Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem34 p119
Problem34 p119
Uploaded by
IENCSOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem34 p119
Problem34 p119
Uploaded by
IENCSCopyright:
Available Formats
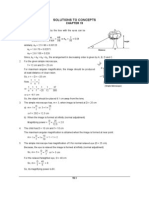
34.
119: a) People with normal vision cannot focus on distant objects under water
because the image is unable to be focused in a short enough distance to form on the
retina. Equivalently, the radius of curvature of the normal eye is about five or six times
too great for focusing at the retina to occur.
b) When introducing glasses, let’s first consider what happens at the eye:
n a nb nb − n a 1.33 1.40 0.07
+ = ⇒ + = ⇒ s 2 = −3.00 cm. That is, the
s 2 s ′2 R s2 2.6 cm 0.74 cm
object for the cornea must be 3.00 cm behind the cornea. Now, assume the glasses are
2.00 cm in front of the eye, then:
1 1 1 1 1 1
s1′ = 2.00 cm + s 2 = 5.00 cm ⇒ + = ⇒ + = ⇒ f1′ = 5.00 cm.
s1 s1′ f 1′ ∞ 5.00 cm f 1′
This is the focal length in water, but to get it in air, we use the formula from
n − nliq 1.52 −1.333
Problem 34.98: f 1 = f1′ = (5.00 cm ) = 1.34 cm .
n liq ( n −1)
1 . 333 (1 . 52 −1)
You might also like
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Physics-Investigatory LASYA PRIYA PDFDocument24 pagesPhysics-Investigatory LASYA PRIYA PDFLasya notes100% (2)
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectAvani GuptaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Interference PatternsDocument8 pagesInterference PatternsAsa mathewNo ratings yet
- Zemansky Capitulo 34 Solucionario (Farfismat)Document42 pagesZemansky Capitulo 34 Solucionario (Farfismat)Rubén Lucas Flores Ayala100% (4)
- Problem34 p112Document1 pageProblem34 p112IENCSNo ratings yet
- Abc Part 29Document1 pageAbc Part 29Ilias AchhabNo ratings yet
- Solutions 17Document7 pagesSolutions 17Patrick GareauNo ratings yet
- Cwps-Refraction at Spherical Surfaces & Lenses - SolutionsDocument12 pagesCwps-Refraction at Spherical Surfaces & Lenses - Solutionsthalassophobic11No ratings yet
- DPP - 07 (Solution) - Geometrical Optics NJ - 247Document5 pagesDPP - 07 (Solution) - Geometrical Optics NJ - 247gaurankkingNo ratings yet
- PHYS 202: Professor Stephen Thornton March 28, 2006Document41 pagesPHYS 202: Professor Stephen Thornton March 28, 2006SATYA NARAYAN SAHUNo ratings yet
- TUTO 1 Geometrical OpticsDocument10 pagesTUTO 1 Geometrical OpticsTuyenITNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful World: Question From Ncert TextbookDocument22 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful World: Question From Ncert TextbookNafees FarheenNo ratings yet
- Physics-ProjectDocument9 pagesPhysics-ProjectSindhuNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 SolutionsDocument5 pagesHomework 2 SolutionsggyulajNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument29 pagesNCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsVidyakulNo ratings yet
- Sunbeam School, Sultanpur: Subject: PhysicsDocument11 pagesSunbeam School, Sultanpur: Subject: PhysicsmitaliNo ratings yet
- Geometric OpticDocument8 pagesGeometric OpticSharonNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument9 pagesPhysics ProjectsamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Geometric Optics: CK-12 Physics Concepts - Intermediate Answer KeyDocument7 pagesChapter 14: Geometric Optics: CK-12 Physics Concepts - Intermediate Answer KeyRegine AngelesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Geometric Optics: CK-12 Physics Concepts - Intermediate Answer KeyDocument7 pagesChapter 14: Geometric Optics: CK-12 Physics Concepts - Intermediate Answer KeyRegine AngelesNo ratings yet
- Phys Int CC CH 14 - Geometric Optics - Answers PDFDocument7 pagesPhys Int CC CH 14 - Geometric Optics - Answers PDFRegine AngelesNo ratings yet
- PSC Assignment 6Document5 pagesPSC Assignment 6nsamkelo019No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectSourima DeyNo ratings yet
- Phy212 CH34 Worksheet-KeyDocument4 pagesPhy212 CH34 Worksheet-KeyAmirul Hissan Che RajjabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Optical InstrumentsDocument7 pagesChapter 19 Optical Instrumentsabbh07No ratings yet
- NEET Ray Optics Important Questions - Free PDF DownloadDocument28 pagesNEET Ray Optics Important Questions - Free PDF DownloadkavithavenkatesanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Thin LensesDocument25 pagesChapter 4 Thin LensesEric Doctore KrageNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Compress@BDocument8 pagesPhysics Project Compress@BDevansh RawatNo ratings yet
- Perhatikan Gambar Di Bawah Ini:: Analisis DataDocument3 pagesPerhatikan Gambar Di Bawah Ini:: Analisis DataseptiNo ratings yet
- Shan Armaine Cabela - Week 3 and 4 - Ligt As EM Wave and Plane MirrorDocument3 pagesShan Armaine Cabela - Week 3 and 4 - Ligt As EM Wave and Plane MirrorShan Armaine CabelaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 and 4 - Light As EM Wave and Plane MirrorDocument3 pagesWeek 3 and 4 - Light As EM Wave and Plane MirrorShan Armaine CabelaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solution Cbse Class 10 Sci Chap 10Document10 pagesNcert Solution Cbse Class 10 Sci Chap 10Lakshay MalikNo ratings yet
- Solutions PDFDocument5 pagesSolutions PDFrelcucNo ratings yet
