0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views18 pagesAverage Velocity and Limits Explained
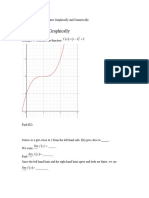
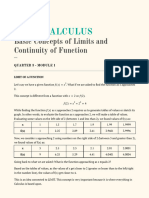
This document discusses average velocity and limits graphically and numerically. It defines average velocity as the distance traveled divided by the elapsed time. It also defines a limit as the value a function approaches as the input value approaches a given number. A limit may not exist if the function grows without bound as it approaches the given number. The formal definition of a limit states that for any epsilon value defining how close we want to get to the limit, there exists a corresponding delta value for how close we need to get to the input value.
Uploaded by
Engelbert AntodCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views18 pagesAverage Velocity and Limits Explained
This document discusses average velocity and limits graphically and numerically. It defines average velocity as the distance traveled divided by the elapsed time. It also defines a limit as the value a function approaches as the input value approaches a given number. A limit may not exist if the function grows without bound as it approaches the given number. The formal definition of a limit states that for any epsilon value defining how close we want to get to the limit, there exists a corresponding delta value for how close we need to get to the input value.
Uploaded by
Engelbert AntodCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd