Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Social Psych Notes 01.24.11
Uploaded by
Jessica Boggs0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Social Psych notes 01.24.11
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesSocial Psych Notes 01.24.11
Uploaded by
Jessica BoggsCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Social Psych
1. Social Psych vs. Individual Differences Approach
a. We tend to think that behavior is mostly influenced by individual differences
i. Individual approach
1. Internal process out
2. Stable internal differences, no quick changes
ii. Social psychology
1. In certain situation most people act in a particular way
a. Situational
i. Important in determining behavior
2. Individual characteristics are overwhelmed by social situations
3. Bystander effect
a. The larger the number of people witnessing an emergency, the
less likely someone is to help/respond
4. Subtle changes can affect our behavior
2. Theoretical approaches
a. Role Theory
i. Sociology
ii. Particular contrast with the individual differences approach
iii. Most social behavior is a product of the roles that we take on at any given time
1. The student role
2. The sister role
3. The boss role
a. Shifting of gears as moving in and out of these different roles
b. Value is higher if playing the roles better
i. The higher the value the larger amount of flexibility a
given person has in their role
b. Learning emphasis
i. Reinforcement or reward of past behaviors
1. Rewards strengthen the response
2. Good/positive response more likely to repeat behavior
a. Doesn’t take much to be reinforced
3. Direct reinforcement
4. Modeling on imitation
a. Seeing other people react a certain way to certain behavior
5. People tend to copy behavior that they see
c. Cognitive approach
i. Emphasizes the importance of mental processes
1. Bias in thought processes – confirmation bias
ii. Controlled vs. Automatic responses
1. Controlled – explicit
2. Automatic – implicit
a. They can be conflicting
b. Doesn’t mean incorrect, can actually be very accurate (more
often than not it is)
th
iii. 1/20 of a second can make judgments about facial features
1. The longer you think about it (controlled thinking)you can change ideas
2. 70% of winners from congressional elections were chosen based on
“competency” in 1/20th second flashes
d. Evolutionary theory
i. Social behavior is substantially a product of natural selection over the course of
evolution
ii. Biologically hardwired
You might also like
- How We Change Volume 1: Theories of ChangeFrom EverandHow We Change Volume 1: Theories of ChangeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Chapter 14 Social PsychologyDocument4 pagesChapter 14 Social PsychologyAfiya KhanNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 03.02.11Document3 pagesSocial Psychology Notes 03.02.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 1.31.11Document2 pagesSocial Psychology Notes 1.31.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology OutlineDocument4 pagesSocial Psychology OutlineKristen TillyerNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 03.09.11Document3 pagesSocial Psychology Notes 03.09.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Communications Chapter 4Document5 pagesInterpersonal Communications Chapter 4randomscribduser2012No ratings yet
- #51 Sampayan, Juliana P. 12 HUMSS A: Week 1 Continuing ActivitiesDocument4 pages#51 Sampayan, Juliana P. 12 HUMSS A: Week 1 Continuing ActivitiesNathanielNo ratings yet
- Attitude Notes For PostingDocument4 pagesAttitude Notes For PostingSteve Premier NaiveNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 02.21.11Document3 pagesSocial Psychology Notes 02.21.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Materi 4 - Prosocial Behavior - Bu LiliDocument13 pagesMateri 4 - Prosocial Behavior - Bu Lilinadeafebrilautari15No ratings yet
- Chapter I: Introduction (Day 1) Social Psychology (Allport) : A Person Influences A Group and Vice VersaDocument20 pagesChapter I: Introduction (Day 1) Social Psychology (Allport) : A Person Influences A Group and Vice VersaDenise DianeNo ratings yet