- Light - Intext & ExerciseDocument8 pagesLight - Intext & ExerciseTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 01-05-2023 - INCOMING SR - CO-SUPER CHAINA STAR-II (NEW) - JEE MAIN MODEL-CTM - 3 - KEY&SOL PDFDocument8 pages01-05-2023 - INCOMING SR - CO-SUPER CHAINA STAR-II (NEW) - JEE MAIN MODEL-CTM - 3 - KEY&SOL PDFD. JivitesNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project: Year:-2017-2018Document18 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Year:-2017-2018Mohammad AyaanNo ratings yet
- Problem34 09Document1 pageProblem34 09IENCSNo ratings yet
- Optical Instruments Physics ProblemsDocument2 pagesOptical Instruments Physics ProblemsgatorpremedNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument11 pagesPhysics Projectadatta546No ratings yet
- 「9781337616249 - CalcMetric - Explorations.pdf」複本 的副本Document25 pages「9781337616249 - CalcMetric - Explorations.pdf」複本 的副本shawn wuNo ratings yet
- Sam Prince Franklin - 20MIS1115 - Physics Lab 7Document4 pagesSam Prince Franklin - 20MIS1115 - Physics Lab 7SamNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Physics Project PRDocument16 pagesToaz - Info Physics Project PRUtkarshNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument20 pagesPhysics Projectvishaljinjala7No ratings yet
- Geometrical OpticsDocument35 pagesGeometrical Opticsthinkiit90% (10)
- Physics Project MDocument20 pagesPhysics Project Mvishaljinjala7No ratings yet
- Physics (Investigatory Project)Document21 pagesPhysics (Investigatory Project)shreyamohanty298No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument20 pagesPhysics Projectvishaljinjala7No ratings yet
- General Chemistry NYA by Yann Brouillette Revised05 F2016Document229 pagesGeneral Chemistry NYA by Yann Brouillette Revised05 F2016Hoomehr TayariyanNo ratings yet
- Concave LensDocument17 pagesConcave LensMathiNo ratings yet
- Physics Project 3Document15 pagesPhysics Project 3SurianandhanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set in Science 10Document11 pagesProblem Set in Science 10Peter Jay CorrosNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project KENDRIYA VDocument17 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project KENDRIYA VNavneethan PillaiNo ratings yet
- CH 05Document34 pagesCH 05Atif AbbasiNo ratings yet
- SRN Class Xii PhyDocument16 pagesSRN Class Xii Phybabumohana1979No ratings yet
- Optical InstrumentsDocument11 pagesOptical InstrumentsPankaj MishraNo ratings yet
- Physics-Investigatory To Find The Refractive Indices of (A) Water (B) Oil (Transparent) Using A Plane Mirror, An Equiconvex LensDocument17 pagesPhysics-Investigatory To Find The Refractive Indices of (A) Water (B) Oil (Transparent) Using A Plane Mirror, An Equiconvex Lensnagendra.bncNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercises in Astronomy: Solutions and AnswersFrom EverandLaboratory Exercises in Astronomy: Solutions and AnswersNo ratings yet
- Problem21 p105Document1 pageProblem21 p105IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 p100Document1 pageProblem21 p100IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 98Document1 pageProblem21 98IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 p104Document1 pageProblem21 p104IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 85Document1 pageProblem21 85IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 p102Document1 pageProblem21 p102IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 99Document1 pageProblem21 99IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 86Document1 pageProblem21 86IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 p101Document1 pageProblem21 p101IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 93Document1 pageProblem21 93IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 88Document1 pageProblem21 88IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 89Document1 pageProblem21 89IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 95Document1 pageProblem21 95IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 94Document1 pageProblem21 94IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 75Document1 pageProblem21 75IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 77Document1 pageProblem21 77IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 91Document1 pageProblem21 91IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 79Document1 pageProblem21 79IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 87Document1 pageProblem21 87IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 82Document1 pageProblem21 82IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 80Document1 pageProblem21 80IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 68Document1 pageProblem21 68IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 74Document1 pageProblem21 74IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 73Document1 pageProblem21 73IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 69Document1 pageProblem21 69IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 72Document1 pageProblem21 72IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 71Document1 pageProblem21 71IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 66Document1 pageProblem21 66IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 70Document1 pageProblem21 70IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 64Document1 pageProblem21 64IENCSNo ratings yet