Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brian 7
Brian 7
Uploaded by
Indra_Rama_2776Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Brian 7
Brian 7
Uploaded by
Indra_Rama_2776Copyright:
Available Formats
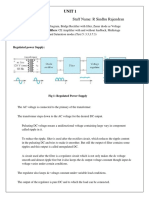
LAPORAN RESMI
SIMULASI RANGKAIAN ELEKTRONIKA
DAYA
NAMA : BRIAN PERMANA
7308040013/ 3 D4 ELIN
INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOVEMBER
POLITEKNIK ELEKTRONIKA NEGERI SURABAYA
2011
WORKSHOP ON
POWER ELECTRONIC SIMULATION
Prepared by Gigih Prabowo and Suryono
Experiment VII
DC-DC CONVERTER
(BUCK CHOPPER)
Objective : The objective is to study the operation and characteristics of a
dc buck converter under various load conditions.
Application : the dc buck (step-down) chopper is used to control power flow
in many applications (e.g. power supplies, dc motor control,
and input stage to inverters).
Basic Theory: The dc buck chopper circuit is
Figure 5-1 DC buck (down) chopper circuit
When the switch is closed the circuit is
Figure 5-2 DC buck (down) chopper circuit S close
Diode is reverse bias condition, the result in positive inductor
voltage i.e:
o d L
V V V =
It causes linear increase in the inductor current is
dt
di
L V
L
L
= and
= dt V
L
i
L L
1
dt
di
L V V V
L
o d L
= =
L
V V
dt
di
o d L
=
L
V V
DT
i
t
i
dt
di
o d L L L
=
A
=
A
A
=
( ) DT
L
V V
i
o d
close L
|
.
|
\
|
= A
When a switch S is open the circuit will be
Figure 5-3 DC buck (down) chopper circuit S open
Because of inductive energy storage, i
L
continues to flow. Diode is
forward bias current now flow (freewheeling) through the diode. The
inductance voltage can be derived as:
o L
v v =
dt
di
L v v
L
o L
= =
( ) ( )T D
L
V
i
o
opened L
|
.
|
\
|
= A 1
Steady-state operation requires that i
L
at the end of switching cycle is the
same at the beginning of the next cycle. That is the change of i
L
over one
period is zero, i.e.:
( ) ( ) o i i
opened L Closed L
= A + A
( ) 0 1 =
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
T D
L
V
DT
L
V V
o L d
The output voltage on the inductor is
d o
DV V =
The maximum and the minimum values of the inductor current
are computed as
( )
( )
+ =
+ =
A
+ =
Lf
T D
R
Vo
T D
L
Vo
R
Vo
i
I I
L
L
2
1 1
1
2
1
2
max
( )
( )
=
A
=
Lf
T D
R
Vo
T D
L
Vo
R
Vo
i
I I
L
L
2
1 1
1
2
1
2
min
From this equation can be used to determine the combination of
L and f that will result continuous current. Since I
min
=0 is the
boundary between continuous and discontinuous current
( )
( )
f
R D
L
Lf
T D
R
Vo I
2
1
2
1 1
0
min
min
= =
The ripple as a fraction of the output voltage:
( )
2
8
1
LCf
D
V
V
o
o
=
A
Component :
1. Source DC voltage 100V.
2. One switch (BJT/MOSFET)
3. Firing pulse generator ciruit
4. One diode
5. Two DC volt
6. One D~CA-meter
7. Resistance load 10O
8. Inductance load 25 mH.
Experiment Procedure :
1. Set up the circuit as shown fig. 5-4 through the PSIM. Used
the load resistance R only.
2. Set the chopping frequency to fc= 1 kHz and the duty cycle
to d= 50%
3. Draw the firing pulse circuits and connect to appropriate
BJT/MOSFET.
4. Observe and record the waveforms of the load voltage (V
o
),
the load current (i
o
), and the input current (I
s
).
5. Measure the average load voltage V
o(dc)
, the average load
current I
o(dc)
, the rms transistor current I
T(rms)
, the average input
current I
s(dc)
, and the load power P
L
.
6. Repeat step 2 until 5 with both load resistance R and load
inductance L.
Report :
1. Present all record wave forms and discuss all significant
points
2. Compare the step 3 with basic theory.
Figure 5-4 dc buck converter with resistive R load
Buck Coverter
1. Dengan Beban R
Vout
Iout
Is
Arus transistor rms
Load Power
2. Dengan Beban RL
Vout
Iout
Arus Input Is
Arus transistor rms
Load Power
Perhitungan teori
Beban R
Beban R-L
Analisa
Dari hasil simulasi rangkaian buck converter menggunakan PSIM di dapatkan
data-data berupa bentuk gelombang dan nilai dari parameter yang di ukur seperti
Tegangan,arus dan daya output.