- General Psychology Notes - Social PsychologyDocument3 pagesGeneral Psychology Notes - Social PsychologySabahat TanoliNo ratings yet
- Psychological PerspectiveDocument10 pagesPsychological PerspectiveHelen SteinhoferNo ratings yet
- Mental Illness Schizophrenia - Greek For "Split" (From Reality) and "Mind"Document7 pagesMental Illness Schizophrenia - Greek For "Split" (From Reality) and "Mind"Alaina AndersonNo ratings yet
- UCSP Fourth Quarter Reviewer PDFDocument16 pagesUCSP Fourth Quarter Reviewer PDFPuyatnakoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Social PsychologyDocument8 pagesChapter 14: Social PsychologydanieljohnarboledaNo ratings yet
- AttitudeDocument5 pagesAttitudemaverickvivekNo ratings yet
- Psychology Chapter 19Document19 pagesPsychology Chapter 19Adam TillyaNo ratings yet
- PSY 704 Notes For Bandura LectureDocument6 pagesPSY 704 Notes For Bandura LectureAF Ann RossNo ratings yet
- Existentialism and Phenomenology (Social) Reconstructionism BehaviorismDocument1 pageExistentialism and Phenomenology (Social) Reconstructionism BehaviorismGlenn Ramesis PiadNo ratings yet
- What Is PerceptionDocument11 pagesWhat Is PerceptionNeha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Final Psych Study GuideDocument246 pagesFinal Psych Study Guidea_ronaghi100% (3)
- Psychology "Social Influence" 11/02/2010Document5 pagesPsychology "Social Influence" 11/02/2010Mike WazowskiNo ratings yet
- College of Criminal Justice Midterm Examination: Rizwoods CollegesDocument4 pagesCollege of Criminal Justice Midterm Examination: Rizwoods CollegesVin SabNo ratings yet
- Ethics Reviewer Midterm 1Document3 pagesEthics Reviewer Midterm 1smreyes0203No ratings yet
- 1 Test ReviewDocument2 pages1 Test ReviewChristian McDonaldNo ratings yet
- Diss Final ExamDocument3 pagesDiss Final ExamAngelou SantosNo ratings yet
- Psychology Applied To Modern Life Adjustment in The 21St Century 11Th Edition Weiten Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument39 pagesPsychology Applied To Modern Life Adjustment in The 21St Century 11Th Edition Weiten Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFdiemdac39kgkw100% (9)
- Introduction To Psychology-Exam 2 ReviewF20Document2 pagesIntroduction To Psychology-Exam 2 ReviewF20moNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document12 pagesChapter 4Tasfia MeherNo ratings yet
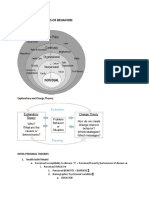
- Theories of Behavior:: Health Promotion The Ecological ModelDocument6 pagesTheories of Behavior:: Health Promotion The Ecological ModellizNo ratings yet
- Psy202 NotesDocument22 pagesPsy202 Notesleo mendozaNo ratings yet
- Discipline and Ideas in The Social Sciences Week 1, Quarter 2Document5 pagesDiscipline and Ideas in The Social Sciences Week 1, Quarter 2Jennie KimNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric NursingDocument13 pagesPsychiatric NursingJanely EstreraNo ratings yet
- Biography of Albert Bandura: LearningDocument6 pagesBiography of Albert Bandura: LearningRustumme Mirelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Human Beh and VictimologyDocument3 pagesSyllabus in Human Beh and VictimologyLadylyn Batac67% (6)
- Course Module in Social PsychologyDocument7 pagesCourse Module in Social PsychologyArvie ChavezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Developmental PsychologyDocument6 pagesChapter 9 Developmental PsychologyAfiya KhanNo ratings yet
- WEEK 9 LessonDocument3 pagesWEEK 9 LessonKyle Danielle GabrielNo ratings yet
- Differences Debate.) : II. Sources of Personality A. Heredity. (The "Nature-Nurture"Document5 pagesDifferences Debate.) : II. Sources of Personality A. Heredity. (The "Nature-Nurture"Deogratias LaurentNo ratings yet
- AP Psych Master GuideDocument128 pagesAP Psych Master GuideDavidNo ratings yet
- Social Thought Social Behaviour - 2021Document14 pagesSocial Thought Social Behaviour - 2021Akshita BatraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 PsychDocument3 pagesChapter 13 PsychAustin ChildsNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Communications Chapter 3Document9 pagesInterpersonal Communications Chapter 3randomscribduser2012No ratings yet
