Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic English Grammar Cheat Sheet (Draft #1)
Uploaded by
MEGOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic English Grammar Cheat Sheet (Draft #1)
Uploaded by
MEGCopyright:
Available Formats
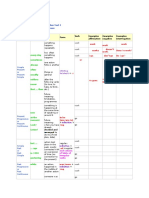
Articles Promise Plan Refuse Want
Need Decide hope
- Use ‘a’ and ‘an’ with not a specific object.
- Use ‘the’ with a specific object.
- The first time you speak of something use ‘a’ or ‘an’, the next Present Simple
time you repeat that object use ‘the’.
Use the present simple to talk about activities or routines which take
- DO NOT use an article with countries, states, counties or
place on a regular basis.
provinces, lakes and mountains except when the country is a
collection of states such as "The United States". Positive: Subject + present conjugation of verb + objects.
- Use an article with bodies of water, oceans and seas.
- DO NOT use an article when you are speaking about things in Negative: Subject + do not + base form of verb + objects.
general.
Question: WH? + do + subject + base form of verb ?
- DO NOT use an article when you are speaking about meals,
places, and transport.
Expression time: everyday, on …, at the moment, now, always, usually,
Past Tense Irregular Verbs sometimes. Days of the weeks followed by 's'.
Present Past Present Past Adverbs of Frequency
Be Was/Were Become Became
Begin Began Break Broke Adverbs of frequency include: always, usually, often, sometimes,
Bring Brought Build Built occasionally, seldom, rarely and never.
Buy Bought Come Came
Cost Cost Cut Cut * If the sentence has one verb put the adverb in the middle of the
Do Did Drink Drank sentence after the subject and before the verb.
Eat Ate Find Found
Fly Flew Get Got * If the sentence has more than one verb (e.g. auxiliary verb), put the
Give Gave Go Went adverb of frequency before the main verb.
Have Had Keep Kept
Know Knew Leave Left * When using adverbs of frequency in the question or negative form, put
Make Made Meet Met the adverb of frequency before the main verb.
Pay Paid Put Put
Read Read Say Said Modal Form
See Saw Sell Sold
Positive: Subject + Modal + Base Form of Verb + Objects.
Send Sent Speak Spoke
Spend Spent Take Took
Negative: Subject + Modal + Not + Base Form of Verb + Objects.
Teach Taught Tell Told
Think Thought
Question: Modal + Subject + Base Form of Verb + Objects?
Pronouns * The most common modals are: Can, Should and Must.
Subject Object Possessive Possessive adjectives Future
I Me Mine My
You You Yours Your Future with 'Will'
He Him His His Positive: Subject + will + base form of verb + object(s).
She Her Hers Her
It It Its Its Negative: Subject + will + not + base form of verb + object(s).
We Us Ours Our
They Them Thiers Their Question: Question Word + will + subject + base form of verb?
Demonstrative Pronouns * `Will` used for quick decisions, predictions, scheduled public events and
Pronoun Singular Plural promises.
Near This These
Future with 'Going to'
Far That Those
Positive: Subject + to be + going to + base form of verb + object(s).
Verbs Followed by the Gerund or the Infinitive Negative: Subject + to be + not + going to + base form of verb +
object(s).
Common Verbs + Gerund e.g. verb + verb + ing
Question: Question Word + to be + subject + going to + base form of
Go Enjoy Quit Discuss
Mind Can't stand Suggest verb?
Expression time: next …, tomorrow, by … and in … time.
Common Verbs + Infinitive e.g. verb + to + verb
* ‘Going to’ used for planned decisions, predicting an action that you see The past simple is used to express a finished past action which occurs at
is about to happen and future intentions. a specific moment in the past.
Countable and Uncountable Positive: Subject + past form of verb + object(s) + time.
Negative: Subject + did + not + base form of verb + object(s) + time.
* Uncountable name like water and countable name like minute. Question: WH? + did + subject + base form of verb + object(s) + time?
* Use “most, much, lots of, a lot of, some, a little and little” with
uncountable nouns. Expression time: when, last …, yesterday, ago.
* Use “many, lots of, a lot of, several, some, not many, only a few and
few” with countable nouns. Present Continuous
* Use a/an only with countable nouns preceded by an adjective(s).
Use the present continuous to speak about what is happening at the
List of some of the most common confused uncountable present moment in time, around the present moment, or for a future
scheduled event.
Accommodation Advice Baggage Bread
Equipment Furniture Garbage Information Positive: Subject + to be + verb + ing + objects.
Knowledge Luggage Money News Negative: Subject + are not + verb + ing + objects.
