Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tektronix - Oscilloscopes - Basic Features and Functions
Uploaded by
mikementzer1230 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageTektronix - Oscilloscopes - Basic Features and Functions
Uploaded by
mikementzer123Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
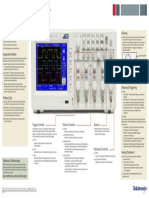
The Oscilloscope
Basic Features & Functions
Capturing Your Signal: 2 Aliasing
Easy as 1, 2, 3 Aliasing occurs when the oscilloscope does not sample
the signal fast enough to construct an accurate
1. Set the vertical scale (volts/div). waveform record. When this happens, the oscilloscope
2. Set the horizontal scale (sec/div). displays a waveform with a frequency lower than the
3. Set the trigger type, source and levels. actual input waveform, or triggers and displays an
unstable waveform.
Acquisition Modes Aliased Waveform
Determine how the oscilloscope digitizes the signal before 3 Aliased Waveform
displaying it. Typically chosen in the “Acquire” menu.
Sample: Samples are taken in evenly spaced intervals
1 4 Actual Waveform
Actual Waveform
to construct the waveform. This mode accurately
represents signals most of the time. To avoid aliasing, the oscilloscope must sample the
signal more than twice as fast as the highest frequency
Peak Detect: The highest and lowest values of the
component of the signal (Nyquist Theorem). Tektronix
input signal are captured and used to construct the oscilloscopes sample at least five times as fast as their
waveform. This mode will capture narrow pulses that highest bandwidth, substantially minimizing the chance
may be missed in Sample Mode. of aliasing.
Average: Several waveforms are acquired and
averaged point-by-point to obtain the average voltage
at each time sample in the acquisition. This mode is
Advanced Triggering
used to reduce random noise. Modes
- Auto Mode: The oscilloscope sweeps, even without
Probing Tips a trigger.
- Normal Mode: The oscilloscope only sweeps if the
Choose a probe that exceeds the signal’s bandwidth input signal reaches the set trigger point; otherwise
by 5 times for accurate reconstruction of the signal. the last acquired waveform remains on the display.
Remember to connect the probe’s ground clip to a - Single Sequence Mode: After a trigger is detected,
known ground in the circuit under test. Measuring the oscilloscope acquires and displays one
a signal requires two connections: the probe tip waveform.
connection and the ground connection. Coupling
Don’t forget to compensate passive voltage probes Note: Trigger coupling only affects the signal passed to the
to the oscilloscope. 1 Vertical Controls 2 Horizontal Controls 4 Trigger Controls trigger system, not the bandwidth or coupling of the signal
Position Position The trigger circuit acts as a comparator. When the signal on the screen.
- Moves the waveform up and down on the display. - Moves the waveform left and right on the display. matches the trigger setting, the oscilloscope generates a - DC Coupling: Passes all components of the signal.
trigger and captures the signal. Edge triggering is used - HF Reject: Attenuates the high frequency
Scale (Volts-Per-Division) Scale (Seconds-Per-Division)
most often; it captures the signal on a rising or falling edge. components of the signal.
- Varies the size of the waveform on the screen. - Determines the amount of time displayed.
Common settings for edge triggering are: - LF Reject: Blocks the DC component and attenuates
Bandwidth Limit the low-frequency components of the signal.
Source
- Limits the bandwidth of the oscilloscope to the - Noise Reject: Adds hysteresis to the trigger circuitry
frequency selected to reduce displayed noise. - Determines which signal is compared to the
to reduce the chance of falsely triggering on noise.
Restricts frequencies above the limit from being 3 Autoset trigger settings.
displayed and also from affecting the trigger. Level
Input coupling
Identifies the type of waveform and adjusts controls
- Determines where on the edge the trigger Having Problems?
to produce a usable display of the input signal.
point occurs. If you do not see a signal, check the following:
- Determines which part of the signal is displayed.
- DC Coupling: Shows all of the input signal. Slope - Is the channel on?
- Is the waveform off screen?
Tektronix Oscilloscopes - AC Coupling: Blocks the DC component of the
signal, centering the waveform at 0 volts.
- Determines whether the trigger point is on the rising
edge (positive slope) or the falling edge (negative - Adjust the vertical position and scale.
