - Course-1 Too Imp 2Eman HassanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Formula SheetDocument5 pagesIGCSE Physics Formula SheetBrandly NyamapnziNo ratings yet
- Physics-Ewanpdf 230529 084636Document17 pagesPhysics-Ewanpdf 230529 084636Ed Lawrence MontalboNo ratings yet
- Released Phys SciDocument24 pagesReleased Phys SciAnthony CharlesNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Formula BookletDocument4 pagesIGCSE Formula BookletNisalNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Revision 1278598555 Phpapp01Document2 pagesPhysics Formula Revision 1278598555 Phpapp01Nauman ShehryarNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula ListDocument2 pagesPhysics Formula ListMomeena Nouman100% (1)
- CIE IGCSE Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesCIE IGCSE Physics Formula SheetthusvigNo ratings yet
- Physics Review PapersDocument18 pagesPhysics Review Papersyoonmimikyaw2008No ratings yet
- Phy - Equation EditedDocument5 pagesPhy - Equation Edited908642256No ratings yet
- Let Me DownloadDocument5 pagesLet Me DownloadMyra TzqNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet (Motion)Document1 pageCheat Sheet (Motion)AOE SalmonellaNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheetPREM OfFiCiAlNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheeteltytanNo ratings yet
- O' Level Physics Formula Sheet: MeasurementsDocument2 pagesO' Level Physics Formula Sheet: MeasurementsXOXOuser39938No ratings yet
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheetJereme Cheong93% (56)
- Physics Formula Sheet For OlevelsDocument2 pagesPhysics Formula Sheet For OlevelsMomin BabarNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheetAukasha AhmedNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheetMomin BabarNo ratings yet
- The Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64From EverandThe Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Work Sample 2 - Eoc and CrucibleDocument35 pagesWork Sample 2 - Eoc and Crucibleapi-259791703No ratings yet
- VRARAIDocument12 pagesVRARAIraquel mallannnaoNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Wiring Degradation StudyDocument275 pagesAircraft Wiring Degradation Study320338No ratings yet
- Citibank CaseDocument6 pagesCitibank CaseLalatendu Das0% (1)
- Addendum ESIA Oct 2019Document246 pagesAddendum ESIA Oct 2019melkamuNo ratings yet
- DL Manual - Com Vs Controller Gs Driver p100 Operating ManualDocument124 pagesDL Manual - Com Vs Controller Gs Driver p100 Operating ManualThiago Teixeira PiresNo ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument3 pagesReaction PaperLois DolorNo ratings yet
- Bill of Quantities 16FI0009Document1 pageBill of Quantities 16FI0009AJothamChristianNo ratings yet
- Domesticity and Power in The Early Mughal WorldDocument17 pagesDomesticity and Power in The Early Mughal WorldUjjwal Gupta100% (1)
- Gobekli TepeDocument2 pagesGobekli TepeCarl Feagans100% (1)
- Operating Instructions: Rotary Lobe PumpDocument77 pagesOperating Instructions: Rotary Lobe PumpRuslan SlusarNo ratings yet
- Consumer Protection ActDocument34 pagesConsumer Protection ActshikhroxNo ratings yet
- Assignment November11 KylaAccountingDocument2 pagesAssignment November11 KylaAccountingADRIANO, Glecy C.No ratings yet
- Ferobide Applications Brochure English v1 22Document8 pagesFerobide Applications Brochure English v1 22Thiago FurtadoNo ratings yet
- CV Ashish PDFDocument3 pagesCV Ashish PDFRoshan KejariwalNo ratings yet
- Agenda - 2 - Presentation - MS - IUT - Thesis Proposal PPT Muhaiminul 171051001Document13 pagesAgenda - 2 - Presentation - MS - IUT - Thesis Proposal PPT Muhaiminul 171051001Tanvir AhmadNo ratings yet
- Catalogo PukangDocument41 pagesCatalogo PukangClarita Muller LeigueNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19 Code Standards and ReviewDocument27 pagesLecture 19 Code Standards and ReviewAdhil Ashik vNo ratings yet
- ARIIX - Clean - Eating - Easy - Ecipes - For - A - Healthy - Life - Narx PDFDocument48 pagesARIIX - Clean - Eating - Easy - Ecipes - For - A - Healthy - Life - Narx PDFAnte BaškovićNo ratings yet
- Aharonov-Bohm Effect WebDocument5 pagesAharonov-Bohm Effect Webatactoulis1308No ratings yet
- SHS G11 Reading and Writing Q3 Week 1 2 V1Document15 pagesSHS G11 Reading and Writing Q3 Week 1 2 V1Romeo Espinosa Carmona JrNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Doing Business in Grenada & OECSDocument14 pagesGuidelines For Doing Business in Grenada & OECSCharcoals Caribbean GrillNo ratings yet
- Module 7 NSTP 1Document55 pagesModule 7 NSTP 1PanJan BalNo ratings yet
- Ubicomp PracticalDocument27 pagesUbicomp Practicalvikrant sharmaNo ratings yet
- B-GL-385-009 Short Range Anti-Armour Weapon (Medium)Document171 pagesB-GL-385-009 Short Range Anti-Armour Weapon (Medium)Jared A. Lang100% (1)
- PM 50 Service ManualDocument60 pagesPM 50 Service ManualLeoni AnjosNo ratings yet
- FIREBASE Edited PresentationDocument12 pagesFIREBASE Edited PresentationNiraj MirgalNo ratings yet
- Bharti Airtel Strategy FinalDocument39 pagesBharti Airtel Strategy FinalniksforloveuNo ratings yet
- Libya AIP Part1Document145 pagesLibya AIP Part1Hitham Ghwiel100% (1)
- S-Sapfico-Satyanarayanamaterial 121212Document183 pagesS-Sapfico-Satyanarayanamaterial 121212mpsing1133No ratings yet