Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Which Method of Integral Do You Use
Uploaded by
A LamperougeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Which Method of Integral Do You Use
Uploaded by
A LamperougeCopyright:
Available Formats
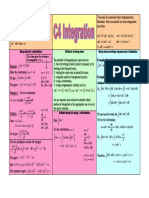
Which method of integration do you use?
The methods of integrating an expression are:
1) directly writing it down (either by memory or by looking in the formula book);
2) writing the expression in partial fractions;
3) using the method of integration by parts;
4) using a substitution;
5) using a trigonometric identity (such as sin 2 x = 12 (1 − cos 2 x) or cos 2 x = 12 (1 + cos 2 x) )
First look to see if the question tells you (or gives you a hint) about which method of integration you
should be using!!
First look to see if the integral is easy to work out: Is it one that you should remember (see my sheet)
5x + 2
or is it one in the formula book? Also is the integral easier to work out than it looks – e.g. ∫ x
dx
If you are asked to integrate an algebraic Other quotients (where the denominator cannot
ax + b be factorised into linear factors) can usually be
fraction of the form or integrated using a substitution.
(cx + d )(ex + f )
Examples are:
ax 2 + bx + c
, you could try writing it in x
(dx + e) 2 ( fx + g ) • ∫x +1
2
dx put u = x 2 + 1
partial fractions.
sin x
(Note: you might be asked in the first part of • ∫ put u = cos x
the question to express it in partial fractions)
cos x
2x +1
Examples are: • ∫ 2 dx put u = x 2 + x − 1
4 ( x + x − 1)2
• ∫ (2 x + 1)( x − 2) dx
4+ x
• ∫ x(4 − x)dx
Use a substitution if you have to integrate a Use integration by parts to integrate other
product of two functions in the form products, especially when one function is a simple
f '( x ) × gf ( x) . Substitute u = f ( x) . polynomial.
Examples here are: Examples here are:
∫ xe dx
−x
∫ 2 xe dx
x2
• •
∫ (3x + 1)e dx
2x
∫ x cos( x − 2)dx •
2 3
•
∫ x cos xdx
2
∫ (cos x)e dx •
2sin x
•
∫ 2 x ln xdx
3
∫ (2 x − 5) ln( x − 5 x)dx •
2
•
To integrate even powers of sin x or cos x , use To integrate odd powers of sin x or cos x , start
the formulae sin x = (1 − cos 2 x) or
2 1
2
by using the formula sin 2 x + cos 2 x = 1 and then
use a substitution.
cos x = 12 (1 + cos 2 x) .
2
Examples are:
Examples are:
∫ cos xdx
5
•
• ∫ cos xdx
4
∫ sin xdx
3
•
∫ sin
2
• xdx
You might also like
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Recognize IntegralsDocument1 pageRecognize IntegralsteachopensourceNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document15 pagesLec 1Muhammed YasserNo ratings yet
- MTS 201 181121 2021Document24 pagesMTS 201 181121 2021Godswill AdebayoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3.10 Differentiating Special Functions: Section 1Document5 pagesWorksheet 3.10 Differentiating Special Functions: Section 1Raymart EstavilloNo ratings yet
- Calc1 Week12Document13 pagesCalc1 Week12Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Kalkulus UNDIPDocument31 pagesKalkulus UNDIPRosdian AriefNo ratings yet
- MATH 231 HomeworkDocument11 pagesMATH 231 HomeworkJiaqi TangNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet - I-C2Document2 pagesWork Sheet - I-C2yacobNo ratings yet
- TMK 2023 0405 Chap 0.0Document13 pagesTMK 2023 0405 Chap 0.0Miu MakriNo ratings yet
- methodsOfIntegration PDFDocument6 pagesmethodsOfIntegration PDFkakagoNo ratings yet
- Q3W5 Lesson Differentiability and Continuity and Rules of DifferentiationDocument65 pagesQ3W5 Lesson Differentiability and Continuity and Rules of DifferentiationDannyelle SorredaNo ratings yet
- 5.5 Substitution RuleDocument1 page5.5 Substitution RuletucaoyongNo ratings yet