Dari nilai tegangan output, pada beban R maupun R-L memiliki nilai yang hampir
sama yaitu setengah dari tegangan dc inputnya karena duty cycle yang diberikan adalah
50 % mengingat bahwa nilai tegangan output pada buck converter adalah Vo=D.Vs maka
pada tegangan input 100 V akan menghasilkan tegangan output 50 V pada D=50%.
Dengan membandingkan perhitungan teori dengan hasil simulasi maka
didapatkan nilai error Vout sebesar 0%.
Nilai perbandingan daya antara hasil simulasi dengan teori maka didapatkan nilai
daya dengan beban R W=250 Watt dan dengan beban R-L nilai dayanya W=195 Watt.
Dengan hasil tersebut maka dapat dicari nilai error W beban R = 2,8%. Dan nilai error W
beban R-L = 21,5%.
Pada nilai Arus output yang dihasilkan pada beban R dan beban R-L adalah tidak
sama.Pada beban R-L nilai arus lebih kecil hal ini karena nilai impedansi pada beban R-
L lebih besar dibandingkan beban R saja.Begitu juga dengan nilai arus input yang
dihasilkan terpengaruh dengan bebannya.Pada beban R-L nilai arus input akan lebih
kecil.
Kesimpulan
1. Nilai dutycycle pada rangkaian buck converter akan mempengaruhi besarnya
tegangan output yang akan dihasilkan rangkaian buck converter.
2. Dalam buck converter (step down converter), tegangan keluaran akan lebih rendah
atau sama dengan tegangan masukan karena besarnya nilai tegangan outputnya
adalah hasil kali dutycycle dengan nilai tegangan inputnya.
3. Oleh sebab itu rangkaian buck converter disebut juga step down converter karena
berfungsi untuk menurunkan nilai tegangan inputnya atau paling tidak sama besarnya
dengan tegangan inputnya.
4. Pada proses switching timbul tegangan yang sangat tinggi (spike) akibat switching
pada frekuensi tinggi, untuk mengatasi hal tersebut maka pada rangkaian buck boost
perlu diberikan rangkaian RC snubber untuk mengurangi tegangan spike yang terjadi
saat proses switching.
5. Nilai inductor (L) sangatlah berpengaruh terhadap tegangan output dari buck
converter.
You might also like
- Settlements and Damage Caused by Construction Induced VibratDocument17 pagesSettlements and Damage Caused by Construction Induced VibratwespritNo ratings yet
- BR 3000 PDFDocument407 pagesBR 3000 PDF3d86% (7)
- Lab 6: Buck Regulator L-C Filter Operation: Learning ObjectivesDocument26 pagesLab 6: Buck Regulator L-C Filter Operation: Learning ObjectivesDayana PaucarNo ratings yet
- MANUAL Vdocuments - Site FG Wilson P88e1Document287 pagesMANUAL Vdocuments - Site FG Wilson P88e1eletronica55100% (2)
- Single Phase Half Wave Controlled RectifierpdfDocument14 pagesSingle Phase Half Wave Controlled RectifierpdfRîtzî Saxena92% (37)
- Design of A Non-Ideal Buck ConverterDocument13 pagesDesign of A Non-Ideal Buck ConverterJames Xgun100% (1)
- Report 1 Power eDocument12 pagesReport 1 Power eMuhd HafizzudinNo ratings yet
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierDocument8 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifierArun Jyothi82% (11)
- HV Test Plan Gis 400 KVDocument12 pagesHV Test Plan Gis 400 KVAshiqur Rahman Zitu100% (1)
- Diode Rectifier and Smoothing FiltersDocument3 pagesDiode Rectifier and Smoothing Filtersppat2006No ratings yet
- AEI Power Module 3 NoteDocument35 pagesAEI Power Module 3 NoteNandu JagguNo ratings yet
- Public A CaoDocument23 pagesPublic A CaoShaheer DurraniNo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Half Wave Rectifier On MATLABDocument29 pagesDesign and Simulation of Half Wave Rectifier On MATLABAhmed Ahmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Buck ConverterDocument8 pagesBuck Converterhamza abdo mohamoudNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument4 pagesHalf Wave RectifierrodinooNo ratings yet
- Diode Circuits or Uncontrolled Rectifier: EE 435-Electric Drives Dr. Ali M. EltamalyDocument21 pagesDiode Circuits or Uncontrolled Rectifier: EE 435-Electric Drives Dr. Ali M. EltamalyNaga Surya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Ac Fundamnetals ManualDocument12 pagesAc Fundamnetals ManualRaj Mehra MeharNo ratings yet