Pasta Progress Research Travel Question: WH? + do + subject + verb + ing + objects ?
work
Stative Verbs
Comparative Forms
Stative verbs are verbs which express a state. It can’t be used in the
* Use 'than' to compare between two objects. continuous forms. Action verbs are verbs which express something a
* Add '-er' to end of one or ending in '-y' syllable adjectives. person does.
* Place 'more' before two, three or more syllable adjectives.
Believe Understand Think Want
Hope Smell Taste Feel
EXCEPTIONS:
Sound Look Seem Appear
Adjective Comparative Adjective Comparative
Good Better Bad Worse
Any or Some
Superlative Forms
- Use “any” or “some” in positive sentences.
* Place 'the' before one syllable adjective and add '-est' to end of it.
* Place 'the most' before two, three or more syllable adjectives. - Use “any” in negative sentences.
* Place 'the' before two syllable adjectives ending in '-y' and remove the - Use “any” or “some” in questions.
'y' from it and add 'iest'. - Use “some” words - somebody, someone, somewhere
EXCEPTIONS: and something - in positive sentences.
Adjective Superlative Adjective Superlative - Use “any” words - anybody, anyone, anywhere and
Good The best Bad The worst anything - in negative sentences or questions.
Imperative Form In, On, To and At for Places
Positive: Base Form of Verb + Objects. - Use ‘in’ with spaces, bodies of water and lines.
Negative: Do + Not + Base Form of Verb + Objects.
- Use ‘at’ with places.
Adverb and Adjective - Use ‘on’ with surfaces, directions and small islands.
- Use ‘to’ with movement from one place to another.
* Adjectives are placed directly before a noun. Also it used in simple
sentences with the verb 'to be' to describe the subject. - But don’t use 'to' with 'home'.
* Adverbs ends in '-ly' (with a few exceptions!). It are often used at the In, At and On for Time
end of a sentence to modify the verb.
- Use 'in' with months, years and periods of time.
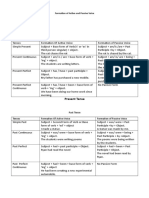
Present Perfect Tense - Use 'at' with precise time.
- Use 'on' with days of the week or specific calendar days.
Positive: Subject + have + past participle + object(s).
Negative: Subject + have + not + past participle + object(s). - Use 'in' with “morning”, “afternoon” or” evening”.
Question: WH? + have + subject + past participle? - Use 'at' with “night”.
Expression time: Like
- Use 'for' to indicate a duration or period of time.
- Use 'since' to indicate a specific point in time. - [Preposition] What's he like?
- Use 'How long' to ask about duration. - [Verb] What does he like?
- Others: yet, already and just. - [Preposition] What does she look like?
- [Verb] What would you like to drink?
Past Simple
You might also like
- EnglishGrammar Cheat Sheet For TeachersDocument2 pagesEnglishGrammar Cheat Sheet For TeachersAA11mm2289% (9)
- Grammar Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesGrammar Cheat Sheetapi-243050568No ratings yet
- Prepositions and Conjunctions Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPrepositions and Conjunctions Cheat Sheetbraindead_91100% (3)
- B1 Citam I PricamDocument66 pagesB1 Citam I PricamMaša Knežević100% (2)
- English - PrepositionsDocument5 pagesEnglish - PrepositionsBbook One97% (30)
- English Tenses ChartDocument2 pagesEnglish Tenses ChartMEG100% (2)
- Complete English Tenses PDF Chart DownloadDocument3 pagesComplete English Tenses PDF Chart DownloadSumit Thakur79% (58)
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocument3 pagesActive and Passive Tenses Chartrondick93% (29)
- Grammar Cheat Sheet: 40+ Key Terms ExplainedDocument4 pagesGrammar Cheat Sheet: 40+ Key Terms Explainedicon6970No ratings yet
- Formula of VerbDocument3 pagesFormula of Verbrezaulaktel100% (2)
- English Grammar Shortcut Rules PDFDocument15 pagesEnglish Grammar Shortcut Rules PDFNiranjan Sharma79% (14)
- English Grammar Cheat SheetDocument1 pageEnglish Grammar Cheat Sheetapi-341767113No ratings yet
