COMMUNICATION BASED TRAIN
CONTROL
PRESENTED BY,
VIPIN V
vipinquilon@[Link] 1
� TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction
Train control
Train control block diagram
Existing system
CBTC block diagram
Trainborne equipments
Message formats
Communication systems
Advantages & disadvantages
Reference
2
� INTRODUCTION
• Communication-based train control (CBTC) is an automated
control system for railways that ensures the safe operation of
rail vehicles using RF data communication between various
control entities that make up the system.
• CBTC is a modern successor of the traditional railway signaling
systems which provide a limited control using track circuits ,
interlocking , and signals.
3
�TRAIN CONTROL
[Link] Protection
[Link] Operation
[Link] Supervision
4
�[Link] PROTECTION
•Train detection
•Train separation
•Route interlocking
•Overspeed protection
•Train and track surveillance
5
�[Link] OPERATION
•Train starting
•Train speed regulation
•Train stopping
6
�[Link] SUPERVISION
•Schedule design and implementation
•Route assignment
•Performance monitoring
7
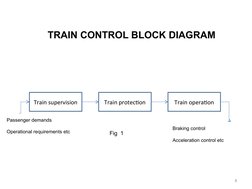
� TRAIN CONTROL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Train supervision Train protection Train operation
Passenger demands
Braking control
Operational requirements etc Fig 1
Acceleration control etc
8
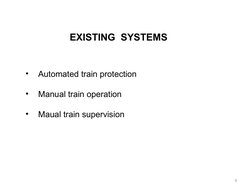
� EXISTING SYSTEMS
• Automated train protection
• Manual train operation
• Maual train supervision
9
� SIGNALING SYSTEMS
• Give visual display of track conditions
• Operate devices according to these signals
10
� BLOCK
•Fixed block : block have fixed length.
•Moving block: computers calculate block distance
(CBTC), Can increase track capacity
Only one train at a block
Low speed
Fig 2
11
� TRAIN DETECTION
1. Track circuits
2. Axle counters
In CBTC function of both are doing by trasponders called TAGS
12
� [Link] UNOCCUPIED
insulated
Fig 3
13
�[Link] OCCUPIED
Fig 4
14
� [Link] COUNTERS
comparator
counter counter
1 2
Axile couters have many advantages over track ciruit.......
Fig 5
15
�For giving visual identification of ahead track
[Link] SIGNALLING
Fig 6
16
� [Link] SIGNALLING
Modified cab signaling is Used in CBTC.
Fig 8
17
�CAB SIGNALLING
Fig 9
18
�[Link] SIGNALLING
1. Clear display of track conditions
2. Can used with CBTC
3. Can used for high speed raiway
4. Free from fog, rain, and snow
Fig 7
19
� INTERLOCKING
An interlocking is an arrangement of signals and signal
appliances so interconnected that functions must succeed
each other in a predetermined sequence, thus permitting safe
train movements along a selected route without collision.
20
� INTERLOCKING
Train 1 Train 2
Interlocking
device
Fig 10
•Mechanical interlocking
•Electro-mechanical interlocking
•Electronic interlocking (used in CBTC)
21
�CBTC PROVIDES
[Link] automated remote Train Protection
2. Automatic Train Operation
3. Automatic Train Supervision
22
�CBTC BASIC FUNCTIONAL ARCHITECTURE
Fig 11
23
� CBTC BASIC FUNCTIONAL ARCHITECTURE
[Link] unit
Interrogator antenna (AI)
Antenna (A)
Trainborne equipments
24
� CBTC BASIC FUNCTIONAL ARCHITECTURE
2. Wayside units
RF trasmitting cables
Optical fiber cables
Inter locking and other control equipments
25
� CBTC BASIC FUNCTIONAL ARCHITECTURE
2. Control centers
Base data radio (BDR)
User terminal (UT)
System controller (SC)
communication controller (CC)
communication equipments (CE)
26
�CBTC BLOCK DIAGRAM
Fig 12
27
� TRAINBORNE EQUIPMENTS
On board computers (OBC)
Mobile data radio (MDR)
Control unit(CU)
28
�TRAINBORNE EQUIPMENTS
Fig 13
29
� TRAIN – TRAIN COMMUNICATION
Train 1 Train 2
Train 3
Fig 14
30
� WAYSIDE TO TRAIN MESSAGE FORMAT
Fig 15
N :train number
Nc :cab number
Xe :tocken number
Nr :BDR identification number
L :train length
Vob :obstacle speed
Dp :direction of motion
ES :emergency stop
31
� TRAIN TO WAYSIDE MESSAGE FORMAT
Fig 17
N :train number
Nc :cab number
Xi :tag number
Xj :distance from tag
Lt :train length
Vt :train speed
M :mode of operation
BR :brake state
32
�COMMUNICATIONS CHANNEL ARCHITETURE
Fig 18
33
� COMMUNICATIONS STANDARDS
Protocol using : high data link connection (HDLC)
Fig 19
34
� COMMUNICATIONS STANDARDS
Type of link : fullduplex type
Digital modulation Methods : BFSK
Channel access method : CDMA
35
� ADVANTAGES
1. Increased rail capacity through closer train operation
2. Improved efficiency and flexibility ofthe rail network
3. Improved service reliability
4. Increased safety
5. Reduced operation and maintenance cost for the trackside infrastructure
36
� DISADVANTAGES
1. Complex system
2. Intial cost high
3. Need experienced workers
37
� REFERENCES
What is communication-based train control?, Rober d pascoe and Thomas, IEEE 2009
Development of the communications-based train control system for Moscow Metro ,
Minin, V.A.; Shishliakov, V.A.; Holyoak, IEEE 2007
Towards modeling and evaluation of availability of communication based train control
(CBTC) system, Hongli Zhao, Tianhua Xu. IEEE 2009
Evolution of Communication Based Train Control worldwide , Morar s, IEEE 2010
Automatic restart for communication based train control systems, Mirtchev, IEEE 2005
38
�39