- Design of 22-32 To 15 V Buck ConverterDocument7 pagesDesign of 22-32 To 15 V Buck ConverterAnuar Alfredo Gonzalez SolarNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics 1: ENEL371S2Document30 pagesPower Electronics 1: ENEL371S2bpd21No ratings yet
- Aula Conversores CC-CC BásicosDocument44 pagesAula Conversores CC-CC BásicosVirgílio TávoraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NotesDocument33 pagesUnit 1 NotesAer ZNo ratings yet
- Buck - Boost ConverterDocument9 pagesBuck - Boost Converterhamza abdo mohamoud100% (1)
- Buck and Boost Converter Using PSPICEDocument9 pagesBuck and Boost Converter Using PSPICEmohanrajgupta19100% (1)
- Pe Lab ManualDocument55 pagesPe Lab ManualNorbert John IberaNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 1: Figure 1: Circuit DiagramDocument4 pagesExperiment # 1: Figure 1: Circuit DiagramMahnoor Siddiqi100% (1)
- Power Electronic Module - Chapter 2Document43 pagesPower Electronic Module - Chapter 2jayxcellNo ratings yet
- Buck Boost ReportDocument10 pagesBuck Boost ReportKarThiNo ratings yet
- 4 SMPS ConvertersDocument6 pages4 SMPS ConvertersChristine AllenNo ratings yet
- Switch Mode ConvertersDocument28 pagesSwitch Mode ConvertersHemantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Switch Mode ConvertersDocument28 pagesSwitch Mode ConvertersAniruddh KashyapNo ratings yet
- DC DC ModellingDocument5 pagesDC DC ModellingBejoy BabuNo ratings yet
- 9.half Wave RectifierDocument3 pages9.half Wave RectifierSumithNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument10 pagesFull Wave RectifierVenkata PavanNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converters PDFDocument7 pagesDC-DC Converters PDFRidaNo ratings yet
- Ex No:6 Modelling and Simulation of Buck and Boost Converter 10.11.2014Document6 pagesEx No:6 Modelling and Simulation of Buck and Boost Converter 10.11.2014dhineshpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Chopper)Document14 pagesChapter 2 (Chopper)Zaf FiNo ratings yet
- Ade NotesDocument128 pagesAde NotesKiranmai KonduruNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.3Document4 pagesExperiment No.3sarav03No ratings yet
- Taller Corte 2 de Electrónica de PotenciaDocument23 pagesTaller Corte 2 de Electrónica de Potencianicolas lamilla vegaNo ratings yet
- Lect 3Document42 pagesLect 3Supriya Rakshit0% (1)
- Ee366 Chap 4 2Document28 pagesEe366 Chap 4 2Michael Adu-boahen50% (2)
- Main Objective:: Student Name: Ga Name: Matric NumberDocument19 pagesMain Objective:: Student Name: Ga Name: Matric NumberlionNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab 4Document10 pagesEDC Lab 4Z S PlaysNo ratings yet
- PSCAD Power System Lab ManualDocument23 pagesPSCAD Power System Lab ManualShiva Kumar100% (2)
- Electronics Laboratory DC Power Supply CircuitsDocument10 pagesElectronics Laboratory DC Power Supply CircuitsDen CelestraNo ratings yet
- SEPIC ConverterDocument16 pagesSEPIC ConverterDina GaranNo ratings yet
- ECT 246 Week 1 IlabDocument17 pagesECT 246 Week 1 IlabKrystle HaleyNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1-DC Power SupplyDocument30 pagesUNIT 1-DC Power SupplyMuizz ZainolNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier Circuits Part (1-A) : Experiment: DiodeDocument13 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier Circuits Part (1-A) : Experiment: DiodeCatalina ZelayaNo ratings yet
- DC DC Power SuppliesDocument33 pagesDC DC Power SuppliesrsrtnjNo ratings yet
- Buck-Boost Converter: Principle of OperationDocument9 pagesBuck-Boost Converter: Principle of OperationRohanMishraNo ratings yet
- Buck Boost ConverterDocument32 pagesBuck Boost ConverterJanmejay MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Laporan Boost AisDocument20 pagesLaporan Boost Aisdedy SetyoNo ratings yet