- WEEK 8 LessonDocument4 pagesWEEK 8 LessonKyle Danielle GabrielNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Foundation in The Study of ValuesDocument5 pagesTheoretical Foundation in The Study of ValuesJimmy returanNo ratings yet
- Mastery Test in PhiloDocument2 pagesMastery Test in PhiloReglyn RosaldoNo ratings yet
- Adolescence 3-Day Handouts PDFDocument7 pagesAdolescence 3-Day Handouts PDFRodríguez YurazeckNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behaviour: PersonalityDocument19 pagesOrganizational Behaviour: PersonalityBlazio M ManoboNo ratings yet
- BM3 M1 Lesson2Document17 pagesBM3 M1 Lesson2sagedrick6No ratings yet
- CH 2 - Personality Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesCH 2 - Personality Lecture NotesOmarYasserShalashNo ratings yet
- HBO Chapter 3 and 4Document7 pagesHBO Chapter 3 and 4Elai TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Topado, Jma-Assessment IIIDocument4 pagesTopado, Jma-Assessment IIIJoshua Enmoceno FortezaNo ratings yet
- Hdev 3Rd Edition Rathus Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument37 pagesHdev 3Rd Edition Rathus Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmichaelweaveranfeyxtcgk100% (11)
- Waleed BrochureDocument2 pagesWaleed Brochuresyed waleed shahNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 NotesDocument10 pagesUnit 14 Notesapi-300762638No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Sociology Canadian 9Th Edition Macionis Gerber 0134308042 9780134308043 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Sociology Canadian 9Th Edition Macionis Gerber 0134308042 9780134308043 Full Chapter PDFchristy.saraiva416100% (10)
- BAT 4 Final ExamDocument7 pagesBAT 4 Final ExamQueenie TubianoNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 04.18.11Document2 pagesSocial Psychology Notes 04.18.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 04.04.11Document2 pagesSocial Psychology Notes 04.04.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 04.13.11Document1 pageSocial Psychology Notes 04.13.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 03.14.11Document2 pagesSocial Psychology Notes 03.14.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 03.16.11Document2 pagesSocial Psychology Notes 03.16.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 03.21.11Document2 pagesSocial Psychology Notes 03.21.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 03.07.11Document1 pageSocial Psychology Notes 03.07.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 02.16.11Document1 pageSocial Psychology Notes 02.16.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 02.23.11Document2 pagesSocial Psychology Notes 02.23.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 02.28.11Document3 pagesSocial Psychology Notes 02.28.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 02.14.11Document2 pagesSocial Psychology Notes 02.14.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 02.21.11Document3 pagesSocial Psychology Notes 02.21.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psych Notes 01.26.11Document2 pagesSocial Psych Notes 01.26.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- AstronomyDocument1 pageAstronomyJessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 02.09.11Document2 pagesSocial Psychology Notes 02.09.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology Notes 02.07.11Document2 pagesSocial Psychology Notes 02.07.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Social Psych Notes 01.19.10Document1 pageSocial Psych Notes 01.19.10Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Notes 04.11.11Document3 pagesAstronomy Notes 04.11.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Notes 04.18.11Document3 pagesAstronomy Notes 04.18.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Notes 04.13.11Document1 pageAstronomy Notes 04.13.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Notes 03.21.11Document3 pagesAstronomy Notes 03.21.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Notes 03.16.11Document4 pagesAstronomy Notes 03.16.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Notes 04.04.11Document3 pagesAstronomy Notes 04.04.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Notes 03.14.11Document3 pagesAstronomy Notes 03.14.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Notes 03.09.11Document3 pagesAstronomy Notes 03.09.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Notes 03.02.11Document3 pagesAstronomy Notes 03.02.11Jessica BoggsNo ratings yet
