Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scan
Uploaded by
Friska Sidabutar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageBrain swelling occurs when the gyri become larger and sulci become smaller. The sylvian fissure separates the frontal and temporal lobes and contains carotid arteries that supply blood to the brain. Clots are characterized by size, symptoms, shifts in the brain, side affected, and site of clotting. Subfalcine herniation, significant midline shift to the left, and enlarged temporal horn on the contralateral side indicate intracerebral bleeding and hydrocephalus. Bleeding into the subarachnoid space is called subarachnoid hemorrhage, which is usually caused by aneurysm rupture and must be treated urgently to address the underlying aneurysm.
Original Description:
Original Title
scan
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBrain swelling occurs when the gyri become larger and sulci become smaller. The sylvian fissure separates the frontal and temporal lobes and contains carotid arteries that supply blood to the brain. Clots are characterized by size, symptoms, shifts in the brain, side affected, and site of clotting. Subfalcine herniation, significant midline shift to the left, and enlarged temporal horn on the contralateral side indicate intracerebral bleeding and hydrocephalus. Bleeding into the subarachnoid space is called subarachnoid hemorrhage, which is usually caused by aneurysm rupture and must be treated urgently to address the underlying aneurysm.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageScan
Uploaded by
Friska SidabutarBrain swelling occurs when the gyri become larger and sulci become smaller. The sylvian fissure separates the frontal and temporal lobes and contains carotid arteries that supply blood to the brain. Clots are characterized by size, symptoms, shifts in the brain, side affected, and site of clotting. Subfalcine herniation, significant midline shift to the left, and enlarged temporal horn on the contralateral side indicate intracerebral bleeding and hydrocephalus. Bleeding into the subarachnoid space is called subarachnoid hemorrhage, which is usually caused by aneurysm rupture and must be treated urgently to address the underlying aneurysm.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
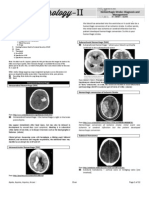
BRAIN SWELLING
The next important concept is this: whenever the brain swells, it means the gyri get larger and the sulci get smaller
The sylvian fissure separates the frontal and temporal lobes, and it is the area
through which the carotid arteries enter and supply the brain,
and hence the place to look for blood when we are looking for
Clots are defined by:
• Size
• Symptoms and signs
• Shifts
• Side
• site
I expected you to identify were
the subfalcine herniation, the significant midline shift to the left
and contralateral hydrocephalus indicated by the enlarged temporal
horn. All these featu
Bleeding into the subarachnoid space is called subarachnoid
haemorrhage to distinguish it from bleeding into the substance
of the brain proper, which is called intracerebral haemorrhage
or intracerebral haematoma. The distinction is important
because spontaneous subarachnoid haemorrhage is most frequently
caused by aneurysm rupture, which is fatal in one third
of cases. Second haemorrhages carry even a higher fatality rate,
hence it is imperative to detect any subarachnoid haemorrhage
and treat the underlying aneurysm
You might also like
- STROKE: Handbook with activities, exercises and mental challengesFrom EverandSTROKE: Handbook with activities, exercises and mental challengesNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Sub-arachnoid Hemorrhage, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Sub-arachnoid Hemorrhage, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- CT Scan BrainDocument3 pagesCT Scan BrainanggipuspaNo ratings yet
- 4.neurology II Hemorrhagic Stroke 2014ADocument12 pages4.neurology II Hemorrhagic Stroke 2014AAzman HakimNo ratings yet
- CT Scan NotesDocument97 pagesCT Scan NotesMr. Hrisab DebNo ratings yet
- Subdural HematomaDocument54 pagesSubdural HematomaNuzhat Noor Ayesha100% (1)
- CVA Bleed vs. InfarctDocument33 pagesCVA Bleed vs. InfarctPaul Henry RoxasNo ratings yet
- Head CT Scan: Dr. Rani MariaDocument42 pagesHead CT Scan: Dr. Rani MariaAnonymous byUCks0OUNNo ratings yet
- Basic Approch To CT BrainDocument62 pagesBasic Approch To CT BrainS B SayedNo ratings yet
- 1 Approachtoheadct 130418093230 Phpapp01Document71 pages1 Approachtoheadct 130418093230 Phpapp01Sikandar Shahzad YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Subdural HematomaDocument3 pagesSubdural HematomaAngga ToragarryNo ratings yet
- C.tscan Pathology by FaisalDocument82 pagesC.tscan Pathology by FaisaldrmalikarifNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Circulation and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)Document68 pagesCerebral Circulation and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)Hanung FirmanNo ratings yet
