Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brain Aneurysm Summary
Uploaded by
EvaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Brain Aneurysm Summary
Uploaded by
EvaCopyright:
Available Formats
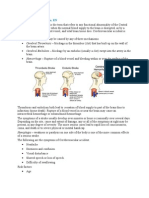
What is a cerebral aneurysm?
A cerebral aneurysm (also known as a brain aneurysm) is a weak or thin spot on an artery
in the brain that balloons or bulges out and fills with blood. The bulging aneurysm can put
pressure on the nerves or brain tissue. It may also burst or rupture, spilling blood into the
surrounding tissue (called a hemorrhage). A ruptured aneurysm can cause serious health
problems such as hemorrhagic stroke, brain damage, coma, and even death.
Cerebral aneurysms can occur anywhere in the brain, but most form in the major arteries
along the base of the skull.
Brain aneurysms can occur in anyone and at any age. They are most common in adults
between the ages of 30 and 60 and are more common in women than in men. People with
certain inherited disorders are also at higher risk.
What are the symptoms?
pain above and behind the eye
numbness
weakness
paralysis on one side of the face
a dilated pupil in the eye
vision changes or double vision.
double vision
nausea
vomiting
stiff neck
sensitivity to light
seizures
loss of consciousness (this may happen briefly or may be prolonged)
cardiac arrest.
How are aneurysms classified?
Type
hree types of cerebral aneurysms:
Saccular aneurysm. A saccular aneurysm is a rounded sac containing
blood, that is attached to a main artery or one of its branches.
Fusiform aneurysm. A fusiform aneurysm balloons or bulges out on all
sides of the artery.
Mycotic aneurysm. A mycotic aneurysm occurs as the result of an infection that can
sometimes affect the arteries in the brain
Size
Aneurysms are also classified by size: small, large, and giant.
How are cerebral aneurysms diagnosed?
Computed tomography (CT).
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Cerebral angiography.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis.
What are the complications of a ruptured
cerebral aneurysm?
After an aneurysm has ruptured it may cause serious complications such as:
Rebleeding. Once it has ruptured, an aneurysm may rupture again before
it is treated
Change in sodium level. Bleeding in the brain can disrupt the balance of sodium in the
blood supply and cause swelling in brain cells.
Hydrocephalus. Subarachnoid hemorrhage can cause hydrocephalus. Hydrocephalus is
a buildup of too much cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, which causes pressure that can lead
to permanent brain damage or death.
Vasospasm. This occurs frequently after subarachnoid hemorrhage when the bleeding
causes the arteries in the brain to contract and limit blood flow to vital areas of the brain.
Seizures. Aneurysm bleeding can cause seizures (convulsions),
How are cerebral aneurysms treated?
Treatments for unruptured and ruptured cerebral aneurysms
Surgery
Microvascular clipping. This procedure involves cutting off the flow of blood to the
aneurysm and requires open brain surgery. These procedures carry some risk such as
possible damage to other blood vessels, the potential for aneurysm recurrence and
rebleeding, and a risk of stroke.
Endovascular treatment
Platinum coil embolization. This procedure is a less invasive A doctor will insert a
hollow plastic tube (a catheter) into an artery, usually in the groin, and thread it through the
body to the brain aneurysm.
Flow diversion devices. Other endovascular treatment options include placing a small
stent (flexible mesh tube) similar to those placed for heart blockages, in the artery to
reduce blood flow into the aneurysm. his procedure is used to treat very large aneurysms
and those that cannot be treated with surgery or platinum coil embolization.
Other treatments
Antiseizure drugs (anticonvulsants).
Calcium channel-blocking drugs.
Rehabilitative therapy.