- Measures The Status of The FamilyDocument7 pagesMeasures The Status of The FamilyKitkat Aquino Cabugwas100% (1)
- fcs160 SyllabusDocument10 pagesfcs160 Syllabusapi-408733519No ratings yet
- KHDA Gems Our Own Indian School 2015 2016Document25 pagesKHDA Gems Our Own Indian School 2015 2016Edarabia.comNo ratings yet
- Fst511 - Sulam GuidelineDocument1 pageFst511 - Sulam Guidelinefatin umairahNo ratings yet
- Transcultural - Pertemuan 11 - Budi - Diversity at WorkDocument24 pagesTranscultural - Pertemuan 11 - Budi - Diversity at WorkRahayu Nurhayati100% (1)
- Mental Health Powerpoint WeeblyDocument16 pagesMental Health Powerpoint Weeblyapi-357279757No ratings yet
- Leading With IntegrityDocument21 pagesLeading With IntegritySreejith SurendranNo ratings yet
- MID TERM TEST - UCS3093 - QuestionDocument2 pagesMID TERM TEST - UCS3093 - QuestionSiti KhadijahNo ratings yet
- Types of TextDocument4 pagesTypes of TextJas Dela Serna SerniculaNo ratings yet
- Significance of LanguageDocument2 pagesSignificance of LanguageMohammad UmarNo ratings yet
- Agoncillo College Inc.: The Learner Produces A Detailed The Learner Acquires Knowledge ofDocument17 pagesAgoncillo College Inc.: The Learner Produces A Detailed The Learner Acquires Knowledge ofMarichelle Idmilao PurosNo ratings yet
- Cara Eft English PDFDocument4 pagesCara Eft English PDFTiwie Titian AnaghttanbcNo ratings yet
- Bhat ThesisDocument158 pagesBhat ThesisRiyaz BhatNo ratings yet
- BACC 2 Human Resource Management OBTLDocument16 pagesBACC 2 Human Resource Management OBTLNelvin VallesNo ratings yet
- Gartner Calendar Alwayson GB Networking 2022Document1 pageGartner Calendar Alwayson GB Networking 2022Mul YadiiNo ratings yet
- A MatrixDocument11 pagesA MatrixChristian MakandeNo ratings yet
- FDB Brochure - Deep Learning For Computer Vision From 05.02.2024 To 10.02.2024Document2 pagesFDB Brochure - Deep Learning For Computer Vision From 05.02.2024 To 10.02.2024publicationNo ratings yet
- Basic Between-Subjects DesignDocument18 pagesBasic Between-Subjects DesignmenmenNo ratings yet
- Instruction Method For Learning EducationDocument8 pagesInstruction Method For Learning Educationgian sollerNo ratings yet
- An Organisation of The Ministry of Small Scale Industries, GovernmentDocument15 pagesAn Organisation of The Ministry of Small Scale Industries, Governmentshashi_patel100% (1)
- Prepared By: Harris Khaliq Tayyab Roll Number:11339 Subject: Self Management SkillsDocument9 pagesPrepared By: Harris Khaliq Tayyab Roll Number:11339 Subject: Self Management Skillssana_571No ratings yet
- Anger, Rage, and Hatred: A Powerpoint PresentationDocument20 pagesAnger, Rage, and Hatred: A Powerpoint PresentationJane GilgunNo ratings yet
- LP SENTENCErrorsDocument3 pagesLP SENTENCErrorsJoannara Mae Jabines BeriñaNo ratings yet
- Analyze Mood and Tone Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesAnalyze Mood and Tone Lesson Planlookmoo50No ratings yet
- Educational Practices For Improvement of Entrepreneurial Skills at Secondary School LevelDocument14 pagesEducational Practices For Improvement of Entrepreneurial Skills at Secondary School LevelHannajane SateraNo ratings yet
- Technology Has Always Flourish For The Gain of MankindDocument1 pageTechnology Has Always Flourish For The Gain of MankindJennifer BanteNo ratings yet
- Intercultural CommunicationDocument4 pagesIntercultural CommunicationlilychengmiNo ratings yet
- Understanding SelfDocument3 pagesUnderstanding SelfAnn Mariellene GacerNo ratings yet
- EFQM Excellence Model TeaserDocument5 pagesEFQM Excellence Model TeaserMehmet SinanNo ratings yet
- Anthropology As A ScienceDocument40 pagesAnthropology As A ScienceJomai NorinejarNo ratings yet