- Simple Present QuestionsDocument2 pagesSimple Present QuestionsPontevedro English CentreNo ratings yet
- English Grammar SecretsDocument72 pagesEnglish Grammar SecretsEskender Ahmed87% (15)
- English TensesDocument30 pagesEnglish TensesMohamed Tayeb SELT100% (65)
- Summary of Verb Tenses-NEWDocument3 pagesSummary of Verb Tenses-NEWsamirNo ratings yet
- English Tense SystemDocument25 pagesEnglish Tense SystemMOhammad ZOhaib100% (10)
- TensesDocument61 pagesTensesmy wanna beNo ratings yet
- Free English GrammarDocument32 pagesFree English Grammarlivr100% (5)
- The Verb To BeDocument1 pageThe Verb To BeAran TxaNo ratings yet
- Tenses FormulaDocument1 pageTenses Formularrusmita75% (4)
- 100 Golden Grammar RulesDocument29 pages100 Golden Grammar RulesTimcsa82100% (2)
- Active Passive VoiceDocument3 pagesActive Passive VoiceKamesh Eshwar100% (2)
- Verb TensesDocument3 pagesVerb TensesVeronicaGelfgren92% (12)
- Notes - English (Grammar)Document3 pagesNotes - English (Grammar)Angeline BruceNo ratings yet
- Verb CollocationsDocument6 pagesVerb CollocationsMubarak Abdessalami100% (29)
- ACT Grammar Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesACT Grammar Cheat SheetsuriyadaruwaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Cheat Sheet To Use With BellworkDocument8 pagesGrammar Cheat Sheet To Use With Bellworksaed ahmad100% (1)
- English Grammar RulesDocument105 pagesEnglish Grammar RulesTaqi Mohammed100% (4)
- PrepositionsDocument4 pagesPrepositionsiesaznalcollar98% (59)
- EnglishTensesChartDocument4 pagesEnglishTensesChartNediaPrameswariNo ratings yet
- Grammar o Comparative Adjectives: Look Like Tobe LikeDocument8 pagesGrammar o Comparative Adjectives: Look Like Tobe LikeLuis Nguyen HaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Cheat Sheet 2016Document3 pagesGrammar Cheat Sheet 2016임민수No ratings yet
- English TensesDocument3 pagesEnglish TensesIbrahim Elmogy50% (10)
- English PrepositionsDocument4 pagesEnglish PrepositionsJoaquin Morales100% (2)
- NounsDocument16 pagesNounsBender AweshumNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs PDFDocument152 pagesModal Verbs PDFIsabelle Doncea100% (2)
- English Tenses Timeline ChartDocument11 pagesEnglish Tenses Timeline Chartjaenglez011100% (1)
- PrepositionDocument4 pagesPrepositionKhai RulNo ratings yet
- Grammar BookDocument119 pagesGrammar BookBetsabe Tejada100% (3)
- PrepositionsDocument3 pagesPrepositionsvalmeenglish86% (7)
- Modal: Verbs Music Describing PeopleDocument18 pagesModal: Verbs Music Describing PeopleMontse Camps0% (1)
- 66 Essential Phrasal Verbs EnglishDocument6 pages66 Essential Phrasal Verbs EnglishNarcisVega100% (15)
- Abdul Aziz - Identifying Parts of SpeechDocument1 pageAbdul Aziz - Identifying Parts of SpeechAbdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Edsl 350 MicroteachingDocument22 pagesEdsl 350 Microteachingapi-383710279No ratings yet
- Formation of Active and Passive VoiceDocument4 pagesFormation of Active and Passive VoiceHavewala VirafNo ratings yet
- Ingles. Investigacion Condicional 0 y 1. Passive y Active VoiceDocument2 pagesIngles. Investigacion Condicional 0 y 1. Passive y Active Voicelloyd23No ratings yet
- accuracy in written french languageDocument1 pageaccuracy in written french languagetfqg6yn6gjNo ratings yet
- Class 3 NovemberDocument24 pagesClass 3 NovemberMarcela FernandezNo ratings yet
- Study Guide - 20231115 - 104343 - 0000Document4 pagesStudy Guide - 20231115 - 104343 - 0000bryanspartan07No ratings yet
- Verb Tense StudyDocument33 pagesVerb Tense Studymat tamsiNo ratings yet
- Grammar RulesDocument11 pagesGrammar RulesAkshay Shukla100% (1)
- Verb Tenses ExplainedDocument7 pagesVerb Tenses ExplainedSwara PandeyNo ratings yet
- Tenses Review TDocument5 pagesTenses Review T2dcdm684pxNo ratings yet
- Trip TicoDocument2 pagesTrip Ticob22030233No ratings yet
- Topic 4 - VerbsDocument30 pagesTopic 4 - VerbsrhashigkaNo ratings yet