Individuals who have suffered a subarachnoid hemorrhage often need physical, speech,
and occupational therapy to regain lost function
You might also like
- STROKE: Handbook with activities, exercises and mental challengesFrom EverandSTROKE: Handbook with activities, exercises and mental challengesNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Disorders GuideDocument100 pagesNervous System Disorders GuidenipoNo ratings yet
- Ankle Block GuideDocument14 pagesAnkle Block GuideNur Aliah Amirah AmranNo ratings yet
- Disease of Nervous System Lect 2Document62 pagesDisease of Nervous System Lect 2Monirul IslamNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Cerebral Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Cerebral Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Aneurysm: TypesDocument12 pagesAneurysm: TypesSofia Isabelle GarciaNo ratings yet
- Assignment: ON Learning Resource MaterialDocument18 pagesAssignment: ON Learning Resource MaterialMegha lakraNo ratings yet
- Understanding Subdural Hematomas - Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument54 pagesUnderstanding Subdural Hematomas - Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentNuzhat Noor Ayesha100% (1)
- Brain Hemorrhage Symptoms: The Worst Headache of Your LifeDocument2 pagesBrain Hemorrhage Symptoms: The Worst Headache of Your LifeuzmajbnNo ratings yet
- Diajukan Untuk Memenuhi Salah Satu Tugas Profesi Ners Stase GADARDocument19 pagesDiajukan Untuk Memenuhi Salah Satu Tugas Profesi Ners Stase GADARFitria hs FitriaNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument18 pagesHemorrhagic StrokeNdan RahmaNo ratings yet
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesStroke PathophysiologyMaureen Balagtas89% (9)
- Cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVMDocument7 pagesCerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVMCj UritaNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terms: I. Anatomic VariationDocument8 pagesAnatomical Terms: I. Anatomic VariationNellen BastismoNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Disease Types and SymptomsDocument14 pagesCerebrovascular Disease Types and Symptomsbasinang_jangilNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Aneurysms: Aneurysms Posterior Circulation Basilar Artery Vertebral Arteries Posterior Communicating ArteryDocument10 pagesCerebral Aneurysms: Aneurysms Posterior Circulation Basilar Artery Vertebral Arteries Posterior Communicating ArteryRani SujithNo ratings yet
- Cerebral AneurysmsDocument45 pagesCerebral AneurysmsJerinNo ratings yet
- Cerebral AneurysmDocument6 pagesCerebral AneurysmNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Neurovascular Conditions Treated at PennDocument7 pagesNeurovascular Conditions Treated at PennFatrawati BahuaNo ratings yet
- Neurovascular DisordersDocument42 pagesNeurovascular DisordersAlexandra Nedelcoff-GhiranlieffNo ratings yet
- Neurovascular Conditions: Stroke and Transient Ischemic AttackDocument7 pagesNeurovascular Conditions: Stroke and Transient Ischemic AttackGinNo ratings yet
- Rle RequirementDocument101 pagesRle RequirementJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- By. ScribdDocument3 pagesBy. Scribdchreazy__021906No ratings yet
- Brain Aneurysm Artery Blood Brain Stroke Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument7 pagesBrain Aneurysm Artery Blood Brain Stroke Subarachnoid Hemorrhagebank bjbNo ratings yet
- AneurysmDocument7 pagesAneurysmLillabinNo ratings yet
- Intracranial Berry Aneurysm - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesIntracranial Berry Aneurysm - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAniket MittalNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage - Stroke (CVA) - Merck Manual Home Edition2Document8 pagesSubarachnoid Hemorrhage - Stroke (CVA) - Merck Manual Home Edition2Noval LiadyNo ratings yet
