Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Nervous System
Uploaded by
Johanna BuhagiarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Nervous System
Uploaded by
Johanna BuhagiarCopyright:
Available Formats
The nervous system
Sensory input → going towards the brain (senses)
Motor input → response to stimuli, it is complex because it consists of glands, and there are stimuli
which calm you down, example slow music stimuli to sleep (parasympathetic)
PNS → peripheral nervous system (peripheral), the nerves that come out of the spinal cord. If the
nerves do not function these will harm the person example he/she is touching something hot and the
person do not feel the burn, so this may cause a severe burn
Sensory (afferent) division [meta tiehu xi qata, titlaq tigri] → motor is the result
Sensory afferent →going in
Motor efferent → going out
Somatic nervous system
The part of the nervous system that you have control on
Test of the elderly: assessing, see them walking (ataxia) mobility, sometimes with assistance
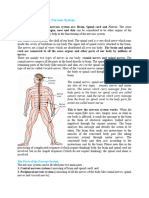
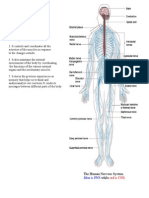
A very good picture of the nervous system
Assessing neurologically
Stroke affects the somatic motor function ( soma means body)
Autonomic
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Astrocytes are cells which function is to hold the neurons (you find a lot of these since there are a lot
of neurons)
Epididymal
Produce the cerebrospinal fluid
Are the ventricles of the brain
Epilepsy (like a “short circuit”) shaking, saliva oozing, possibly urine and faeces going out
Support cells
Satellite cells – protect neuron cell bodies
You might also like
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiologyzairis21No ratings yet
- CHP 3 PSYCHDocument8 pagesCHP 3 PSYCHEmma Mahoney100% (1)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Nervous System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Nervous System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandNervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Para Sympathetic NsDocument21 pagesPara Sympathetic NsMonicaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 1Document2 pagesNervous System 1Anthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 1Document2 pagesNervous System 1Anthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Sympathetic Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesStructure and Function of The Sympathetic Nervous SystemAnthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Nervous Systemzainab umerNo ratings yet
- Co OrdinationDocument4 pagesCo OrdinationBalakrishnan MarappanNo ratings yet
- General Psychology Notes Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesGeneral Psychology Notes Nervous SystemRj BengilNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous SystemJhunelynNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomy ScriptDocument2 pagesBasic Anatomy ScriptBenedict Del MundoNo ratings yet
- The Biological Perspective 2Document11 pagesThe Biological Perspective 2Radhey SurveNo ratings yet
- SpinalDocument40 pagesSpinalVenkathachala BgNo ratings yet
- PNA100 Chapter 11 ReviewDocument5 pagesPNA100 Chapter 11 ReviewaamenaNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous System in The Head and NeckDocument11 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous System in The Head and NeckIsmail Bazly ZarirNo ratings yet
- Organization of The Nervous System (Student)Document4 pagesOrganization of The Nervous System (Student)raquel_kNo ratings yet
- BIOPSYCHOLOGYDocument25 pagesBIOPSYCHOLOGYLizzie ShodiyaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2.sensitivityDocument4 pagesUNIT 2.sensitivityAna Rosa Camacho CornejoNo ratings yet
- Delapaz, John Benedict (Performance Task 2)Document1 pageDelapaz, John Benedict (Performance Task 2)John Eric D. WongNo ratings yet
- Nervous System1Document43 pagesNervous System1human anatomy100% (1)
- The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous SystemPaige Buchanan100% (1)
- Ballaran-Anatomy-Bsess-Fsc 2aDocument3 pagesBallaran-Anatomy-Bsess-Fsc 2aMary Joy BallaranNo ratings yet
- KSG-Brain ActivityDocument10 pagesKSG-Brain ActivitySyahirah ZackNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture: (Nervous System)Document2 pagesBiology Lecture: (Nervous System)Jeramae Hope BuatNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesNervous Systemphoebecruz636No ratings yet
- Biological Basis of Behavior: Presented By: Dr. Saima ShaheenDocument31 pagesBiological Basis of Behavior: Presented By: Dr. Saima ShaheenSana FatimaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ReviewDocument18 pagesNervous System Reviewtherenam825No ratings yet
- Science Article The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesScience Article The Nervous SystemNutszNo ratings yet
- Nervous System-Animal ScienceDocument16 pagesNervous System-Animal ScienceBeatrize BernardoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument11 pagesUnit 2 NotespatrickNo ratings yet
- SNS GeneDocument15 pagesSNS Genekerem sanguinoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesNervous SystemGlaizel PanalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Biological Psychology The NSDocument25 pagesUnit 2 - Biological Psychology The NSJad KhalidNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Neurologist: Dr. Luis, Dr. Miriam, Dr. KevinDocument7 pagesNervous System: Neurologist: Dr. Luis, Dr. Miriam, Dr. Kevinmsacosta7No ratings yet
- 14 Nervous SystemDocument31 pages14 Nervous SystemEman 3dilNo ratings yet
- Integration of Nervous System FunctionsDocument19 pagesIntegration of Nervous System Functionshed-ikaquinoNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument17 pagesHuman BrainAkbota KuanishkyzyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Analogy ProjectDocument2 pagesAnatomy Analogy Projectapi-251525028No ratings yet
- Group 1B OutlineDocument3 pagesGroup 1B Outlinejackclaudefajardo15No ratings yet
- Coordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsDocument71 pagesCoordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive Systemsnathanielstanaj.mNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Neurologist: Dr. Luis, Dr. Miriam, Dr. KevinDocument7 pagesNervous System: Neurologist: Dr. Luis, Dr. Miriam, Dr. Kevinmsacosta7No ratings yet
- Brainthe ControllerDocument4 pagesBrainthe ControllerJacklynlim LkcNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument5 pagesUntitled DocumentKennedy BNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Journal #1Document9 pagesNervous System Journal #1TonyDiazNo ratings yet
- Influence of Nervous System On BehaviorDocument2 pagesInfluence of Nervous System On BehaviorcynthiasenNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordination in HumansDocument14 pagesCo-Ordination in HumansRahulBansumanNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous SystemJohanan Suarez CaceresNo ratings yet
- Physiology ReviewDocument65 pagesPhysiology ReviewNandita KNo ratings yet
- Coordination & ResponseDocument152 pagesCoordination & ResponseChan Chiew WairNo ratings yet
- Nervous System OverviewDocument5 pagesNervous System Overviewapi-306398192No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument1 pageThe Nervous SystemNaomi FenechNo ratings yet
- Reporting Module 5Document12 pagesReporting Module 5Emarre BaronNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Biology of The MindDocument110 pagesUnit 2 Biology of The Mindleon222428No ratings yet
- 5 Psychology BiopsychologyDocument7 pages5 Psychology BiopsychologyKawthar MajedNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination Class10Document10 pagesControl and Coordination Class10shallowNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 - Organ Systems Nervous Muscle Endocrine and SensoryDocument3 pagesChap 4 - Organ Systems Nervous Muscle Endocrine and Sensory•[InsertnameHere]• (Aadika)No ratings yet
- Coordination - Human Bio HB10Document5 pagesCoordination - Human Bio HB10Zah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Bio Unit 5 ArticleDocument20 pagesBio Unit 5 Articlemyacerlaptop15No ratings yet