- TEST 5. Integrals-Rate of Change (2016)Document10 pagesTEST 5. Integrals-Rate of Change (2016)Aaryan KushwahNo ratings yet
- Derivatives Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesDerivatives Cheat SheetalexNo ratings yet
- Some Key Results (To Learn) : You Need To Remember These Trigonometric Formulae-They Are Needed in Some Integration QuestionsDocument1 pageSome Key Results (To Learn) : You Need To Remember These Trigonometric Formulae-They Are Needed in Some Integration QuestionsJie Shen ShenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To IntegrationDocument2 pagesIntroduction To IntegrationPaul ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Economia Matemática - Lista de Exercícios 1 - Integrais - 01-20Document4 pagesEconomia Matemática - Lista de Exercícios 1 - Integrais - 01-20Samuel CostaNo ratings yet
- E DX X X X DX DX X: Tutorial Sheet 8 Improper Integral, Beta and Gamma FunctionDocument1 pageE DX X X X DX DX X: Tutorial Sheet 8 Improper Integral, Beta and Gamma FunctionJunglie jooNo ratings yet
- Integration ApplicationsDocument3 pagesIntegration ApplicationsAWENABAH THOMASNo ratings yet
- Summative 4.3 - IntegralDocument2 pagesSummative 4.3 - IntegralChristine Angelie GranadaNo ratings yet
- Summative 4.3 - IntegralDocument2 pagesSummative 4.3 - IntegralChristine Angelie GranadaNo ratings yet
- Integración Por Sustitución 1Document6 pagesIntegración Por Sustitución 1jose_dino10005190No ratings yet
- 8.indefinite IntegrationPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae SheetDocument6 pages8.indefinite IntegrationPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae Sheetyodel23957No ratings yet
- AS-Level Maths:: Core 1Document18 pagesAS-Level Maths:: Core 1NovrizalNo ratings yet
- Lec 1-DikonversiDocument16 pagesLec 1-DikonversiSiti HartatiNo ratings yet
- Integration by Partial Fractions 2021Document1 pageIntegration by Partial Fractions 2021Ameer KhanNo ratings yet
- Integration techniques for economicsDocument6 pagesIntegration techniques for economicsRoba Jirma BoruNo ratings yet
- JC1 EOY Solutions (For Students)Document23 pagesJC1 EOY Solutions (For Students)BooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 IntegrationDocument57 pagesChapter 5 IntegrationThomas GuoNo ratings yet
- Unit-I MathsDocument4 pagesUnit-I MathsAman AwanaNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic Functions (Cont.) and Exam 1 ReviewDocument5 pagesHyperbolic Functions (Cont.) and Exam 1 Reviewakirank1No ratings yet
- Quiz IntegralDocument1 pageQuiz IntegralJerrySemuelNo ratings yet
- #Quizonintegral: 1 + 6 X 4 X + 5 + SinDocument1 page#Quizonintegral: 1 + 6 X 4 X + 5 + SinJerrySemuelNo ratings yet
- Mat1322NotesS19 Part1Document27 pagesMat1322NotesS19 Part1dongmianjunNo ratings yet
- Techniques of IntegrationDocument6 pagesTechniques of IntegrationFahrettin CakirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Angelo Paolo CamotaNo ratings yet
- MTH517 MATLAB integralsDocument2 pagesMTH517 MATLAB integralsShavin ChandNo ratings yet
- Test 1Document3 pagesTest 1Lisiew ThiangNo ratings yet
- Module 6. Differentiation of Transcendental FuntionsDocument23 pagesModule 6. Differentiation of Transcendental FuntionsMark Daniel RamiterreNo ratings yet
- Genmath Graphic OrganizerDocument1 pageGenmath Graphic Organizerdstelsh.2907No ratings yet
- Integrating Standard FunctionsDocument26 pagesIntegrating Standard FunctionsZenonissya Galwan BataraNo ratings yet
- Integral CalculusDocument16 pagesIntegral CalculusSilvaSunnyNo ratings yet
- 1 - Integration by PartsDocument8 pages1 - Integration by PartsAika GalinoNo ratings yet
- 12 Unit5Document64 pages12 Unit5mesfinNo ratings yet
- MAVT Differential Equations 1Document15 pagesMAVT Differential Equations 1viji08No ratings yet