Tektronix’ oscilloscopes are easy-to-use, with dedicated slope) of a signal. - Adjust vertical coupling if the signal has a large
- Ground Coupling: Disconnects the input signal to
front-panel controls, automatic measurements, built-in FFT DC component.
show where 0 volts is on the screen.
and waveform math and intuitive user-interfaces. To find
If your waveform is indistinguishable, adjust the
which oscilloscope is right for you, visit us at:
horizontal scale.
www.tektronix.com/oscilloscopes
Copyright © 2010, Tektronix. All rights reserved. Tektronix products are covered by U.S. and foreign patents, issued and pending. Information in this
publication supersedes that in all previously published material. Specification and price change privileges reserved. TEKTRONIX and TEK are registered
trademarks of Tektronix, Inc. All other trade names referenced are the service marks, trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
08/10 EA 3GW-25714-0
You might also like
- Basic Features & Functions: Capturing Your Signal: Easy As 1, 2, 3 AliasingDocument1 pageBasic Features & Functions: Capturing Your Signal: Easy As 1, 2, 3 AliasingMinh LuanNo ratings yet
- 2-Pg Feature SummaryDocument2 pages2-Pg Feature Summaryqwert 12345No ratings yet
- Oscilloscope Parts and FunctionsDocument2 pagesOscilloscope Parts and Functionsxavier cabriaNo ratings yet
- Picoscope 6 PosterDocument1 pagePicoscope 6 PosterShiva GlennNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Charlotte VibracionesDocument1 pageTabla de Charlotte VibracionesXavier Diaz100% (1)
- Terminologie Osciloscoape PDFDocument20 pagesTerminologie Osciloscoape PDFRobertNo ratings yet
- Fong Godsill Icassp02Document4 pagesFong Godsill Icassp02IrenataNo ratings yet
- TS337A BrochureDocument2 pagesTS337A Brochuremoro2No ratings yet
- 1 Fase Cero MinimaDocument8 pages1 Fase Cero MinimaLaura AlvarezNo ratings yet
- KeySight - Oscilloscope Quick Setup Tips PosterDocument1 pageKeySight - Oscilloscope Quick Setup Tips PosterCA_KenNo ratings yet
- Automotive Oscilloscopes PosterDocument1 pageAutomotive Oscilloscopes PosterFernando Díaz Pérez100% (3)
- Keysight - TODAY'S OSCILLOSCOPEDocument1 pageKeysight - TODAY'S OSCILLOSCOPEraduseica100% (1)
- Advanced Wire Tracer Series: Locate and Trace Energized and De-Energized Wires, Automatically Identify BreakersDocument3 pagesAdvanced Wire Tracer Series: Locate and Trace Energized and De-Energized Wires, Automatically Identify Breakerskickone_No ratings yet
- MeasurIT FCI FLT93 - F S 0803Document1 pageMeasurIT FCI FLT93 - F S 0803cwiejkowskaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Phased Array Ultrasonic Technology Applications 26-30Document5 pagesIntroduction To Phased Array Ultrasonic Technology Applications 26-30Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Order Analysis PDFDocument2 pagesOrder Analysis PDFrizzo8No ratings yet
- AR6110/6110e User Guide: 30 Paces (90 Feet/28 Meters)Document2 pagesAR6110/6110e User Guide: 30 Paces (90 Feet/28 Meters)renspurNo ratings yet
- Varying Signa: Hold or Signal. 3) Ngs AdjustedDocument7 pagesVarying Signa: Hold or Signal. 3) Ngs AdjustedKeerthiSahaNo ratings yet
- Ditexscopebasics PDFDocument17 pagesDitexscopebasics PDFMaurihuaanaa Navarro Santana100% (1)
- Gamma Ray LogDocument13 pagesGamma Ray LogkittyiiiNo ratings yet
- Mechanics: Generating Circular and Straight Water WavesDocument4 pagesMechanics: Generating Circular and Straight Water WavesJeison BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Two-Way Radio: (High) P (Low)Document2 pagesTwo-Way Radio: (High) P (Low)Oliver Cruz AranibarNo ratings yet
- Oscilloscope Fundamentals Poster 3GW 60028 0 11x17Document1 pageOscilloscope Fundamentals Poster 3GW 60028 0 11x17scrt5No ratings yet
- TruMonitorSoftwareUserMan PDFDocument31 pagesTruMonitorSoftwareUserMan PDFSimurNo ratings yet
- 13monitoreo Vibracion AxialDocument27 pages13monitoreo Vibracion AxialJesus Omar Sagrero GomezNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Network of DSP Articles On WikipediaDocument1 pageKnowledge Network of DSP Articles On WikipediaHuJayNo ratings yet