- Pe AneurruptDocument4 pagesPe Aneurruptrungthanaporn4No ratings yet
- Stroke HemoragikDocument34 pagesStroke HemoragikTeuku AndyNo ratings yet
- Intracranial HemorrhageDocument66 pagesIntracranial HemorrhageKaif Khan100% (1)
- CT ScanDocument84 pagesCT ScanHafiz Wajid SadiqNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid HaemorrhageDocument13 pagesSubarachnoid HaemorrhageTuliNo ratings yet
- Cerebral AneurysmsDocument45 pagesCerebral AneurysmsJerinNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Aneurysm: By: Cristi Ne Reyes Al-Sundal, RN, MN NCM 118 InstuctorDocument21 pagesCerebral Aneurysm: By: Cristi Ne Reyes Al-Sundal, RN, MN NCM 118 InstuctorVhince Norben PiscoNo ratings yet
- A Brain Hemorrhage Is A Type of StrokeDocument2 pagesA Brain Hemorrhage Is A Type of StrokeuzmajbnNo ratings yet
- Life Threatening Brain PathologiesDocument33 pagesLife Threatening Brain Pathologiesnithin shenoiNo ratings yet
- Intracranial Hemorrhage IntroDocument5 pagesIntracranial Hemorrhage IntroPat Vierneza-CalalangNo ratings yet
- DR HJ Asmah Yusuf SP - Rad DR Evo Elidar HRP SP - RadDocument86 pagesDR HJ Asmah Yusuf SP - Rad DR Evo Elidar HRP SP - RadnikiNo ratings yet
- The Radiology Assistant Traumatic Intracranial HemorrhageDocument1 pageThe Radiology Assistant Traumatic Intracranial HemorrhageMahmudah AlkatiriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document41 pagesLecture 3issrafil mussaNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage - Stroke (CVA) - Merck Manual Home Edition2Document8 pagesSubarachnoid Hemorrhage - Stroke (CVA) - Merck Manual Home Edition2Noval LiadyNo ratings yet
- What Is A Brain Aneurysm?Document2 pagesWhat Is A Brain Aneurysm?shinNo ratings yet
- The CNS CVADocument21 pagesThe CNS CVAfatima.noor0747No ratings yet
- Group 4 - Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument60 pagesGroup 4 - Hemorrhagic StrokeKitz T AnasarioNo ratings yet
- By. ScribdDocument3 pagesBy. Scribdchreazy__021906No ratings yet
- A Subdural HematomaDocument6 pagesA Subdural HematomaKal El DadiNo ratings yet
- Brain Aneurysm SummaryDocument3 pagesBrain Aneurysm SummaryEvaNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument3 pagesSubarachnoid Hemorrhagetenaj_purpleNo ratings yet
- 01 VascularDocument31 pages01 VascularMalinda KarunaratneNo ratings yet
- CT BRAIN AnatomyDocument32 pagesCT BRAIN AnatomydrsalilsidhqueNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain Injury: Department of Neurosurgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University Xu BinDocument95 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury: Department of Neurosurgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University Xu Binapi-19916399No ratings yet
- CT Head InterpretationDocument14 pagesCT Head InterpretationrutcinthamyNo ratings yet
- REPORTDocument34 pagesREPORTClaire GidoNo ratings yet
- MeningesDocument28 pagesMeningesayesha rajputNo ratings yet
- Head CT Scan PDFDocument89 pagesHead CT Scan PDFLiri AndiyaniNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Aneurysms: Aneurysms Posterior Circulation Basilar Artery Vertebral Arteries Posterior Communicating ArteryDocument10 pagesCerebral Aneurysms: Aneurysms Posterior Circulation Basilar Artery Vertebral Arteries Posterior Communicating ArteryRani SujithNo ratings yet
- Emergency Radiology Course - Brain, Bleed: 5 Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesEmergency Radiology Course - Brain, Bleed: 5 Review QuestionsEmaardiantariNo ratings yet
- Imaging in Acute StrokeDocument98 pagesImaging in Acute StrokeOmar Duran CastroNo ratings yet
- Brain VentriclesDocument40 pagesBrain Ventriclesahmad72 raza72No ratings yet
- Symptoms of A Subarachnoid HaemorrhageDocument1 pageSymptoms of A Subarachnoid HaemorrhageVivek BaligaNo ratings yet
- Stroke (Brain Attack) : Frontal Lobe (Blue)Document6 pagesStroke (Brain Attack) : Frontal Lobe (Blue)Pauline ChanNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Aneurysm: Mohamed Mamdouh Al-BannaDocument31 pagesCerebral Aneurysm: Mohamed Mamdouh Al-BannasharenNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument26 pagesSubarachnoid HemorrhageancillaagraynNo ratings yet
- Head Injury-1Document74 pagesHead Injury-1Aviral BishtNo ratings yet
- Epidural HematomaDocument33 pagesEpidural HematomaRupak GhimireNo ratings yet
- FINAL Imaging in Stroke - Haris & PuspaDocument45 pagesFINAL Imaging in Stroke - Haris & PuspaPuspa OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Perdarahan IntrakranialDocument21 pagesPerdarahan IntrakranialTyas RivaiNo ratings yet
- Approach To Head CTDocument31 pagesApproach To Head CTElisabeth F. Ojha100% (2)
- NeuroradiologyDocument25 pagesNeuroradiologysarguss14100% (2)
- Hydro Cep Hal UsDocument65 pagesHydro Cep Hal UsKrisna MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Venous InfaractDocument5 pagesVenous InfaractJuned A AnsariNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis FormatDocument2 pagesDifferential Diagnosis FormatRalph Francis Flores Palma100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)