- Passive (Autosaved)Document32 pagesPassive (Autosaved)Aulia Shahnaz Pratiwi auliashahnaz.2019No ratings yet
- Ingles EstructurasDocument1 pageIngles EstructurasNaobi Porras MillánNo ratings yet
- Summer '23Document44 pagesSummer '23mvela8No ratings yet
- B2 Booklet 6-10Document7 pagesB2 Booklet 6-10ninacalle0782No ratings yet
- Unit 16 Day 4 (Last Day)Document24 pagesUnit 16 Day 4 (Last Day)Paúl Andrés YungánNo ratings yet
- Days of The Week: Unit 1Document3 pagesDays of The Week: Unit 1ceracalNo ratings yet
- Nef Beg File Tests 02Document5 pagesNef Beg File Tests 02Abdujabbor ZarifiNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Key Concepts and Perspectives in DiscourseDocument7 pagesAnalyzing Key Concepts and Perspectives in DiscourseAndrea De Almeida RegoNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: Detailed Lesson Plan in English For Grade 7 Prepared By: Shirnel C. Siaotong & Lovely Elaine MacaraigDocument5 pagesI. Objectives: Detailed Lesson Plan in English For Grade 7 Prepared By: Shirnel C. Siaotong & Lovely Elaine MacaraigLHANG CARNONo ratings yet
- Lembar Kerja Peserta Didik Teks ProcedureDocument5 pagesLembar Kerja Peserta Didik Teks ProcedureNikeisha ArdhianaNo ratings yet
- CausativeDocument6 pagesCausativesuhar tiniNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesClass 10 Lesson Planapi-632924559No ratings yet
- L2 Unit 8 Grammar AmE BasicDocument2 pagesL2 Unit 8 Grammar AmE Basicsobrez09No ratings yet
- TNPSC General English - Q&a Set 3-Www - Governmentexams.co - inDocument5 pagesTNPSC General English - Q&a Set 3-Www - Governmentexams.co - inkvnelavarasiNo ratings yet
- Change of MeaningDocument3 pagesChange of MeaningAbhishek AbbyNo ratings yet
- Learning Area Grade Level Quarter Date I. Lesson Title Ii. Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) Iii. Content/Core ContentDocument4 pagesLearning Area Grade Level Quarter Date I. Lesson Title Ii. Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) Iii. Content/Core ContentHoney Jiane B. BautistaNo ratings yet
- KDS118025 File 20180730Document8 pagesKDS118025 File 20180730최광민No ratings yet
- Habits of Effective Writers PDFFDocument2 pagesHabits of Effective Writers PDFFLexthom BalayantoNo ratings yet
- Punctuation Guide - Part IDocument15 pagesPunctuation Guide - Part ILogan DavisNo ratings yet
- Adjective and Noun ClauseDocument5 pagesAdjective and Noun ClauseMutiara Kholizah BatubaraNo ratings yet
- Iveta 2Document112 pagesIveta 2Tami OneNo ratings yet
- Belbin's Team Roles Improve PerformanceDocument16 pagesBelbin's Team Roles Improve PerformanceAlaaNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Wheel Fun Activities Games Games Sentence Transformation 78862Document17 pagesVerb Tenses Wheel Fun Activities Games Games Sentence Transformation 78862Albert LuchyniNo ratings yet
- A World of Differences and SimiliratiesDocument2 pagesA World of Differences and Similiratiesmarina100% (1)
- History of Writing SystemDocument3 pagesHistory of Writing SystemKhriezovo ChakrünoNo ratings yet
- Grammar and vocabulary practiceDocument4 pagesGrammar and vocabulary practiceNguyen Kim NgânNo ratings yet
- December 2020 Usa Reading Test SatDocument23 pagesDecember 2020 Usa Reading Test SatSaeed KhanNo ratings yet
- Developing Academic Writing Skills Booklet - 1920 - Sem1Document44 pagesDeveloping Academic Writing Skills Booklet - 1920 - Sem1WinnieNo ratings yet
- Macro Skills (Lesson Plan)Document4 pagesMacro Skills (Lesson Plan)Jirah Joy PeañarNo ratings yet
- Ngữ Âm Âm Vị Trắc NghiệmDocument14 pagesNgữ Âm Âm Vị Trắc Nghiệmd.duongnguyen1901No ratings yet
- JessnerDocument17 pagesJessnerEnikő HorváthNo ratings yet
- Genitivo Sajon (14TH October) 1Document2 pagesGenitivo Sajon (14TH October) 1Vicen PozoNo ratings yet
- Test-For 2nd Term - No2 - No KeyDocument3 pagesTest-For 2nd Term - No2 - No KeyChi Đào KhánhNo ratings yet
- Writing A Descriptive EssayDocument4 pagesWriting A Descriptive Essayayesha sanaNo ratings yet