- Monitoring-Times Magazine May 1996Document116 pagesMonitoring-Times Magazine May 1996Benjamin DoverNo ratings yet
- Oscilloscope For Circuits 2Document39 pagesOscilloscope For Circuits 2John GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Surveying ToolsDocument6 pagesSurveying ToolsAbigail Marie Therese FuentesNo ratings yet
- Re June 2014Document100 pagesRe June 2014indra_idroNo ratings yet
- Sa2100 Specs PDFDocument7 pagesSa2100 Specs PDFClases Estudiantiles ParticularesNo ratings yet
- Operation Matrix Node 1Document1 pageOperation Matrix Node 1brycuellarNo ratings yet
- Plakat Transient Immunity TestingDocument1 pagePlakat Transient Immunity TestingSKN PiorunNo ratings yet
- Analog Oscilloscope GOS SeriesDocument1 pageAnalog Oscilloscope GOS Seriesturboc201No ratings yet
- Singularity:) Keying Nyquist Sampling F-AliasingDocument47 pagesSingularity:) Keying Nyquist Sampling F-AliasingIra CervoNo ratings yet
- Gw-Instek C - 01-20Document10 pagesGw-Instek C - 01-20Jose M PeresNo ratings yet
- VSP Seismic OkDocument11 pagesVSP Seismic OkAlfi CahyaNo ratings yet
- AT-779UV: Instruction ManualDocument2 pagesAT-779UV: Instruction Manualكردن سيدي محمدNo ratings yet
- Installation - Kwh-3 Energy Meter: Reset To InstallDocument2 pagesInstallation - Kwh-3 Energy Meter: Reset To InstalldeetaufikNo ratings yet
- 40G/100G Transmitter Compliance TestingDocument2 pages40G/100G Transmitter Compliance Testingchuang xuNo ratings yet
- Fm/Am Clock Radio: Operating Instructions Bruksanvisning (På Baksidan)Document2 pagesFm/Am Clock Radio: Operating Instructions Bruksanvisning (På Baksidan)cesarbridesNo ratings yet
- 5989-8794EN - What Is The Difference Between An Equivalent Time Sampling Oscilloscope and A Real-Time Oscilloscope PDFDocument8 pages5989-8794EN - What Is The Difference Between An Equivalent Time Sampling Oscilloscope and A Real-Time Oscilloscope PDFskyhorseNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference Guide Maxtesterapplication Max-800 Series English - 1082519Document2 pagesQuick Reference Guide Maxtesterapplication Max-800 Series English - 1082519Abdulmoied OmarNo ratings yet
- TDS3086 January 2013 B - SFI Shock Finder ENDocument5 pagesTDS3086 January 2013 B - SFI Shock Finder ENjayesh gohilNo ratings yet
- EMMI RecordersDocument11 pagesEMMI RecordersMalyaj SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Waves: How Do Waves Travel Through Matter?Document4 pagesWaves: How Do Waves Travel Through Matter?ToyNerd Collectors100% (1)
- 101 11vibrating StringsSp17Document5 pages101 11vibrating StringsSp17beatrice odekaNo ratings yet
- Master The Basics - Oscilloscopes: Heng Wee BooDocument28 pagesMaster The Basics - Oscilloscopes: Heng Wee BooVo_Danh26No ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan 2018 - Physics F5Document12 pagesYearly Lesson Plan 2018 - Physics F5NikAkramRosliNo ratings yet
- OscilloscopeDocument7 pagesOscilloscopewaar lockNo ratings yet
- Tank InstrumentsDocument10 pagesTank InstrumentsihllhmNo ratings yet
- HiZ Faults RecentUtilityExperiencepaperDocument13 pagesHiZ Faults RecentUtilityExperiencepaperDiego José Sandoval AráuzNo ratings yet
- Find & Fic Jdsu PDFDocument1 pageFind & Fic Jdsu PDFoscarNo ratings yet
- IQ2020 - Slides Block 1Document3 pagesIQ2020 - Slides Block 1Mama PigNo ratings yet
- Duplichecker Plagiarism ReportDocument2 pagesDuplichecker Plagiarism ReportJedidiah KoscaNo ratings yet
- Tides: Output Modes Audio Rate OperationDocument2 pagesTides: Output Modes Audio Rate OperationjsjsNo ratings yet
- Boss WL-20Document1 pageBoss WL-20Anonymous 4FVm26mbcONo ratings yet
- Radio Electronics August 1989 PDFDocument100 pagesRadio Electronics August 1989 PDFPierDonneeNo ratings yet
- Guidance On Essay Preparation: Code 00098GDocument3 pagesGuidance On Essay Preparation: Code 00098GJonathan JoesNo ratings yet
- The Old Testament Apocrypha and The Old Testament CanonDocument19 pagesThe Old Testament Apocrypha and The Old Testament CanonSamuel E. Ricra-TimanaNo ratings yet