- CH2Document55 pagesCH2Shantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Boost Converter: Project FileDocument3 pagesBoost Converter: Project FilevackyvipinNo ratings yet
- Basic Switching CircuitsDocument19 pagesBasic Switching Circuitsash1968No ratings yet
- Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument12 pagesDiode Characteristics and ApplicationsZuopan YapNo ratings yet
- Electro PrincipeDocument58 pagesElectro PrincipeShahzaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Analysis, Design and Implementation of An Active Clamp Flyback Converter PDFDocument6 pagesAnalysis, Design and Implementation of An Active Clamp Flyback Converter PDFDeniz UzelNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document84 pagesChap 1lvsaruNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- West Midlands Constraint MapDocument1 pageWest Midlands Constraint Mapdan1_sbNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Newton IDocument2 pagesDynamic Newton IIrvan HasanNo ratings yet
- Ctek Xs800 Uk ManualDocument7 pagesCtek Xs800 Uk ManualiamgarymabbuttNo ratings yet
- Meter Board & EMDB FORMDocument4 pagesMeter Board & EMDB FORMAbdus SalamNo ratings yet
- OX-105-2-rev.L-EngDocument9 pagesOX-105-2-rev.L-EngradevilanNo ratings yet
- Using HysysDocument13 pagesUsing Hysysxuancuong100% (1)
- 01 4ib 51200DDocument106 pages01 4ib 51200Dsebastian coronelNo ratings yet
- Lsi/Csi: Digital Lock For Automotive IgnitionsDocument4 pagesLsi/Csi: Digital Lock For Automotive Ignitionselvergonzalez1No ratings yet
- NREL Airfoil DataDocument69 pagesNREL Airfoil DataPablo Martínez Filgueira0% (1)
- 16 Samss 504Document42 pages16 Samss 504paul reyesNo ratings yet
- Steam Parameters Measurement - Steam Turbine PathDocument5 pagesSteam Parameters Measurement - Steam Turbine PathLTE002No ratings yet
- Cryogenic Coefficient of Thermal Expansion Measurements of Type 440 and 630 Stainless SteelDocument4 pagesCryogenic Coefficient of Thermal Expansion Measurements of Type 440 and 630 Stainless Steel李俊No ratings yet
- Divina DomRAC 3rd Quarter Week 5 8 G 9Document18 pagesDivina DomRAC 3rd Quarter Week 5 8 G 9justine ocomaNo ratings yet
- Amarinth Technical Bulletin Guidance For Completing Fluid Properties On An Api 610 Datasheet To Ensure The Most Suitable Pump SelectionDocument5 pagesAmarinth Technical Bulletin Guidance For Completing Fluid Properties On An Api 610 Datasheet To Ensure The Most Suitable Pump Selectionyou kackNo ratings yet
- Boxer-100-AT-Ktec-1998-2000 AR-BAJAJDocument52 pagesBoxer-100-AT-Ktec-1998-2000 AR-BAJAJJuan Manuel Ortega100% (5)
- Industrial Heat Pumps Industrial Heat PumpsDocument4 pagesIndustrial Heat Pumps Industrial Heat PumpsMaxmore KarumamupiyoNo ratings yet
- Tablas de VaporDocument76 pagesTablas de VaporRaul LinoNo ratings yet
- Formula Lincoln ProgramDocument60 pagesFormula Lincoln ProgramLuizNo ratings yet
- List of Solar Junction Box Manufacturers/Distributors - IndiaDocument3 pagesList of Solar Junction Box Manufacturers/Distributors - IndiaAvnish KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: M.F. M. Sabri, K.A. Danapalasingam, M.F. RahmatDocument10 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: M.F. M. Sabri, K.A. Danapalasingam, M.F. RahmatChandresh TripathiNo ratings yet
- AC - DC Power Supply Reference Design. Advanced SMPS Applications Using The Dspic DSC SMPS FamilyDocument37 pagesAC - DC Power Supply Reference Design. Advanced SMPS Applications Using The Dspic DSC SMPS Familymiengrong anhNo ratings yet
- Kadanwari PDFDocument13 pagesKadanwari PDFAbdul AliNo ratings yet
- DazzLED Lights Catalogue 2019 - HighcompressedDocument24 pagesDazzLED Lights Catalogue 2019 - HighcompressedGyan DevNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines 2 Course Guide RevisedDocument5 pagesElectrical Machines 2 Course Guide RevisedjohnpaulshobayanNo ratings yet
- Gorenje GasDocument20 pagesGorenje GasAkabel BandiNo ratings yet
- WuertzDocument16 pagesWuertzPrashanth PrshnthNo ratings yet