- Unit 6 - AP Calculus BCDocument6 pagesUnit 6 - AP Calculus BCAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Integral Calculus NewDocument106 pagesChapter 6 Integral Calculus NewSIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- C.B.S.E. SAMPLE PAPER 2021-22 (TERM-II) : Mathematics Class-XIIDocument57 pagesC.B.S.E. SAMPLE PAPER 2021-22 (TERM-II) : Mathematics Class-XIIjokes & comedies onlyNo ratings yet
- Math 106: Review For Exam II - SOLUTIONS: Udv Uv Vdu Uv DX Uv U VDXDocument6 pagesMath 106: Review For Exam II - SOLUTIONS: Udv Uv Vdu Uv DX Uv U VDXsakNo ratings yet
- Week 14 (Part 4) - Integrals Yielding Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument12 pagesWeek 14 (Part 4) - Integrals Yielding Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsqweqweNo ratings yet
- MTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 6 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 3.5 To 4.1 Except 3.7Document12 pagesMTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 6 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 3.5 To 4.1 Except 3.7Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Integration WebversionDocument11 pagesIntegration Webversionوادي الابتكار Innovation ValleyNo ratings yet
- Integration basics in 40 charactersDocument11 pagesIntegration basics in 40 charactersShashank S KudlurNo ratings yet
- Notes On AntiderivativesDocument4 pagesNotes On AntiderivativesBella BallNo ratings yet
- Lec 5 DerivativesDocument26 pagesLec 5 DerivativesjorgenovachrolloNo ratings yet
- Indefinite Integrals ExplainedDocument35 pagesIndefinite Integrals ExplainedSelamawit TibebuNo ratings yet
- Further Mathematics p2 With Recalls ReviewedDocument16 pagesFurther Mathematics p2 With Recalls ReviewedKeng ElsonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document44 pagesLecture 8Ray LowNo ratings yet
- C 06 Anti DifferentiationDocument31 pagesC 06 Anti Differentiationebrahimipour1360No ratings yet
- A Dedicated Fourier Analysis For The SimulationDocument21 pagesA Dedicated Fourier Analysis For The SimulationA LamperougeNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Numerical Predictions of Burst Pressure of PipelinesDocument9 pagesTheoretical and Numerical Predictions of Burst Pressure of PipelinesA LamperougeNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Filament Wound Composite Pressure Vessel With Integrated-End DomesDocument9 pagesDesign and Analysis of Filament Wound Composite Pressure Vessel With Integrated-End DomesmrezaianNo ratings yet
- Filament Winding Netting Analysis PDFDocument9 pagesFilament Winding Netting Analysis PDFA.Subin DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document149 pagesChapter 2A LamperougeNo ratings yet
- Ch14Document28 pagesCh14A LamperougeNo ratings yet
- MBB2094 Root Locus Steady State Error ImprovementDocument19 pagesMBB2094 Root Locus Steady State Error ImprovementA LamperougeNo ratings yet
- MBB2094 Root Locus Steady State Error ImprovementDocument19 pagesMBB2094 Root Locus Steady State Error ImprovementA LamperougeNo ratings yet
- Belt Drives and Chain DrivesDocument25 pagesBelt Drives and Chain DrivesA LamperougeNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry 2 Revision SheetDocument2 pagesTrigonometry 2 Revision SheetA LamperougeNo ratings yet
- Ch14Document28 pagesCh14A LamperougeNo ratings yet
- Root Locus - Control Systems PDFDocument23 pagesRoot Locus - Control Systems PDFA LamperougeNo ratings yet
- SOL Assignment 4Document6 pagesSOL Assignment 4A LamperougeNo ratings yet
- Functions Revision SheetDocument1 pageFunctions Revision SheetJasi RopraNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument8 pagesChemistryA LamperougeNo ratings yet