- Design Approaches and Tools in Education and TrainingDocument296 pagesDesign Approaches and Tools in Education and Trainingmutia febri mouliNo ratings yet
- Linkbelt Rough Terrain Crane RTC 8025 II RTC 8030 II Service ManualDocument22 pagesLinkbelt Rough Terrain Crane RTC 8025 II RTC 8030 II Service Manualjilljames090502dze100% (106)
- Quiz 1 - Semana 1 - PDFDocument6 pagesQuiz 1 - Semana 1 - PDFLeonardo AlzateNo ratings yet
- Chapter One The Problem and Its SettingDocument68 pagesChapter One The Problem and Its SettingAce Brian Laraño100% (1)
- Prelim Task De-Vera Angela-KyleDocument6 pagesPrelim Task De-Vera Angela-KyleJohn Francis RosasNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Analysis of The Factors Affecting The Academic Performance in Mathematics of Bsed Math Students of The Polytechnic University of The Philippines Taguig During Covid 19 PandemicDocument105 pagesGroup 2 Analysis of The Factors Affecting The Academic Performance in Mathematics of Bsed Math Students of The Polytechnic University of The Philippines Taguig During Covid 19 PandemicPamela GalveNo ratings yet
- Havells - ProfessionalLuminaires Price ListDocument80 pagesHavells - ProfessionalLuminaires Price ListSuper UserNo ratings yet
- History of Science in The Modern Age: ReadingDocument4 pagesHistory of Science in The Modern Age: ReadingDebashis ChakrabrtyNo ratings yet
- Nternational Phonetic AlphabetDocument3 pagesNternational Phonetic AlphabetFerry SahraNo ratings yet
- Gladys PDFDocument4 pagesGladys PDFUNEXPECTEDNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument102 pagesBlood TransfusionhatirebNo ratings yet
- Interpretation When Layers Are Dipping - Geophysics For Practicing Geoscientists 0.0Document5 pagesInterpretation When Layers Are Dipping - Geophysics For Practicing Geoscientists 0.0abd_hafidz_1No ratings yet
- (PD ISO GUIDE 30) - Reference Materials. Selected Terms and DefinitionsDocument16 pages(PD ISO GUIDE 30) - Reference Materials. Selected Terms and DefinitionsCarolinaNo ratings yet
- BMS Brand ManagementDocument15 pagesBMS Brand ManagementRaviNo ratings yet
- Combinatorial Chemistry Amp High Throughput Screening PDFDocument2 pagesCombinatorial Chemistry Amp High Throughput Screening PDFLamarcusNo ratings yet
- Insulin, Oral Hypoglycaemic Agents, GlucagonDocument63 pagesInsulin, Oral Hypoglycaemic Agents, GlucagonBhavesh kunvarNo ratings yet
- (Advances in Parasitology Volume 86) Kramer, Randall - Yang, Wei-Zhong - Zhou, Xiao-nong-Malaria Control and Elimination Programme in The People's Republic of China-Academic Press, Elsevier (2014)Document448 pages(Advances in Parasitology Volume 86) Kramer, Randall - Yang, Wei-Zhong - Zhou, Xiao-nong-Malaria Control and Elimination Programme in The People's Republic of China-Academic Press, Elsevier (2014)Stoian Goranov100% (1)
- Accountable Talk RubricDocument1 pageAccountable Talk RubricLauren K100% (1)
- Theme: Is Cell Phone Dangerous? Speaker 1 Positive TeamDocument4 pagesTheme: Is Cell Phone Dangerous? Speaker 1 Positive TeamLILIS ROHAYATINo ratings yet
- Strategic DissonanceDocument29 pagesStrategic DissonanceDamian Flori AlinaNo ratings yet
- Causes of The Trojan War PDFDocument3 pagesCauses of The Trojan War PDFTanaya DeoNo ratings yet
- Ifa Tourneeausstellungen 2021 ENDocument112 pagesIfa Tourneeausstellungen 2021 ENsextoNo ratings yet
- The Miracle Morning - The Not-So-Obvious Secret Guaranteed To Transform Your Life Before 8amDocument1 pageThe Miracle Morning - The Not-So-Obvious Secret Guaranteed To Transform Your Life Before 8amPrashanth Bangalore100% (5)
- Catullus Si LucretiusDocument2 pagesCatullus Si LucretiusAntonia MuraruNo ratings yet
- Cue Card English International WeddingDocument2 pagesCue Card English International WeddingTA Kab JombangNo ratings yet
- Booker T. Washington and W. E. B. DuBois EssayDocument5 pagesBooker T. Washington and W. E. B. DuBois Essaydaliahbcap201650% (2)
- Syllabus Master RepsolDocument96 pagesSyllabus Master RepsolsdfjkasNo ratings yet