- What Is A Brain Aneurysm?Document2 pagesWhat Is A Brain Aneurysm?shinNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument29 pagesCerebrovascular DiseaseKamsha UyNo ratings yet
- Stroke: By: Georgina Vega Period 4 AnatomyDocument8 pagesStroke: By: Georgina Vega Period 4 AnatomyGina VegaNo ratings yet
- Types and Causes of Hemorrhagic StrokesDocument7 pagesTypes and Causes of Hemorrhagic StrokesRavinr9No ratings yet
- Brain AneurysmDocument2 pagesBrain Aneurysmmactrina100% (1)
- Stroke 1Document51 pagesStroke 1fatmaabdelazizNo ratings yet
- Regie Delariarte, Trexie Dipa - Khrystle Dote, Clarice Estores BN3A October 3, 2017Document4 pagesRegie Delariarte, Trexie Dipa - Khrystle Dote, Clarice Estores BN3A October 3, 2017random sharkNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument2 pagesCerebrovascular AccidenttintinlovessuNo ratings yet
- Case Study Cva Bleed (: Hemorrhagic Stroke)Document2 pagesCase Study Cva Bleed (: Hemorrhagic Stroke)itheclubhunterNo ratings yet
- C VADocument25 pagesC VAsudeepminz15No ratings yet
- Stroke Causes and TypesDocument9 pagesStroke Causes and TypesEmm Estipona HaoNo ratings yet
- Neuronal Pathways of Communication: Session 8Document84 pagesNeuronal Pathways of Communication: Session 8Michael MerlinNo ratings yet
- Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment of StrokesDocument1 pageCauses, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment of Strokeszairajoy07No ratings yet
- Understanding Cerebral AneurysmsDocument69 pagesUnderstanding Cerebral AneurysmsDiksha chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Stroke Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument2 pagesStroke Pa Tho PhysiologyBrandoSantosNo ratings yet
- OBCL 2 WEEK 2 AneurysmDocument11 pagesOBCL 2 WEEK 2 AneurysmMichelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNo ratings yet
- Cva DocumentationDocument17 pagesCva DocumentationgannadortchNo ratings yet
- Cerebro Vascular AccidentDocument16 pagesCerebro Vascular Accidentaldrich_muncalNo ratings yet
- Cerebral-Vascular Diseases (CVD) Ischemic Heart Diseases (IHD)Document38 pagesCerebral-Vascular Diseases (CVD) Ischemic Heart Diseases (IHD)Faheem MusthafaNo ratings yet
- Anaphysio 9b Cva Bleed Vs InfarctDocument5 pagesAnaphysio 9b Cva Bleed Vs InfarctAngayan, Merry GraceNo ratings yet
- What Is StrokeDocument2 pagesWhat Is StrokeFatma Sari MasithaNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms of StrokeDocument3 pagesSigns and Symptoms of StrokeKen NethNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Aneurysm: By: Cristi Ne Reyes Al-Sundal, RN, MN NCM 118 InstuctorDocument21 pagesCerebral Aneurysm: By: Cristi Ne Reyes Al-Sundal, RN, MN NCM 118 InstuctorVhince Norben PiscoNo ratings yet
- Stroke, Meningitis, and Trauma Management ContactDocument61 pagesStroke, Meningitis, and Trauma Management ContactUmar MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) : 51 CommentsDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) : 51 CommentsRona Vil Ramirez PeliñaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument1 pageCerebrovascular Accidentgeohanna_mariefNo ratings yet
- Stroke - FAST, Symptoms, Causes, Types, Treatment, PreventionDocument20 pagesStroke - FAST, Symptoms, Causes, Types, Treatment, PreventionMustafa AL ShlashNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Diseas1Document47 pagesCerebrovascular Diseas1Jenard Joniel OlivarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway of Acute Stroke: Renz Darwin C. CastañadayDocument32 pagesClinical Pathway of Acute Stroke: Renz Darwin C. CastañadayRenz CastañadayNo ratings yet
- Interventional NeuroradiologyDocument8 pagesInterventional NeuroradiologyAbhinav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Causes, Symptoms and Diagnosis of StrokeDocument7 pagesCauses, Symptoms and Diagnosis of StrokeRose SalviejoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Brain AVMDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Brain AVMCj UritaNo ratings yet
- Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Merck Manual Consumer VersionDocument3 pagesIntracerebral Hemorrhage: Merck Manual Consumer VersionAlamul HudaNo ratings yet
- Symptoms:: Focal Cerebral IschemiaDocument3 pagesSymptoms:: Focal Cerebral IschemiaPatricia JusufNo ratings yet
- Embolic strokes and arrhythmias risk factorsDocument7 pagesEmbolic strokes and arrhythmias risk factorsBemon Subico NelvinNo ratings yet
- Abaqus BioRID-II Crash Dummy ModelDocument7 pagesAbaqus BioRID-II Crash Dummy ModelAlex CarhatNo ratings yet
- Drug Free Pain Solution: Vibracool®Document8 pagesDrug Free Pain Solution: Vibracool®VUpendraNo ratings yet
- Proprioceptive ExercisesDocument5 pagesProprioceptive Exerciseswalaa eldesoukeyNo ratings yet
- 5.children With Physical ImpairmentDocument8 pages5.children With Physical ImpairmentJunadrian GenitoNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesEssentials of Anatomy and PhysiologyAlexandrea ModillasNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Sciences: Study To Reveal The Mandibular Fractures Pattern and Its EtiologyDocument6 pagesPharmaceutical Sciences: Study To Reveal The Mandibular Fractures Pattern and Its EtiologyVincent AriesNo ratings yet
- Maxigas mx104Document24 pagesMaxigas mx104Philippe jean-louisNo ratings yet
- The Flexion Gap in Normal Knees: An Mri StudyDocument4 pagesThe Flexion Gap in Normal Knees: An Mri StudyGERARDO TORRES RUIZNo ratings yet
- Medsurge 2Document10 pagesMedsurge 2LisaNo ratings yet
- VHIMS Dataset Manual 2021-22Document101 pagesVHIMS Dataset Manual 2021-22NeilNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 Notes FinalsDocument44 pagesNCM 116 Notes Finalsyra capiliNo ratings yet
- PhysiotherapyDocument47 pagesPhysiotherapyNaveen BasudeNo ratings yet
- Perkins 800d Series Industrial Engines Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument7 pagesPerkins 800d Series Industrial Engines Operation and Maintenance Manualrichard100% (43)
- Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Patton Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Patton Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFserenafinnodx100% (12)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - FractureDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - FractureAbdallah Alasal100% (1)
- Chapter 6. Overview of The Abdomen, Pelvis, and PerineumDocument5 pagesChapter 6. Overview of The Abdomen, Pelvis, and Perineumleafyislucky 91No ratings yet
- Ming MethodDocument2 pagesMing Methodwalterego58No ratings yet
- Guide to orthopedic examination of the forelimb in dogsDocument4 pagesGuide to orthopedic examination of the forelimb in dogsliz solanoNo ratings yet
- 5 Surgery PreTest Self-Assessment and Review 13th Edition-Pages-47-57,39-43Document16 pages5 Surgery PreTest Self-Assessment and Review 13th Edition-Pages-47-57,39-43Mae Rose Charlene MendozaNo ratings yet
- Hip Made Easy - 220509 - 180656Document29 pagesHip Made Easy - 220509 - 180656rizwan arshadNo ratings yet
- Bab 7 First AidDocument21 pagesBab 7 First AidNadirah KunNo ratings yet
- Los Angeles Personal Injury FundingDocument2 pagesLos Angeles Personal Injury Fundingjack leathersNo ratings yet
- Idoc - Pub Anatomy-Viva PDFDocument6 pagesIdoc - Pub Anatomy-Viva PDFhieulee84No ratings yet
- AO Trauma Asia Pacific Course Calendar 2023Document5 pagesAO Trauma Asia Pacific Course Calendar 2023reginapriscillaNo ratings yet
- Odontoid FractureDocument40 pagesOdontoid FractureMOHMAMMEDSNo ratings yet
- 541 - List of DayCare ProceduresDocument13 pages541 - List of DayCare ProceduresRAJNISHNo ratings yet
- Cuts, Scrapes and Abrasions (Exercises)Document5 pagesCuts, Scrapes and Abrasions (Exercises)Florinel OpreaNo ratings yet
- Acl-Prevention-Program PEPDocument10 pagesAcl-Prevention-Program PEPMohamed BoulahiaNo ratings yet